Overview
In the world of business, the principal agency relationship is vital. It clearly defines the rights and obligations between representatives and their clients, fostering accountability and efficiency in operations. Have you ever considered how this relationship impacts your interactions? Understanding it can make a significant difference.
This article highlights the essential duties that agents owe to their principals, such as loyalty and care. These responsibilities aren't just formalities; they create a foundation of trust and reliability. Recent legislative changes further enhance transparency and accountability in these interactions, ensuring that everyone involved is protected and informed.
As we navigate these complexities together, it's crucial to recognize the importance of these relationships. We encourage you to reflect on how understanding these dynamics can empower you in your business dealings. Let's work together towards a more transparent and accountable future.
Introduction
Navigating the complex world of business transactions can feel overwhelming, and understanding the intricacies of agency law is vital for anyone in this space. The principal agency relationship is a cornerstone of this legal framework, shaping the responsibilities and expectations between representatives and their clients.
However, recent legislative changes remind us that the landscape of agency law is continually evolving. This evolution raises important questions about transparency and accountability. How can we ensure that we are fully aware of our rights and obligations in this dynamic environment?
By staying informed and engaged, we can navigate these changes together. Let’s explore how understanding agency law can empower you and foster a sense of security in your business dealings.
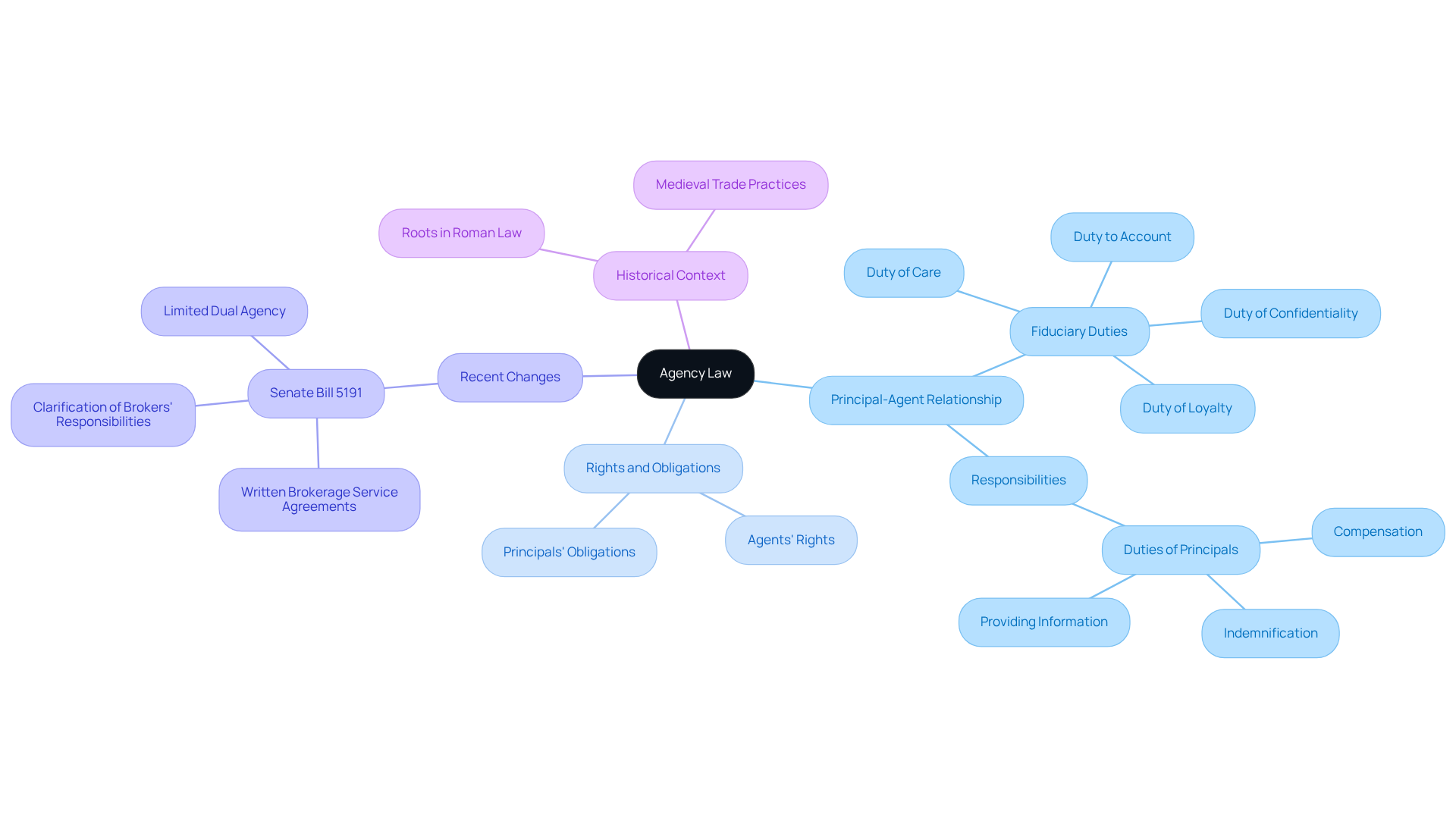
Define Agency Law and Its Importance
Agency law serves as a crucial common law principle that governs the principal agency relationship between representatives and their clients. When a principal creates a by empowering a representative to act on their behalf, a vital connection is formed. This principal agency relationship is particularly significant in business environments, as it enables organizations to streamline operations and leverage representatives' expertise to advocate for their interests. For instance, consider a company appointing a sales agent to negotiate contracts, relying on the agent's specialized knowledge to enhance accountability and efficiency.
Understanding the principal agency relationship is essential for anyone involved in business transactions. It clearly outlines the rights and obligations of both parties within the principal agency relationship, helping to minimize the risk of conflicts and misunderstandings. Agents are entrusted with fiduciary duties, including loyalty, care, and confidentiality, ensuring they act in the best interests of those they represent. On the flip side, the responsibilities that principals have to their agents, such as compensation and indemnification, nurture a balanced principal agency relationship.
Recent changes in representative law, like those introduced by Senate Bill 5191 in Washington, highlight the evolving nature of these connections. Effective January 1, 2024, this legislation mandates written brokerage service agreements and clarifies brokers' responsibilities, underscoring the ongoing need for transparency and accountability. As Carl A. Rubinstein notes, these updates reflect significant shifts in the legal framework of relationships.
Did you know that organizational law has roots tracing back to ancient Roman law? This historical context emphasizes its enduring role in facilitating business transactions and fostering trust among parties. By understanding the principles of representative law, we can navigate our rights and responsibilities more effectively, leading to more successful and harmonious business interactions. Let’s embrace this knowledge together for a brighter future in our professional relationships.
Explore Types of Agents in Principal-Agent Relationships
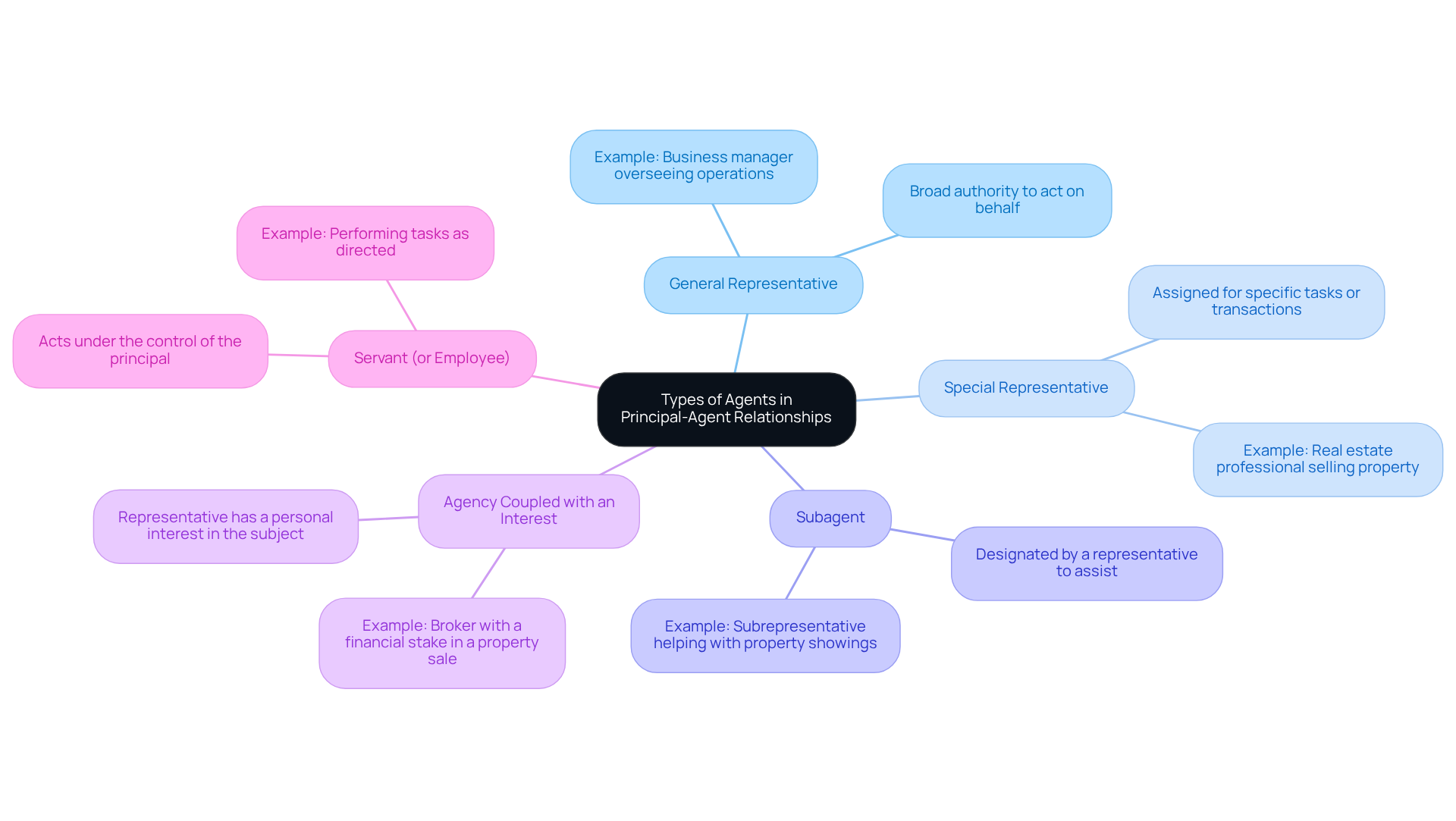
In the context of agency law, it’s important to understand the different types of agents, as each serves unique functions that can impact your experiences.
- General Representative: Think of a general representative as someone who has broad authority to act on your behalf in various matters. For instance, a business manager may take on this role, overseeing daily operations to ensure everything runs smoothly for you.
- Special Representative: A special representative is assigned for a specific task or transaction. Imagine hiring a real estate professional to sell your property; their authority is limited to that particular task, ensuring focused attention on your needs.
- Subagent: Sometimes, a representative may designate a subagent to assist in fulfilling their responsibilities. For example, a real estate professional might employ a subrepresentative to help with property showings, ensuring you receive the support you need throughout the process.
- Agency Coupled with an Interest: This type of agency occurs when a representative has a personal interest in the subject matter. For instance, a broker with a financial stake in a property sale will be particularly motivated to advocate for your best interests.
- Servant (or Employee): A servant acts under the control of the principal, performing tasks as directed. They are there to assist you, ensuring that your needs are met in a timely manner.
Understanding these differences in the principal agency relationship is essential. It helps clarify how representatives function within their roles and the potential consequences for the principal agency relationship. This is especially important in conflict scenarios, where roles may overlap or become misconstrued. Together, we can navigate these complexities with care and understanding.
Examine Duties Between Principal and Agent
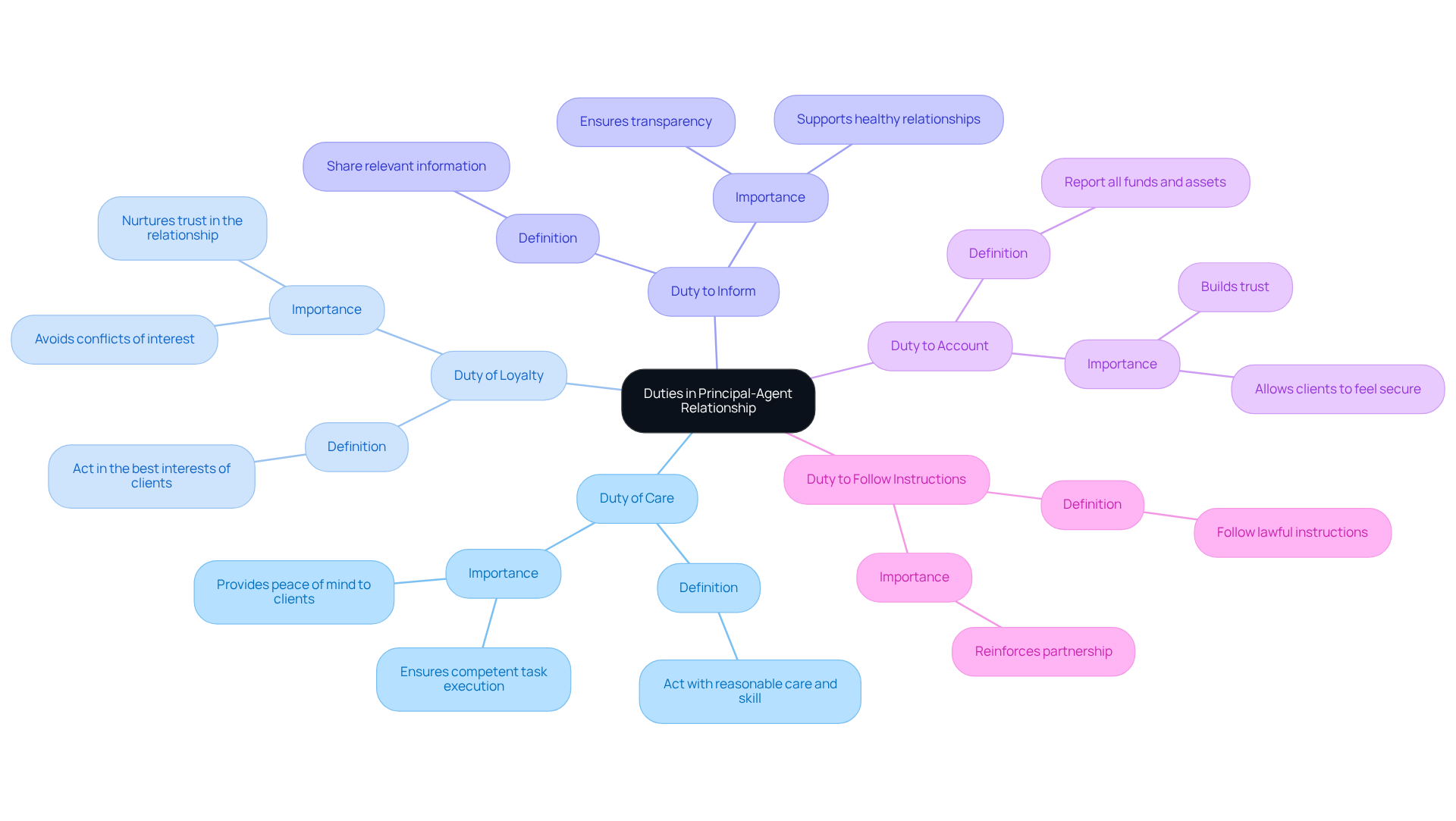
In the principal-agent relationship, there are specific duties that each party owes to one another, fostering a supportive environment:
- Duty of Care: Agents are called to act with the care and skill that a reasonable person would exercise in similar circumstances. This responsibility ensures that representatives carry out their tasks competently, providing peace of mind to clients.
- Duty of Loyalty: Agents have an obligation to act in the best interests of their clients, steering clear of conflicts of interest and self-dealing. For example, an agent should refrain from participating in dealings that benefit themselves at the expense of the client, nurturing trust in the relationship.
- Duty to Inform: Keeping clients informed is crucial. Agents must share all relevant information that may affect their clients' interests, including any potential conflicts or issues that arise during their partnership. This transparency is vital for a healthy relationship.
- Duty to Account: Agents are responsible for reporting all funds and assets acquired on behalf of the client. This duty ensures transparency and builds trust, allowing clients to feel secure in their decisions.
- Duty to Follow Instructions: Agents must follow the principal's instructions, as long as they are lawful and within the scope of the agency agreement. This adherence reinforces a sense of partnership.
Understanding these duties is essential for both parties to effectively . By recognizing and honoring these obligations, we can work together to address any disputes that may arise, fostering a collaborative and supportive environment.
Conclusion
Understanding the principal agency relationship is vital for anyone engaged in business transactions. It outlines the essential rights and obligations between principals and agents, enhancing operational efficiency. This relationship fosters trust and accountability, minimizing the risk of conflicts. By empowering representatives to act on their behalf, principals can leverage specialized knowledge, ensuring their interests are effectively advocated.
Have you considered the different types of agents? Each serves unique functions that significantly influence business interactions. From general representatives with broad authority to special representatives focused on specific tasks, understanding these distinctions is crucial. The duties owed between agents and principals—care, loyalty, and transparency—form the foundation of a successful principal agency relationship. Recent legislative changes, like those introduced by Senate Bill 5191, further emphasize the need for clarity and accountability in these interactions.
Recognizing the importance of agency law and the principal agency relationship can lead to more harmonious and effective business dealings. As we navigate our roles within this framework, a commitment to understanding and honoring these duties will enhance individual relationships. This commitment contributes to a more trustworthy and efficient business environment. Embracing this knowledge and applying it diligently can pave the way for successful collaborations and mutually beneficial outcomes in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is agency law?
Agency law is a common law principle that governs the principal agency relationship between representatives and their clients, allowing a representative to act on behalf of a principal.
Why is agency law important in business?
Agency law is important in business because it streamlines operations and allows organizations to leverage representatives' expertise, enhancing accountability and efficiency in transactions.
What are the rights and obligations in a principal agency relationship?
The principal agency relationship outlines the rights and obligations of both parties, helping to minimize conflicts and misunderstandings. Agents have fiduciary duties such as loyalty, care, and confidentiality, while principals have responsibilities like compensation and indemnification.
What recent changes have occurred in representative law?
Recent changes include the introduction of Senate Bill 5191 in Washington, effective January 1, 2024, which mandates written brokerage service agreements and clarifies brokers' responsibilities, emphasizing the need for transparency and accountability.
What historical context is relevant to agency law?
Agency law has roots in ancient Roman law, highlighting its enduring role in facilitating business transactions and fostering trust among parties involved.
How can understanding agency law benefit business interactions?
Understanding agency law helps individuals navigate their rights and responsibilities more effectively, leading to more successful and harmonious business interactions.




