Overview
Mediated communication is a vital aspect of our interactions, facilitated by technology that bridges distances and time. It allows us to exchange messages, but it comes with unique characteristics, such as asynchronicity, reduced nonverbal cues, and adaptability. Understanding these traits is essential for effective communication, particularly in conflict resolution.
Have you ever felt misunderstood in a conversation? This highlights the importance of clarity and intention in our interactions, especially when we navigate the challenges posed by the absence of physical presence.
As we explore the benefits of mediated communication, it's crucial to recognize how it can foster understanding and resolution. By acknowledging the emotional states of those involved, we can create a more supportive environment. Remember, effective communication isn't just about exchanging words; it's about connecting with others on a deeper level.
In conclusion, I encourage you to reflect on your own experiences with mediated communication. How can you apply these insights to enhance your interactions? Together, we can navigate the complexities of communication and work towards building stronger, more empathetic connections.
Introduction
Mediated communication has profoundly transformed the way we connect with one another, offering a technological bridge that spans distances and time zones. In this article, we will explore the essence of mediated communication, examining its defining characteristics and various forms. Together, we will also uncover strategies that can enhance its effectiveness.
As we increasingly rely on digital interactions, it’s important to acknowledge the challenges that come with them. How can we navigate the complexities of online communication to foster clarity and understanding? This journey is not just about technology; it’s about nurturing our connections and ensuring our voices are heard. Let's delve into this together.
Define Mediated Communication Clearly
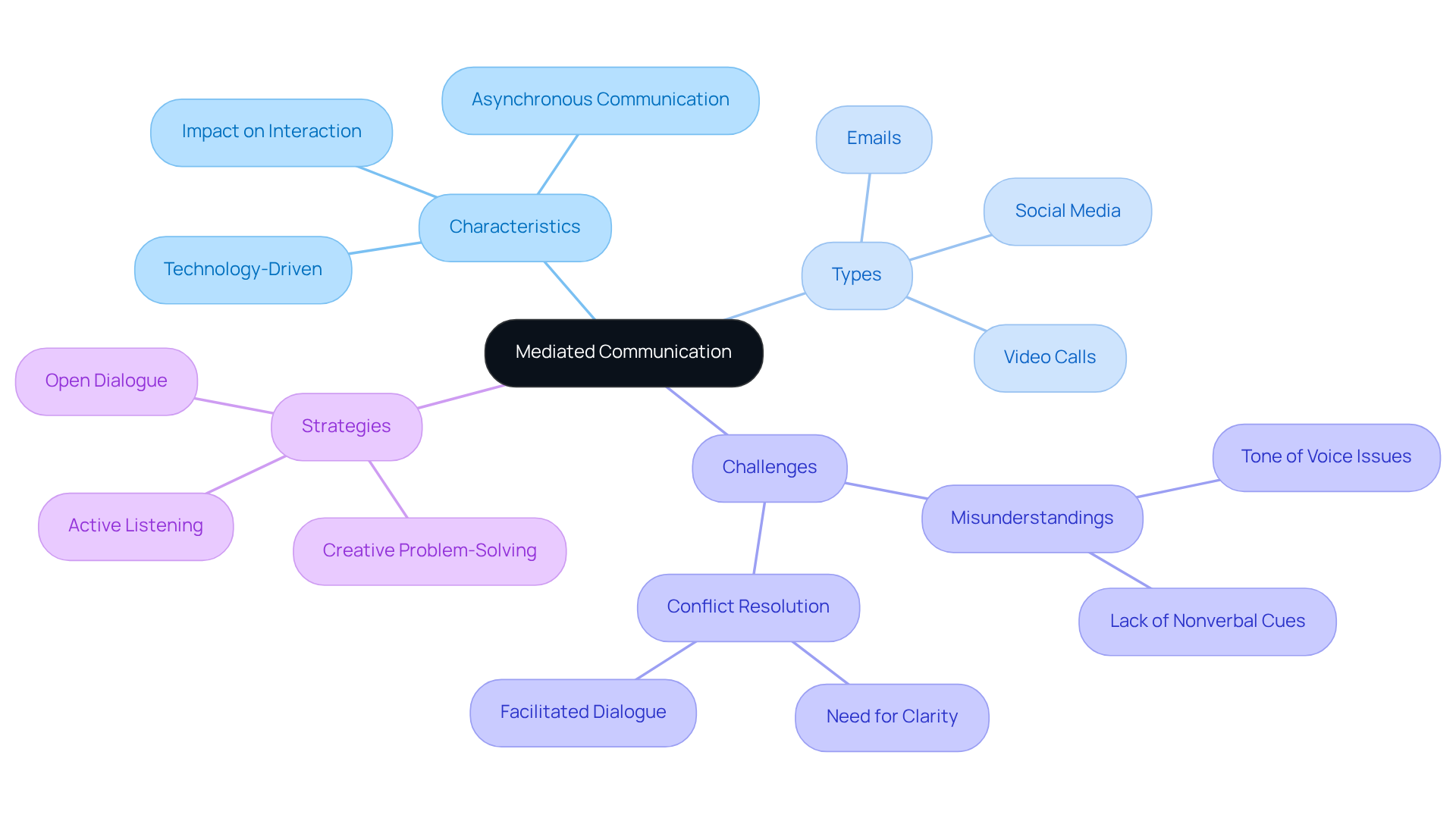
Mediated interaction is a way for us to connect through technology, allowing us to share messages across distances and time. Think about how we use emails, social media, or video calls to communicate. These platforms help us exchange information, but they also change how we interact compared to face-to-face conversations. Understanding this concept is crucial as it lays the groundwork to define mediated communication, along with exploring its characteristics, types, challenges, and strategies involved.
In situations like conflict resolution, having effective facilitated dialogue is vital. It allows us to express our needs and concerns more clearly, fostering understanding and cooperation. Have you ever noticed how open dialogue and creative problem-solving can make a significant difference in resolving issues? These elements are essential in enhancing the effectiveness of our interactions.
Moreover, the adaptability of our interaction methods is evident in the growing use of video conferencing in workplaces. This shift not only improves our connections but also helps minimize misunderstandings, which can often arise from tone and context in more traditional settings. Did you know that 90% of disputes are linked to the wrong tone of voice? This statistic underscores the importance of clarity and intention in our facilitated dialogues. Together, we can work towards more .
Identify Key Characteristics of Mediated Communication
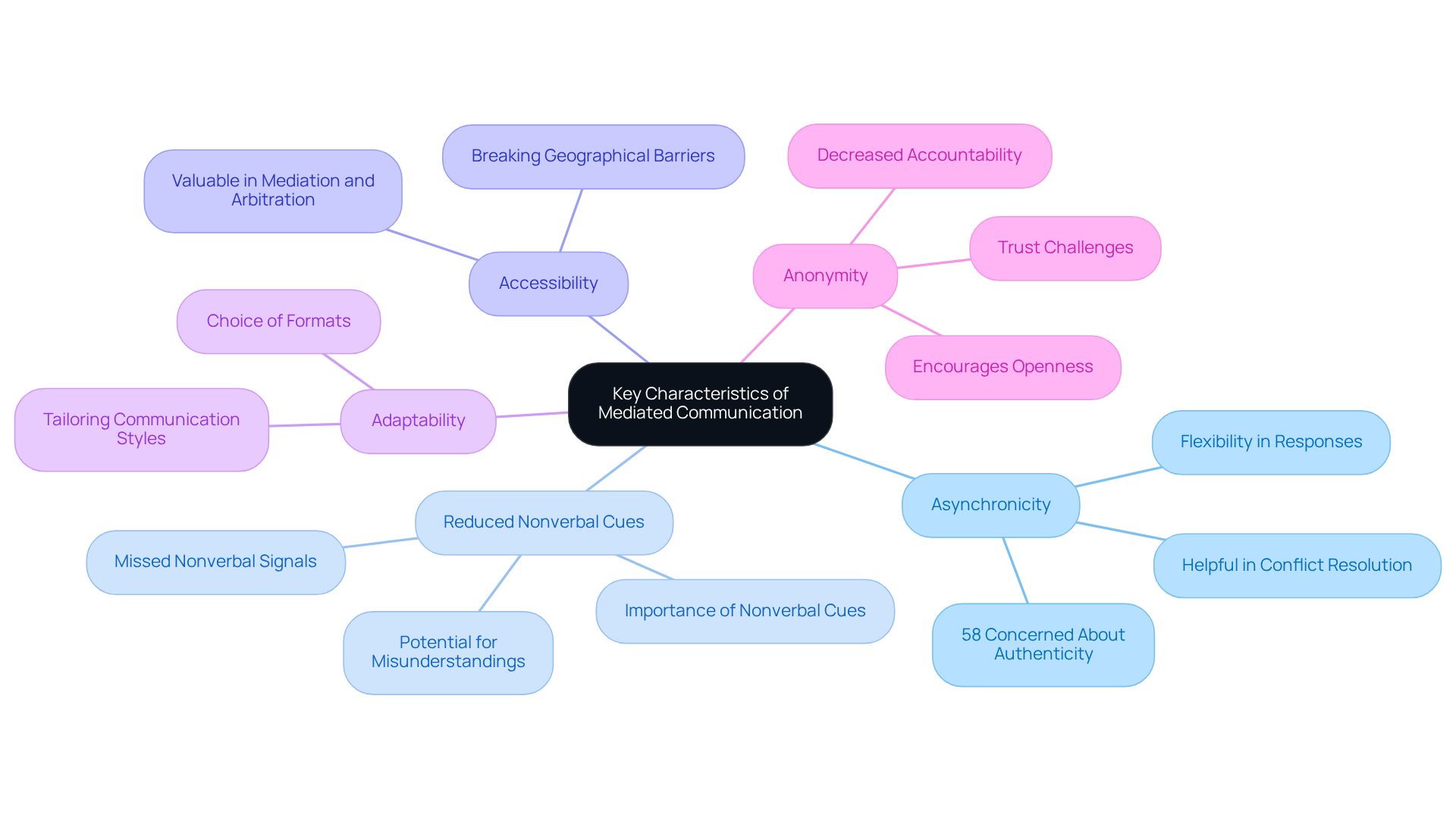
Key characteristics of mediated communication include:
- Asynchronicity: Unlike in-person communication, remote interactions allow conversations to unfold at different times. This flexibility gives participants the chance to respond when it suits them, which can be especially helpful in conflict resolution. Have you ever needed time to reflect before replying? You're not alone. In fact, a recent survey revealed that 58% of participants globally are concerned about authenticity in online news. This highlights the importance of engaging thoughtfully in our communications.
- Reduced Nonverbal Cues: In mediated interactions, we often miss out on the nonverbal signals that enrich face-to-face exchanges, like facial expressions and body language. This absence can lead to misunderstandings. Have you ever misinterpreted a message because you couldn't see the sender's expression? Studies show that nonverbal cues are vital for conveying emotions and intentions. Vivian P. Ta, a NSF LSAMP BD Fellow, reminds us that "although digitally-mediated interactions are becoming increasingly common, they do not provide the same advantages that accompany face-to-face exchanges."
- Accessibility: Technology breaks down geographical barriers, allowing us to connect with others regardless of location. This is particularly valuable in mediation and arbitration, where parties may be far apart. Imagine the possibilities when we can engage with anyone, anywhere.
- Adaptability: We can choose different formats—text, audio, or video—in our interactions, tailoring our communication styles to fit various contexts. This adaptability can make our exchanges more engaging and help us understand each other better. What format do you find most comfortable?
- Anonymity: Some forms of mediated interaction offer anonymity, which can encourage openness and honesty. Yet, this anonymity may also lead to decreased accountability, complicating efforts to resolve disputes. The challenges of trust in these interactions are explored in the case study 'Trust and Its Fragility in Communications,' which discusses how disinformation can impact public trust.
Understanding these traits is essential for , as they help define mediated communication, especially in sensitive situations like dispute resolution, where clarity and mutual understanding are vital. It's also important to recognize that relying too heavily on mediated exchanges can come with emotional costs. Positive feelings from digital interactions often fade more quickly than those from face-to-face encounters. How can we strike a balance that enhances our connections while safeguarding our emotional well-being?
Explore Different Forms of Mediated Communication
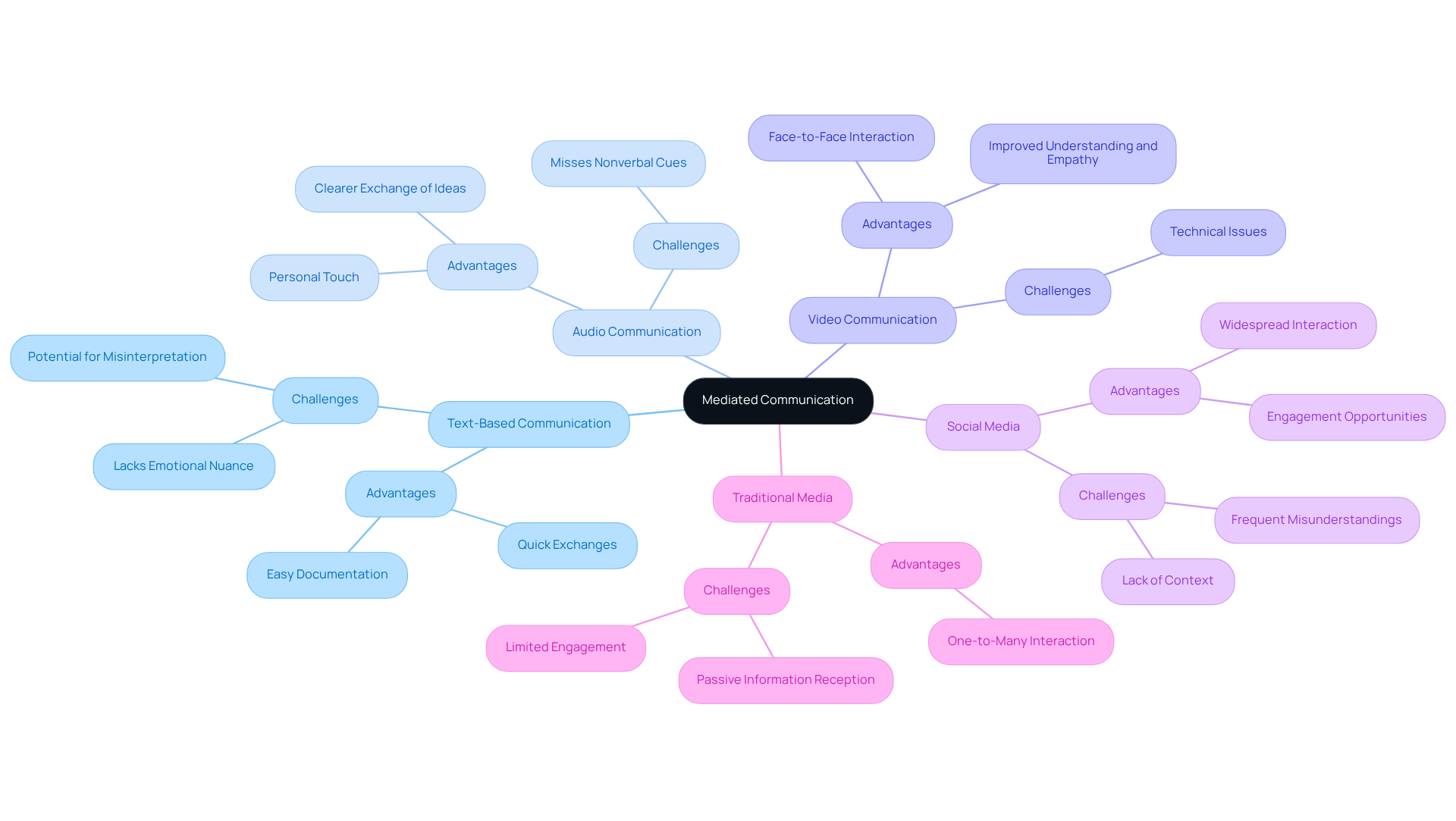
In order to define mediated communication, it encompasses various forms, each presenting unique advantages and challenges that can significantly impact conflict resolution.
- Text-Based Communication: This includes emails, instant messaging, and social media posts. While it allows for quick exchanges and easy documentation, it often lacks emotional nuance. Have you ever found yourself misinterpreting a message? This can lead to misunderstandings, which we want to avoid.
- Audio Communication: Phone calls and voice messages offer a more personal touch compared to text, facilitating a clearer exchange of ideas. However, they still miss nonverbal cues that can enhance understanding. Think about how much a tone of voice can convey beyond words.
- Video Communication: Platforms like Zoom and Skype enable face-to-face interaction through screens, combining visual and auditory elements. This format can significantly improve understanding and empathy, making it especially effective in addressing disputes. A 2012 study from the University of Illinois discovered that video-based interaction results in improved consensus on solutions in high-stress scenarios compared to text or audio methods. Isn’t it comforting to know that seeing each other can help us resolve conflicts more effectively?
- Social Media: Although this method enables widespread interaction and engagement, it can result in misunderstandings because of the lack of context and nonverbal signals, which are essential in disputes. Misinterpreted messaging is a frequent cause of disputes in virtual workplaces. How often have you seen a simple post spiral into a misunderstanding? This highlights the necessity for clarity in our interactions.
- Traditional Media: Television and radio broadcasts illustrate one-to-many interaction, where the audience receives information passively without direct engagement, limiting chances for clarification.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these forms of interaction is crucial for us to define mediated communication as the most for our needs, particularly in challenging situations where clarity and comprehension are vital. As specialists observe, tackling the challenges of distant interaction is essential to avoid misunderstandings and promote effective dispute management. Together, we can navigate these complexities and foster clearer communication.
Analyze Challenges and Benefits of Mediated Communication
To define mediated communication, one must consider how these exchanges present both challenges and benefits that significantly influence interpersonal interactions, especially in contexts.
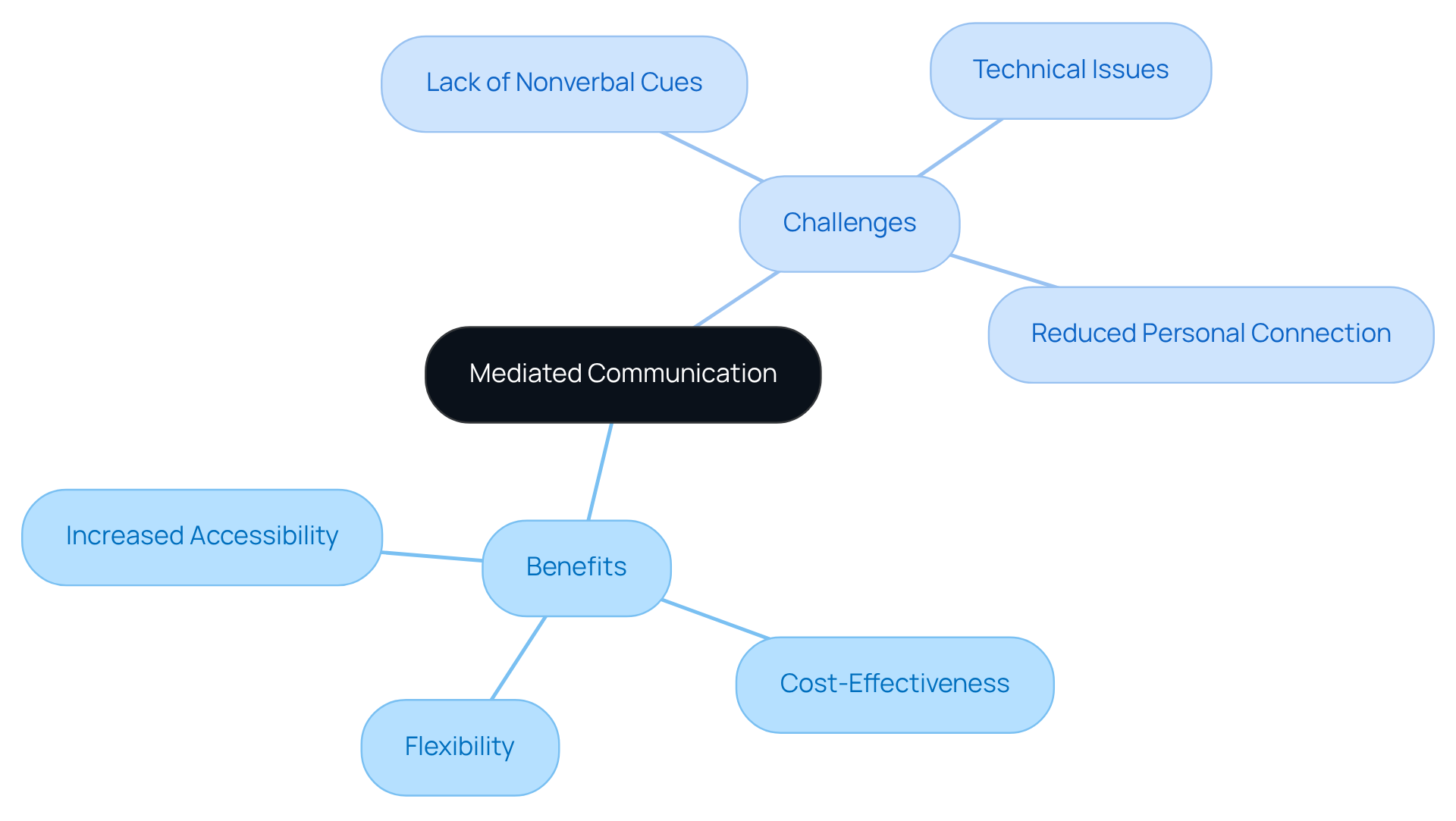
Benefits:
- Increased Accessibility: Mediated communication allows us to connect, regardless of geographical barriers. This fosters relationships that might not otherwise develop, particularly for those in remote areas or with mobility constraints.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many mediated interaction methods, such as video conferencing and messaging apps, are often less expensive than traditional face-to-face meetings. This affordability can be crucial for individuals and organizations seeking to resolve disputes without incurring high costs.
- Flexibility: Participants can engage in dialogue at their convenience, enhancing time management and accommodating varying schedules. This flexibility is especially valuable in conflict resolution, as it helps to define mediated communication, where timely discussions can prevent escalation.
Challenges:
- Lack of Nonverbal Cues: The absence of body language and tone in mediated communication can lead to misunderstandings. Did you know that research indicates up to 93% of interaction is nonverbal? This highlights the potential for significant misunderstandings in digital formats. Stephanie Reich observed that online interactions may be perceived as less intimate, which can affect relationship-building and trust.
- Technical Issues: Our reliance on technology introduces the risk of disruptions due to connectivity problems or software malfunctions. For instance, the manipulation of social media can disrupt important discussions, particularly in high-stakes dispute management situations, as seen in various case studies.
- Reduced Personal Connection: Mediated interaction can feel less personal, which may hinder relationship-building and trust. Research shows that people frequently view online exchanges as less personal, influencing the depth of relationships developed during problem-solving processes.
By acknowledging these advantages and obstacles, we can better define mediated communication and navigate the intricacies of facilitated interaction more efficiently, especially when dealing with conflicts and promoting understanding. Furthermore, balancing facilitated exchanges with in-person interactions is vital for improving relationship quality and ensuring effective conflict resolution.
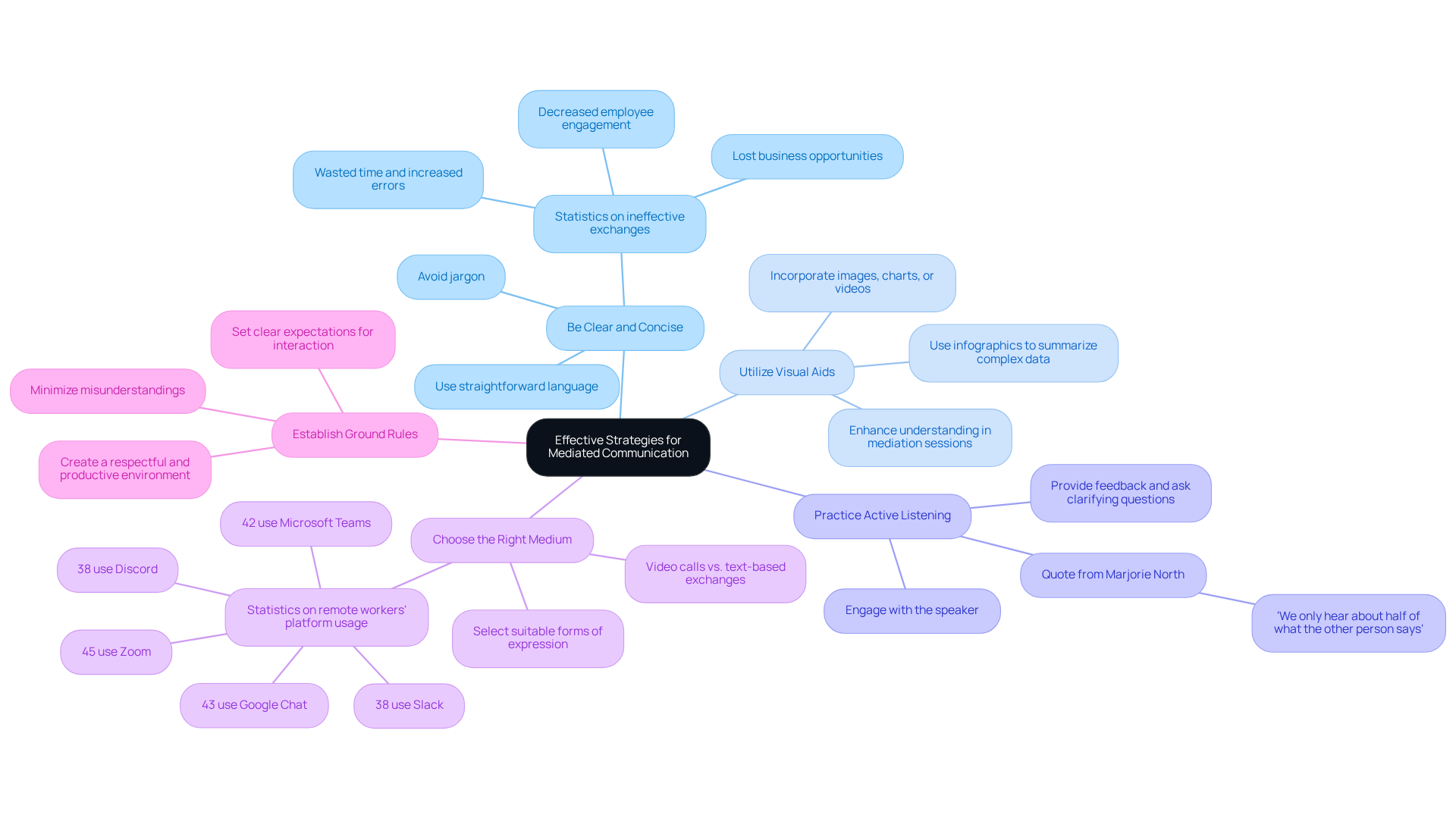
Implement Effective Strategies for Mediated Communication
To enhance mediated communication, let’s explore some supportive strategies together:
- Be Clear and Concise: It’s important to use straightforward language and avoid jargon, as this minimizes misunderstandings. Did you know that statistics show ineffective exchanges can lead to wasted time and increased errors? For instance, the cost of inadequate interaction in the workplace can result in decreased employee engagement and lost business opportunities. This highlights how essential clarity is in our communications.
- Utilize : Incorporating images, charts, or videos can really support your message and provide valuable context. Think about how successful implementation of visual aids, like infographics, can summarize complex data during mediation sessions. This approach can significantly enhance understanding, especially in discussions that may feel overwhelming.
- Practice Active Listening: Engaging with the speaker is crucial. By providing feedback and asking clarifying questions, we ensure understanding. As expert Marjorie North points out, 'we only hear about half of what the other person says during any given conversation.' This underscores the importance of active listening in fostering respectful dialogue and effective conflict resolution.
- Choose the Right Medium: Selecting the most suitable form of expression based on the context is vital. For example, video calls can enable deeper interactions compared to text-based exchanges. In fact, 45% of remote workers reported using Zoom for interaction, showcasing its effectiveness in enhancing engagement.
- Establish Ground Rules: In group settings, let’s set clear expectations for interaction. This helps create a respectful and productive environment, minimizing misunderstandings and promoting effective collaboration.
By implementing these strategies, we can significantly define mediated communication effectiveness. This is especially crucial in conflict resolution scenarios, where clarity and understanding are paramount. Together, let’s take action to foster better communication and support one another in our interactions.
Conclusion
Mediated communication is more than just a tool; it’s a vital bridge that connects us across distances, allowing for the exchange of ideas and information through various technological platforms. In our fast-paced world, this form of interaction reshapes how we communicate, highlighting the importance of understanding its characteristics, forms, and the strategies that can enhance its effectiveness, especially in conflict resolution scenarios.
As we explore mediated communication, let’s consider some key characteristics: asynchronicity, reduced nonverbal cues, and adaptability. Each form—whether text-based, audio, or video—offers unique benefits and challenges that shape how our messages are conveyed and understood. It’s crucial to recognize that clarity and intention play significant roles, as misunderstandings can easily arise from the absence of nonverbal signals and the nuances of tone.
Reflecting on these insights, it becomes evident that mastering mediated communication is essential in today’s interconnected world. By embracing effective strategies such as active listening, utilizing visual aids, and establishing ground rules, we can foster clearer and more meaningful interactions. These practices not only enhance our personal and professional relationships but also pave the way for more effective conflict resolution.
As technology continues to evolve, prioritizing the quality of our mediated exchanges is vital. Let’s commit to nurturing deeper connections and a more profound understanding of one another. Together, we can create a more compassionate and understanding environment in our communications.
Key Benefits of Mediated Communication:
- Enhances clarity in conversations.
- Fosters meaningful relationships.
- Supports effective conflict resolution.
In this journey, let’s remember that every interaction is an opportunity to connect more deeply with one another.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is mediated communication?
Mediated communication refers to interactions that occur through technology, allowing individuals to share messages across distances and time, such as through emails, social media, or video calls.
Why is understanding mediated communication important?
Understanding mediated communication is crucial as it helps define the concept and explores its characteristics, types, challenges, and strategies, which are essential for effective interactions.
How does mediated communication affect conflict resolution?
Effective facilitated dialogue in mediated communication allows individuals to express their needs and concerns clearly, promoting understanding and cooperation, which is vital for resolving conflicts.
What are the key characteristics of mediated communication?
The key characteristics include asynchronicity, reduced nonverbal cues, accessibility, adaptability, and anonymity.
What is asynchronicity in mediated communication?
Asynchronicity allows conversations to occur at different times, giving participants the flexibility to respond when it suits them, which can be particularly helpful in conflict resolution.
How do reduced nonverbal cues impact mediated interactions?
The absence of nonverbal signals, such as facial expressions and body language, can lead to misunderstandings in mediated interactions, as these cues are vital for conveying emotions and intentions.
How does accessibility benefit mediated communication?
Accessibility allows individuals to connect regardless of geographical barriers, which is especially valuable in mediation and arbitration situations where parties may be far apart.
What does adaptability mean in the context of mediated communication?
Adaptability refers to the ability to choose different formats—text, audio, or video—for interactions, allowing communication styles to be tailored to fit various contexts.
What role does anonymity play in mediated communication?
Anonymity can encourage openness and honesty in some forms of mediated interaction, but it may also lead to decreased accountability, complicating dispute resolution efforts.
What are the emotional costs associated with mediated communication?
Relying heavily on mediated exchanges can lead to emotional costs, as positive feelings from digital interactions often fade more quickly than those from face-to-face encounters.




