Introduction
Navigating the complexities of severance laws can feel overwhelming, can’t it? Especially when you consider the significant differences between California's regulations and federal guidelines. California offers a more structured approach with specific requirements, while federal laws provide a broader framework that doesn’t guarantee mandatory compensation.
Understanding these differences is crucial. It can empower you as an employee and guide employers in crafting fair termination agreements. What do these contrasting laws mean for you if you’re facing a job transition? How can you leverage your rights to secure better outcomes?
By delving into the nuances of these two systems, we can uncover valuable insights that may help you navigate this challenging landscape with confidence.
Overview of California Severance Law
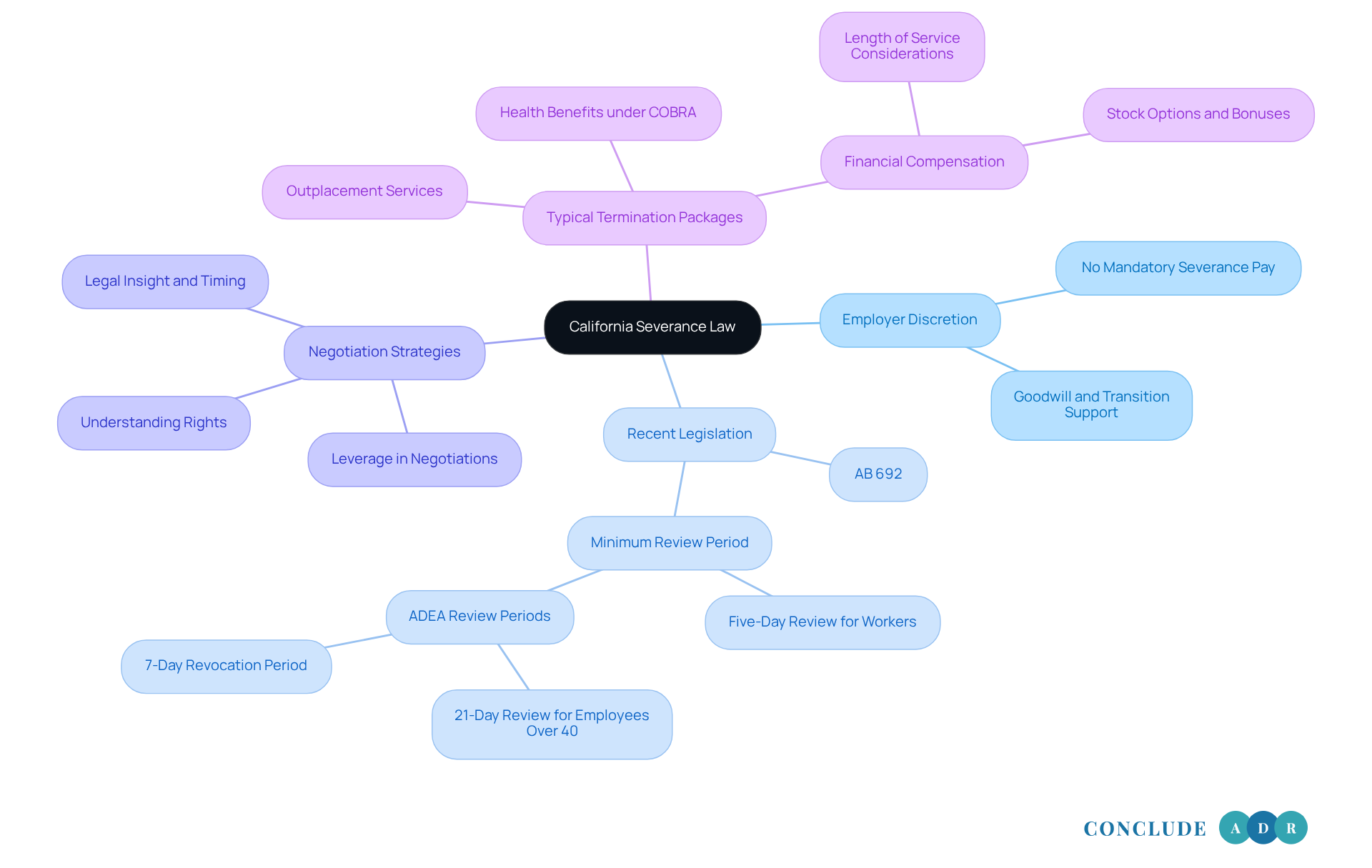
According to California severance law, there is no requirement for termination compensation upon dismissal, which leaves the decision to employers. Yet, many employers choose to offer compensation packages. Why? To maintain goodwill and help staff during transitions.
Recent legislation, like AB 692, has introduced specific requirements for termination contracts. For instance, there’s now a minimum five-day review period for workers. Plus, California prohibits certain provisions in these contracts, such as those that limit a worker's ability to report illegal workplace activities.
As you navigate termination agreements, remember: you often have more leverage than you might think. Successful negotiations hinge on legal insight and timing, both crucial for achieving favorable outcomes.
Typical termination packages in California might include:
- Continued health benefits under COBRA
- Outplacement services
- Financial compensation based on your length of service, which can cover stock options, commissions, bonuses, and retirement benefits.
If you’re over 40, the Age Discrimination Employment Act (ADEA) offers additional protections, including specific clauses regarding termination packages. This evolving legal landscape underscores the importance of being well-informed about your rights and options under California severance law when negotiating termination agreements.
So, as you consider your next steps, take a moment to reflect on your situation. Are you aware of all your rights? Remember, you’re not alone in this process, and being informed can empower you to negotiate effectively.
Understanding Federal Severance Guidelines
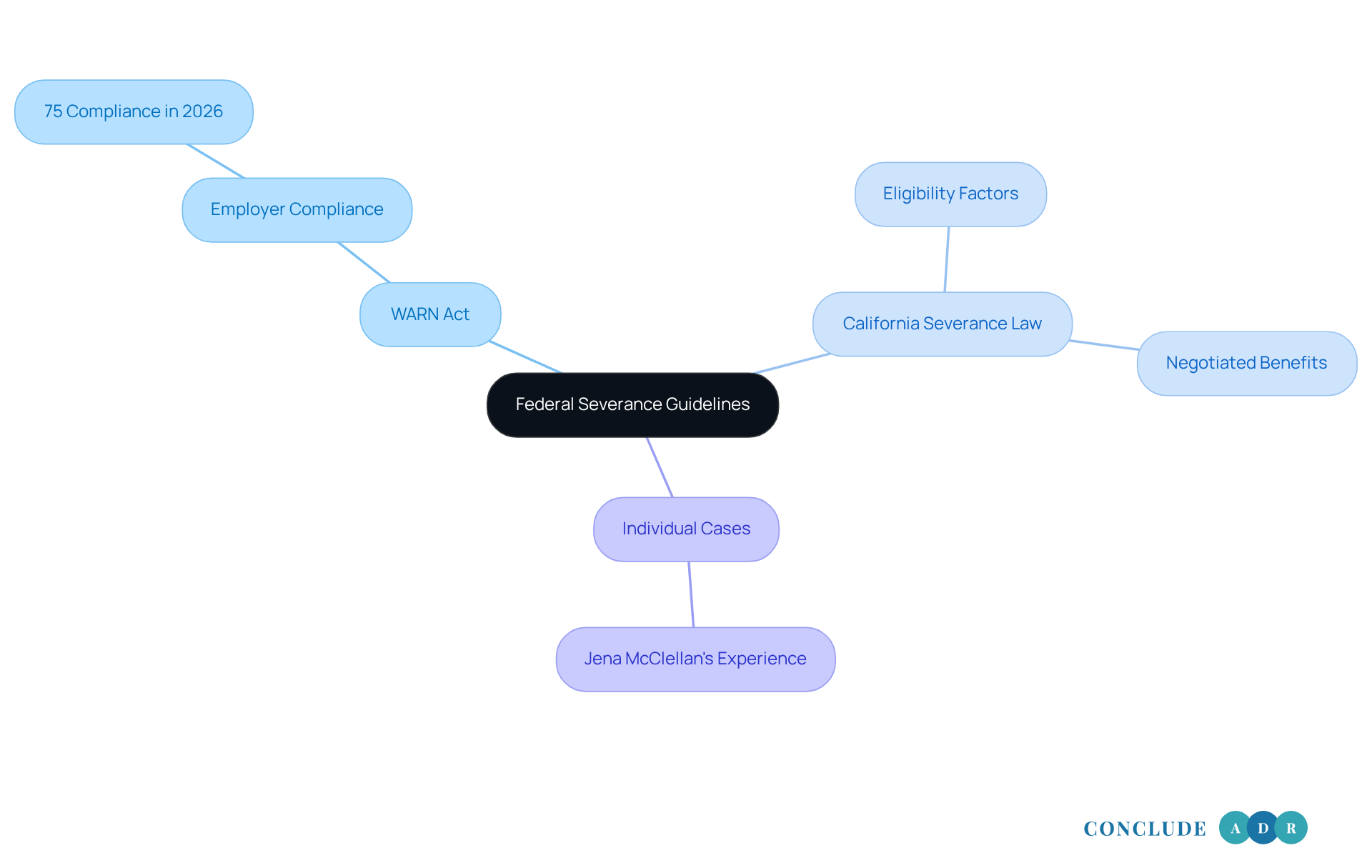
Under federal law, employers aren't required to provide termination pay, which can be a source of concern for many. The Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification (WARN) Act does require certain employers to give prior notice of mass layoffs, but it doesn’t mandate compensation payments. Did you know that in 2026, about 75% of employers were following WARN Act requirements? This highlights how crucial it is to have proper notification procedures during layoffs.
Discussions between employers and employees often lead to severance arrangements that are governed by California severance law. Eligibility can be influenced by factors such as how long someone has worked and specific employment contract conditions, according to California severance law. It’s important to understand that California severance law views exit compensation as a negotiated benefit rather than a legal requirement. This gives companies the flexibility to tailor termination packages according to California severance law to their unique situations.
For instance, termination contracts under federal law might include clauses for compensation based on tenure or specific conditions related to the end of employment. As the Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals pointed out, "the economic realities are that in many instances, the employee will have already expended the funds and will not have the capacity to repay it." This really emphasizes the complexities involved in termination negotiations.
Consider the case of Jena McClellan. Her experience shows how separation contracts can be challenged. She felt pressured into signing a termination contract in exchange for a compensation payment, which led to legal actions. This situation reminds us of the importance of understanding our rights and seeking support when navigating these difficult conversations.
Key Differences Between California and Federal Severance Policies
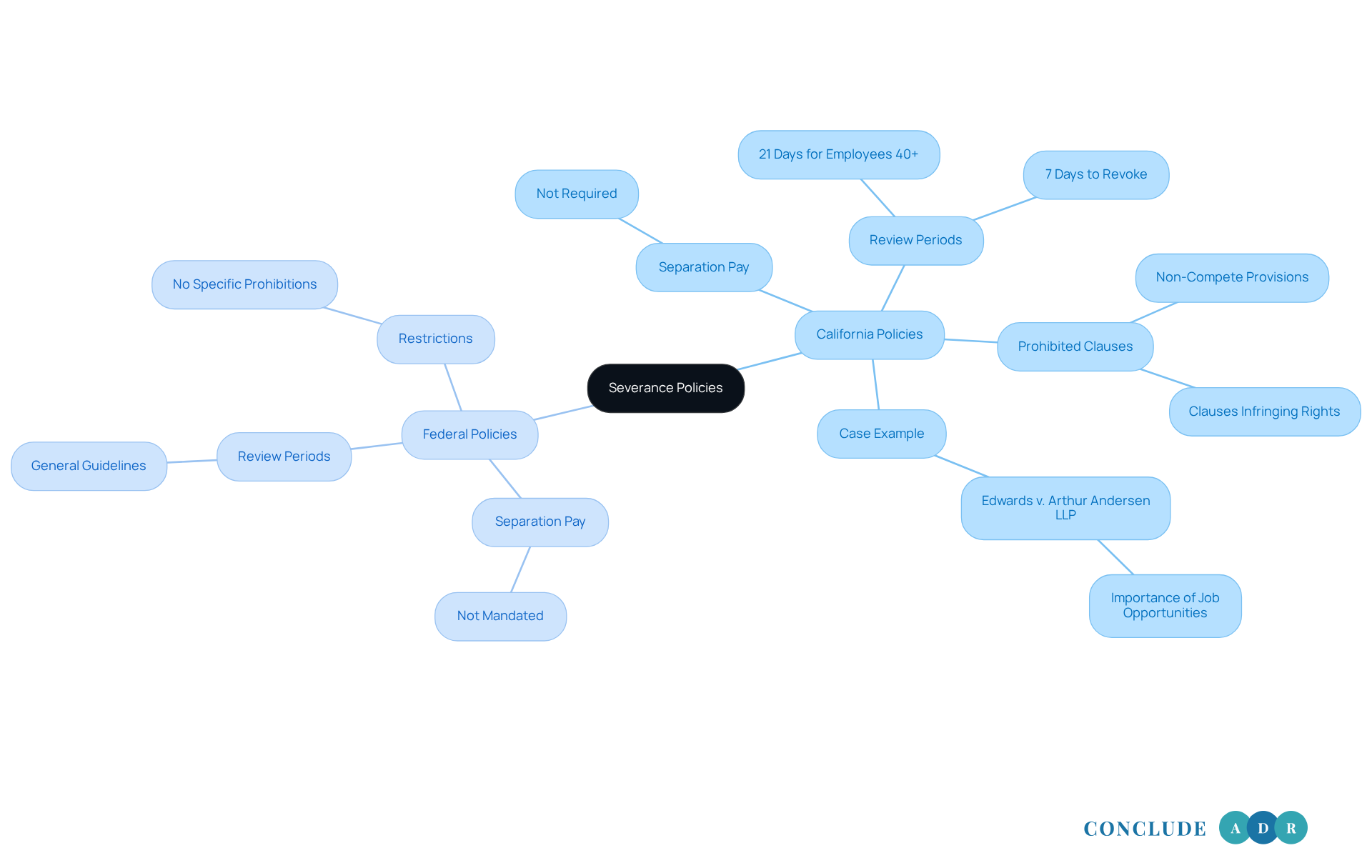
When it comes to termination policies, there’s a significant difference between regional and federal guidelines that you should be aware of. Unlike federal policies, the area doesn’t require separation pay. However, state legislation steps in with specific procedural requirements, like a five-day review period for termination contracts, which you won’t find at the federal level.
If you’re 40 or older, you have the right to a 21-day review period for termination contracts under the Older Workers Benefit Protection Act (OWBPA). Plus, there’s a seven-day window to withdraw from the contract after signing. It’s crucial to know that the California severance law prohibits certain clauses in severance agreements that could infringe on your rights, such as non-compete provisions. Federal guidelines, on the other hand, don’t impose similar restrictions.
Take, for instance, the California Supreme Court case Edwards v. Arthur Andersen LLP. This case underscores the importance of allowing workers to pursue new job opportunities without facing excessive restrictions. Understanding these differences is vital for both employers and employees alike, as it helps clarify your rights and obligations under California severance law.
Moreover, a reasonable termination package can be beneficial for everyone involved. It provides financial stability for workers while helping employers minimize potential legal conflicts. Grasping the negotiation process and the possible tax implications of termination pay is essential for effective compliance and negotiation.
So, as you navigate this complex landscape, remember that you’re not alone. Understanding your rights can empower you to make informed decisions.
Implications of Severance Law Differences for Employees and Employers
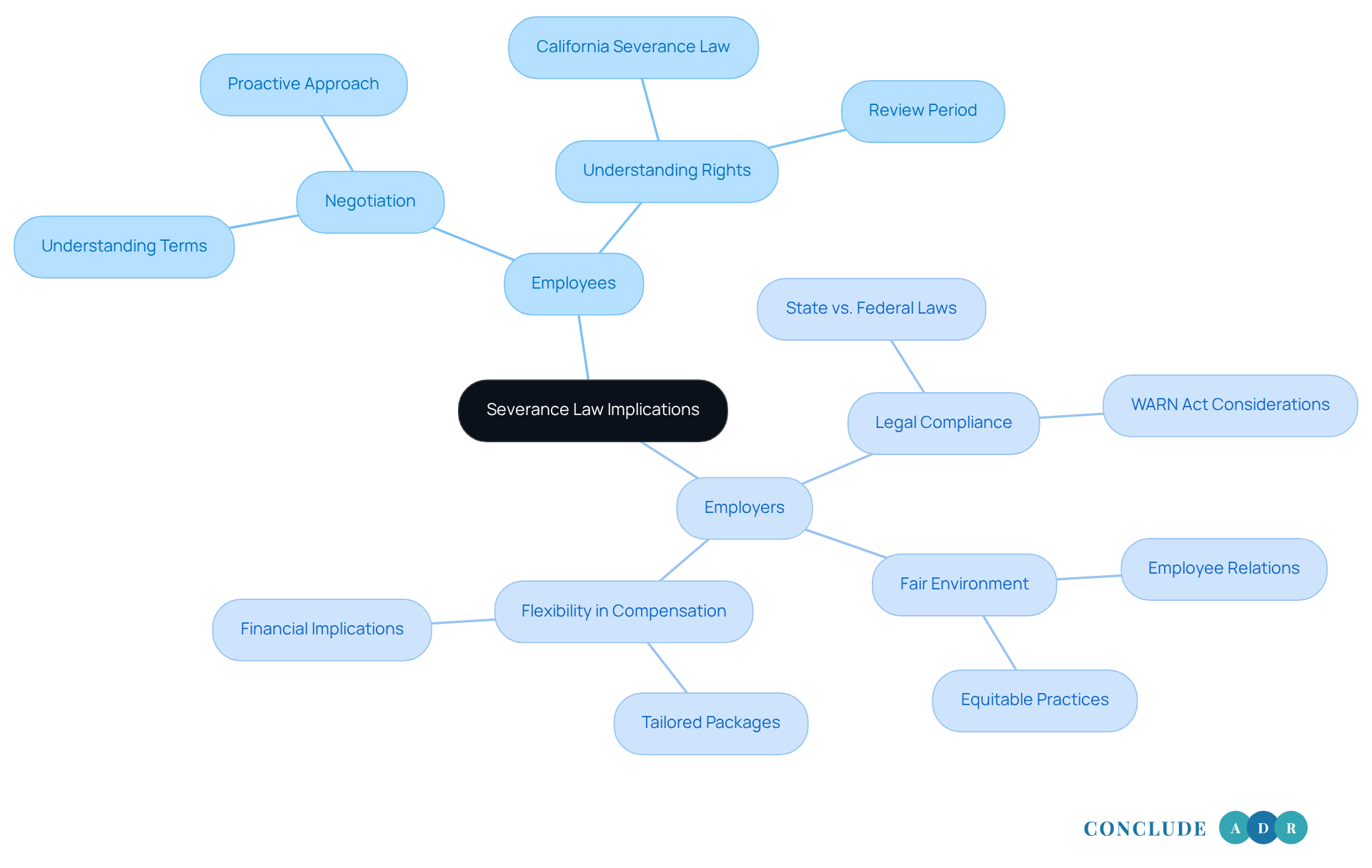
Understanding the differences between state and federal termination policies can feel overwhelming, but it’s crucial for both workers and employers. For workers, realizing that there’s no state requirement for termination compensation according to California severance law means they need to be proactive. It’s essential to negotiate effectively and understand your rights under California severance law, particularly concerning the review period and any prohibited clauses. Have you thought about how this impacts your situation?
Employers face their own challenges. They must navigate the complexities of both legal frameworks to ensure compliance and avoid disputes. It’s not just about following the rules; it’s about creating a fair environment. In California, the focus on equitable practices in relation to the California severance law can lead to better outcomes for employees. Meanwhile, federal guidelines allow employers the flexibility to tailor compensation packages to their specific needs. This adaptability can be beneficial, but it also requires careful consideration.
Ultimately, this dynamic highlights the importance of clear communication and legal awareness in severance negotiations, particularly in the context of California severance law. By fostering open dialogue, both parties can work towards a resolution that respects everyone’s rights and needs. So, let’s prioritize understanding and support in these discussions.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of severance laws can feel overwhelming, can’t it? Especially when you’re trying to compare California’s regulations with federal guidelines. California’s severance law offers specific protections and procedural requirements that differ significantly from the more flexible federal framework. Understanding these distinctions is essential for both employees and employers, as it shapes the negotiation landscape for termination agreements.
Throughout our discussion, several key points have emerged. While California does not mandate severance pay, many employers choose to provide it to foster goodwill and support during transitions. Recent legislative updates, like AB 692, have introduced vital protections for employees, including review periods and restrictions on certain contract clauses. In contrast, federal guidelines lack similar requirements, which highlights the importance of being proactive in negotiations and aware of your rights under California severance law.
Ultimately, grasping the nuances of severance policies is crucial for making informed decisions. Both employees and employers benefit from clear communication and a mutual understanding of the legal landscape. By prioritizing awareness and engagement in severance negotiations, we can work towards equitable outcomes that respect individual rights and foster a fair work environment. So, let’s take the time to understand these laws together and ensure that everyone feels supported during these transitions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does California severance law say about termination compensation?
California severance law does not require employers to provide termination compensation upon dismissal; the decision to offer compensation packages is left to employers.
Why do many employers choose to offer severance packages?
Employers often choose to offer severance packages to maintain goodwill and assist staff during transitions.
What recent legislation has affected termination contracts in California?
Recent legislation, such as AB 692, has introduced specific requirements for termination contracts, including a minimum five-day review period for workers and prohibitions against certain provisions that limit a worker's ability to report illegal workplace activities.
What are some typical components of termination packages in California?
Typical termination packages may include continued health benefits under COBRA, outplacement services, and financial compensation based on the employee's length of service, which can cover stock options, commissions, bonuses, and retirement benefits.
What additional protections does the Age Discrimination Employment Act (ADEA) provide for employees over 40?
The ADEA offers additional protections for employees over 40, including specific clauses regarding termination packages.
What should employees consider when negotiating termination agreements?
Employees should be aware of their rights, understand the legal landscape, and recognize that they often have more leverage than they might think, with successful negotiations depending on legal insight and timing.




