Overview
This article provides an insightful look into the steps and implications of a stipulation of dismissal settlement, a formal agreement to end a lawsuit after a resolution has been achieved. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by the legal process? Understanding the differences between dismissals with and without prejudice is crucial for anyone navigating this path. We want you to feel informed and empowered.
The procedural steps required for execution can seem daunting, but knowing them can ease your concerns. There are benefits and risks involved in this process, and it's important to weigh these carefully. By providing a comprehensive overview, we hope to support you in considering this legal option with confidence.
Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Many have walked this path and found clarity and resolution. As you think about your next steps, reflect on how a stipulation of dismissal could bring you peace of mind. We encourage you to explore this option further, knowing that informed decisions lead to better outcomes.
Introduction
Navigating the legal landscape of dispute resolution can be daunting, especially when it comes to understanding the intricacies of a stipulation of dismissal settlement. This formal agreement not only signifies the end of a lawsuit but also carries significant implications that may affect your future legal options. As recent legal updates broaden the scope of these settlements, it’s important to consider both the potential risks and benefits involved.
What are the critical steps to execute such a settlement effectively? How can you ensure that the terms protect your interests in the long run? By addressing these questions, we can work together to find the best path forward, ensuring that your needs and concerns are prioritized throughout the process.
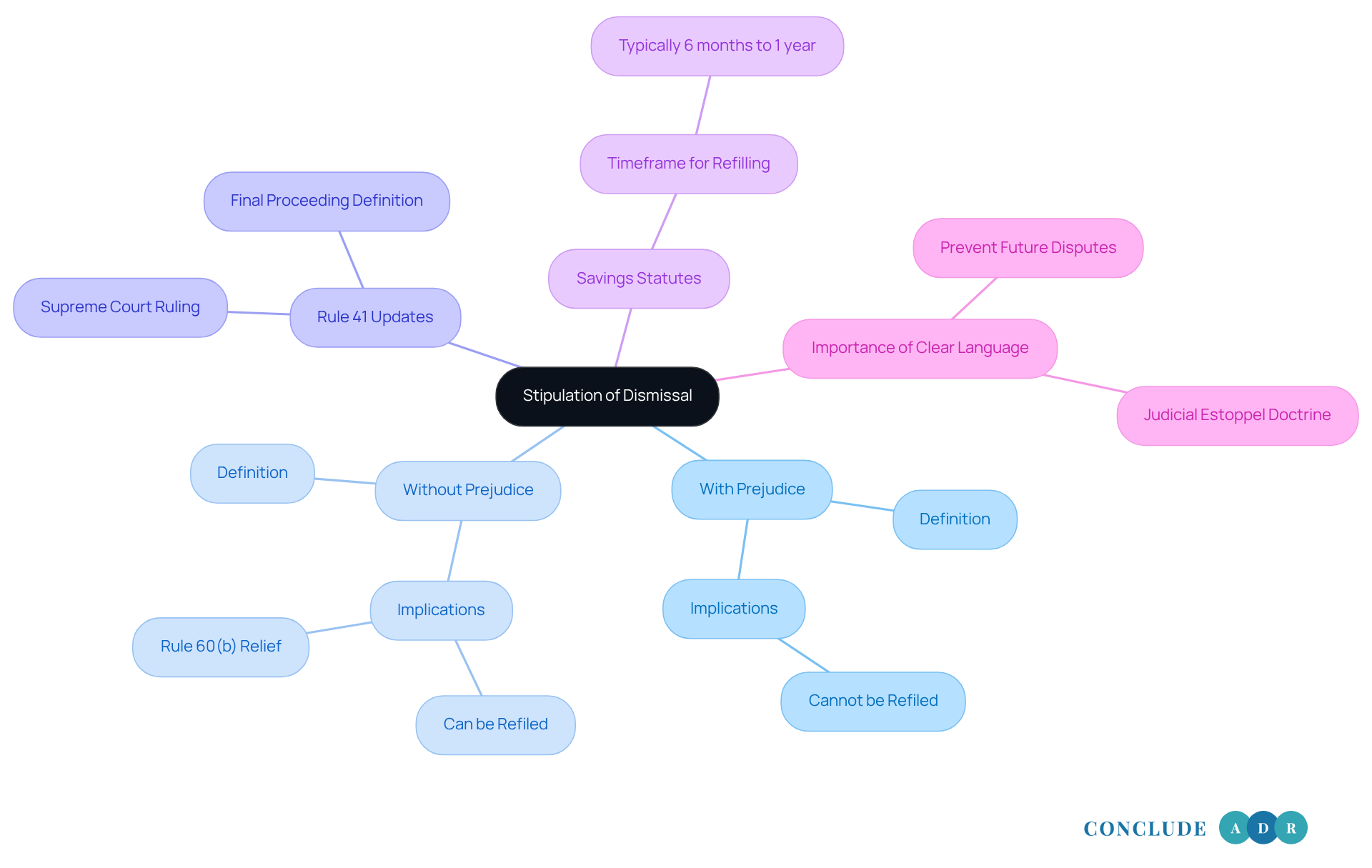
Define Stipulation of Dismissal: Key Concepts and Legal Framework
A stipulation of dismissal settlement is a formal agreement between parties in a lawsuit to terminate the matter, typically after they have reached a settlement. This process is guided by Rule 41 of the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure, which outlines the circumstances under which a matter may be voluntarily dismissed. It's important to understand that stipulations can be 'with prejudice,' meaning the case cannot be refiled, or 'without prejudice,' which allows for the possibility of refiling in the future. Recognizing these distinctions is crucial for stakeholders to navigate their legal choices effectively and avoid unintended consequences.
Recent updates to Rule 41 have expanded its application, particularly regarding voluntary terminations. For example, the U.S. Supreme Court has clarified that a voluntary withdrawal without prejudice qualifies as a 'final proceeding' under Rule 60(b). This change enables parties to seek relief after withdrawal. Such developments underscore the importance of careful consideration when agreeing to conditions, as they can impact the ability to reopen cases long after they've been closed.
Many states have 'savings statutes' that allow a plaintiff to refile a voluntarily dismissed lawsuit within a specific timeframe, typically six months to one year. Understanding this information is vital for grasping the .
Instances of stipulation of dismissal settlement often arise in various litigation contexts, such as employment disputes or contract breaches. These agreements typically outline the conditions of the stipulation of dismissal settlement, including any responsibilities the involved individuals must fulfill after the dismissal. Legal experts emphasize the necessity of clear language in these agreements to prevent future disputes over interpretation. For instance, Dean Pillarella, an Associate, notes that "the judicial estoppel doctrine prevents parties from taking inconsistent positions in litigation, which can complicate the termination process."
In summary, the key concepts related to the agreement for ending a case under Rule 41 include the nature of the termination (with or without prejudice), the implications of recent legal rulings, and the importance of precise drafting in settlement agreements. As litigation evolves, staying informed about these legal frameworks is essential for effective dispute resolution. Remember, you are not alone in this process, and understanding these aspects can empower you to make informed decisions.
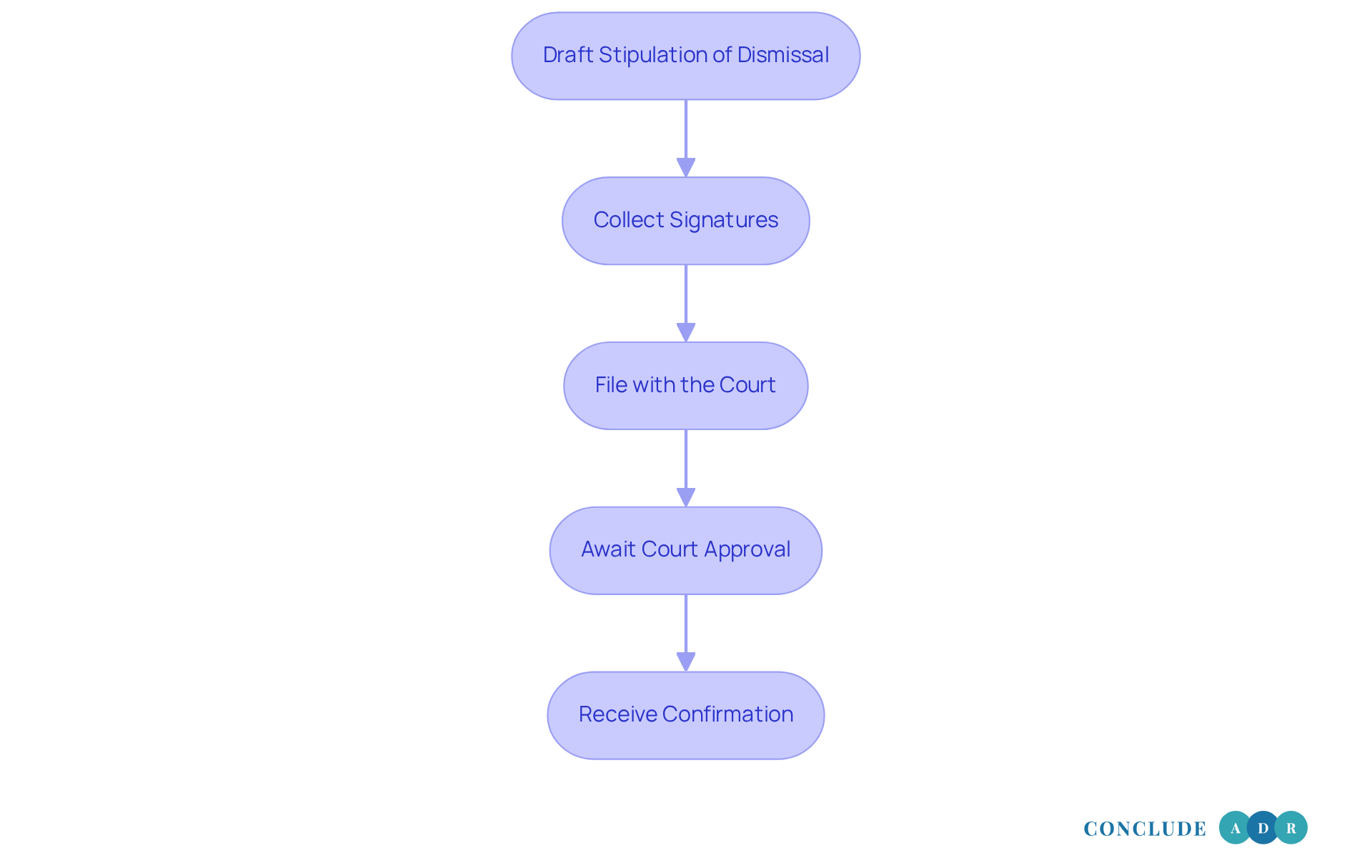
Execute a Stipulation of Dismissal: Step-by-Step Process
To execute a stipulation of dismissal, let's walk through these steps together:
- Draft the stipulation of dismissal settlement by preparing a written document that includes the title of the matter, court details, and a clear statement requesting termination. It’s important to specify whether the stipulation of dismissal settlement is with or without prejudice. Remember, using precise language is essential to avoid any ambiguity and ensure your intentions are clear.
- Collect Signatures: Next, confirm that all individuals involved in the matter endorse the agreement. This step is crucial, as it requires the stipulation of dismissal settlement from everyone involved in the action. You might find it helpful to have a witness or notary present during the signing to validate the agreement, providing an extra layer of security.
- File with the Court: Once you have the signatures, submit the signed agreement to the court where the case is pending. Depending on the court's rules, this can often be done electronically. As we look ahead to 2025, many jurisdictions have streamlined their filing processes, so be sure to check for any specific requirements or updates that may apply to your situation.
- Await Court Approval: In some areas, the court may need to authorize the stipulation of dismissal settlement before it takes effect. It’s wise to check local rules to confirm this requirement. Understanding the average time taken for court approval can help set realistic expectations; typically, this can range from a few days to several weeks, so patience is key.
- Receive Confirmation: Finally, once the court processes the agreement, be sure to obtain a copy of the dismissal order for your records. This document serves as evidence that the matter has been officially dismissed. Reflecting on can provide valuable insights into common pitfalls and best practices, deepening your understanding of the process.
Throughout this journey, remember that you are not alone. We are here to support you every step of the way, ensuring that the process feels manageable and clear.
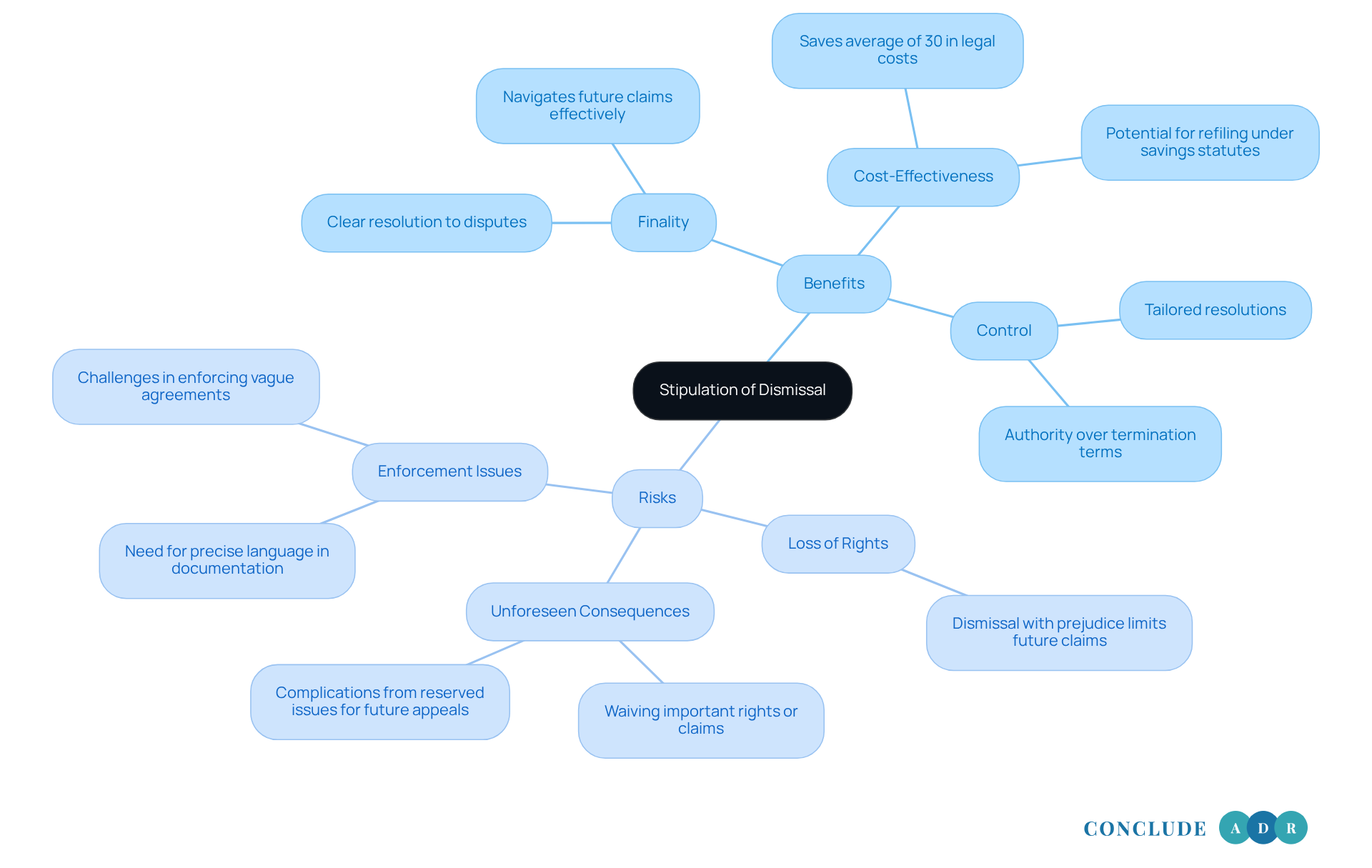
Evaluate Implications: Risks and Benefits of Signing a Stipulation of Dismissal
Signing a stipulation of dismissal settlement can be a significant decision, and it’s important to weigh both the benefits and the risks involved. Let's explore these together:
Benefits:
- Finality: A stipulation provides a clear resolution to disputes, allowing all parties to move forward without the burden of ongoing litigation. This sense of finality is essential, particularly given recent rulings that classify under Rule 60(b). Understanding this can help you navigate potential future claims more effectively.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Choosing this option can lead to considerable savings in legal fees, often reducing expenses tied to drawn-out court battles. Studies show that parties can save an average of 30% in legal costs by opting for stipulations instead of traditional litigation. Additionally, some jurisdictions offer savings statutes that may allow for refiling within a limited timeframe, providing further financial relief.
- Control: You have more authority over the termination terms compared to outcomes determined by the court. This allows for tailored resolutions that can better meet your specific needs.
Risks:
- Loss of Rights: It’s crucial to be aware that a dismissal with prejudice may result in losing the right to pursue the same claims in the future. This could limit your options for recourse down the line.
- Unforeseen Consequences: Without careful consideration, you might inadvertently waive important rights or claims, leading to potential disputes later on. Legal professionals often advise against stipulating to judgments that reserve issues for future appeals, as this can complicate matters later.
- Enforcement Issues: If the agreement lacks precise language, enforcing its terms could become a challenge, potentially leading to further legal conflicts. The importance of clear documentation is underscored by instances where defendants successfully argued against reopening claims by demonstrating that plaintiffs understood the finality of their dismissals. This highlights the necessity of precise language in the stipulation of dismissal settlement, as noted in the case study 'Documenting Plaintiff Representations.'
Navigating these implications is vital for you to manage your legal strategies effectively. It’s essential to ensure that your decisions align with your long-term interests. Remember, you are not alone in this process—consider seeking guidance to help you make the best choice for your situation.
Conclusion
A stipulation of dismissal settlement is more than just a legal formality; it represents a significant opportunity for parties in a lawsuit to bring their disputes to a close with clarity and understanding. Have you considered how the distinction between a dismissal with or without prejudice can impact your future claims? It's essential to grasp these nuances, as they shape the path ahead. Recent legal rulings remind us of the importance of navigating these agreements thoughtfully, ensuring that every party is well-informed about their rights and responsibilities.
In this article, we’ve explored the key steps involved in executing a stipulation of dismissal, from drafting the agreement to seeking court approval. The benefits of such settlements—finality, cost-effectiveness, and control over the resolution—are significant. Yet, we must also acknowledge the potential risks, such as the loss of rights and unforeseen consequences. The importance of precise language in these agreements cannot be overstated; ambiguity can lead to future disputes and complications in enforcement.
Ultimately, mastering the stipulation of dismissal settlement process is vital for anyone involved in litigation. As the legal landscape continues to evolve, it’s crucial to stay informed about the implications and best practices. Whether you’re negotiating terms or contemplating the consequences of a dismissal, seeking expert guidance can empower you to make informed decisions that align with your long-term interests. By taking proactive steps to understand and execute stipulations, you can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your dispute resolution strategies. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a stipulation of dismissal?
A stipulation of dismissal is a formal agreement between parties in a lawsuit to terminate the matter, usually after reaching a settlement.
What rule governs stipulations of dismissal in the U.S.?
Stipulations of dismissal are governed by Rule 41 of the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure, which outlines the circumstances under which a matter may be voluntarily dismissed.
What is the difference between dismissal 'with prejudice' and 'without prejudice'?
A dismissal 'with prejudice' means the case cannot be refiled, while a dismissal 'without prejudice' allows for the possibility of refiling in the future.
How have recent updates to Rule 41 affected voluntary terminations?
Recent updates clarify that a voluntary withdrawal without prejudice qualifies as a 'final proceeding' under Rule 60(b), allowing parties to seek relief after withdrawal.
What are savings statutes?
Savings statutes are laws in many states that allow a plaintiff to refile a voluntarily dismissed lawsuit within a specific timeframe, usually six months to one year.
In what contexts do stipulations of dismissal commonly arise?
Stipulations of dismissal often arise in various litigation contexts, such as employment disputes or contract breaches.
Why is clear language important in stipulation of dismissal agreements?
Clear language is crucial to prevent future disputes over the interpretation of the agreement, as noted by legal experts.
What is the judicial estoppel doctrine?
The judicial estoppel doctrine prevents parties from taking inconsistent positions in litigation, which can complicate the termination process.
What should parties consider when agreeing to a stipulation of dismissal?
Parties should carefully consider the conditions of the dismissal, the implications of recent legal rulings, and the importance of precise drafting in settlement agreements.




