Introduction
Substantive fairness in employee dismissals isn’t merely a legal obligation; it’s a core principle that profoundly influences workplace culture and trust. As organizations face growing scrutiny over their termination practices, it’s essential to navigate this complex landscape with care.
By embracing best practices that ensure fairness, employers can reap significant rewards. Imagine a workplace where morale is high, legal risks are minimized, and the organization enjoys a strong reputation. These outcomes are not just beneficial; they’re achievable through a commitment to fairness.
But here’s the question: how can businesses effectively balance the need for operational efficiency with the ethical imperative of treating employees justly during dismissals? This is a challenge that many face, and it’s one that deserves thoughtful consideration.
Let’s reflect on this together. How can we create an environment where every employee feels valued, even in difficult situations? By prioritizing fairness, we can foster a culture of trust and respect that benefits everyone.
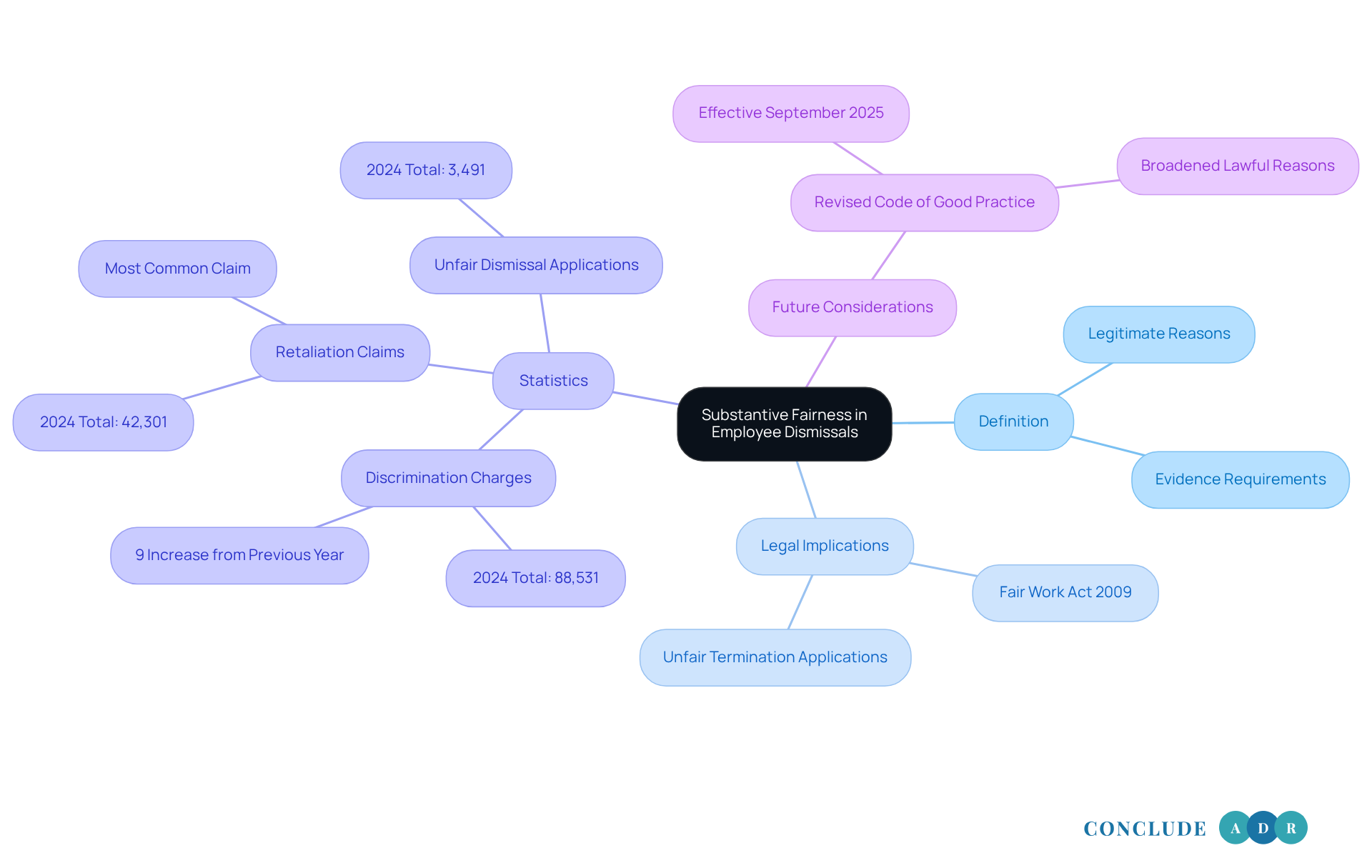
Define Substantive Fairness in Employee Dismissals
Substantive fairness in employee terminations involves ensuring that the reasons for ending someone's contract are both legitimate and justified. It’s crucial that these grounds are not only lawful but also demonstrate substantive fairness. For example, if someone is terminated for misconduct, there should be clear evidence to support that decision. Similarly, if a termination is due to operational necessities, it must reflect genuine business needs.
The Fair Work Act 2009 (Cth) states that a termination can be deemed unfair if it is harsh, unjust, or unreasonable. This highlights the importance of having a solid foundation for any termination decision to achieve substantive fairness. In 2024, we saw 88,531 discrimination charges submitted, marking a 9% increase from the previous year. This rise underscores the growing scrutiny surrounding termination policies. Additionally, 42,301 charges of retaliation were filed in 2024, making it the most common claim. This further emphasizes the need for employers to adhere to substantive fairness in their practices.
Employers must ensure that their reasons for termination adhere to the principles of substantive fairness and are well-documented. This is vital to mitigate potential legal risks, as evidenced by the 3,491 unfair termination applications lodged in the same year. Looking ahead, the revised Code of Good Practice on incapacity terminations, effective September 2025, will broaden the range of lawful reasons for termination. It’s essential for employers to stay informed about these changing regulations.
Recent cases, such as those involving disability discrimination—where an individual was dismissed after being diagnosed with cancer—highlight the critical importance of adhering to valid reasons for termination. By prioritizing substantial equity and maintaining thorough records, employers can navigate the complexities of terminations while fostering a just workplace atmosphere.
Are you ready to ensure fairness in your workplace? Together, we can create an environment where every employee feels valued and respected.
Explore Key Principles of Substantive Fairness
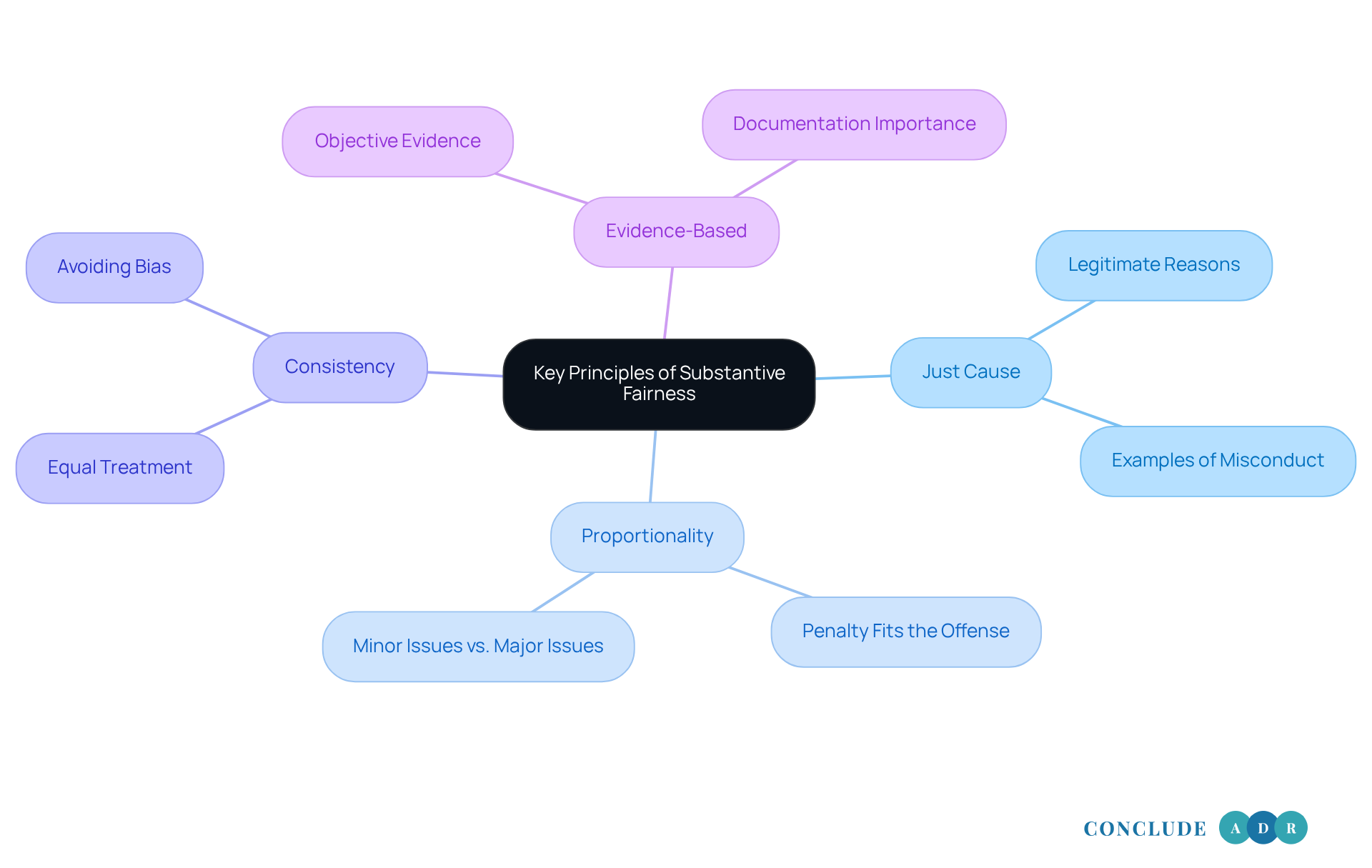
Creating a just workplace environment is crucial, especially when it comes to worker terminations. Understanding the key principles of substantive fairness that guide this process is essential.
-
Just Cause: There should always be a legitimate reason for termination. This could be due to misconduct, incapacity, or redundancy. For example, if a staff member repeatedly violates company policy, it may warrant termination.
-
Proportionality: The penalty should fit the offense. A minor issue, like being late, shouldn’t lead to immediate termination. Instead, a warning or a lesser penalty might be more appropriate.
-
Consistency: It’s vital for employers to treat similar cases alike. This helps prevent any feelings of bias or discrimination. If one employee receives a warning for a specific behavior, others in similar situations should be treated the same way.
-
Evidence-Based: Decisions about dismissal should be based on objective evidence, not personal opinions. Employers should document all relevant facts and circumstances surrounding the termination. This ensures that the reasoning is clear and defensible. Proper documentation is key to preventing wrongful termination claims, as highlighted in the revised Code of Good Practice on Termination, effective September 2025.
By embracing these principles, we can foster a fair termination process that ensures substantive fairness, complies with legal standards, and builds trust within the organization. Remember, fairness in the workplace is not just a policy; it’s a commitment to treating everyone with respect and dignity.
Implement Best Practices for Fair Dismissals
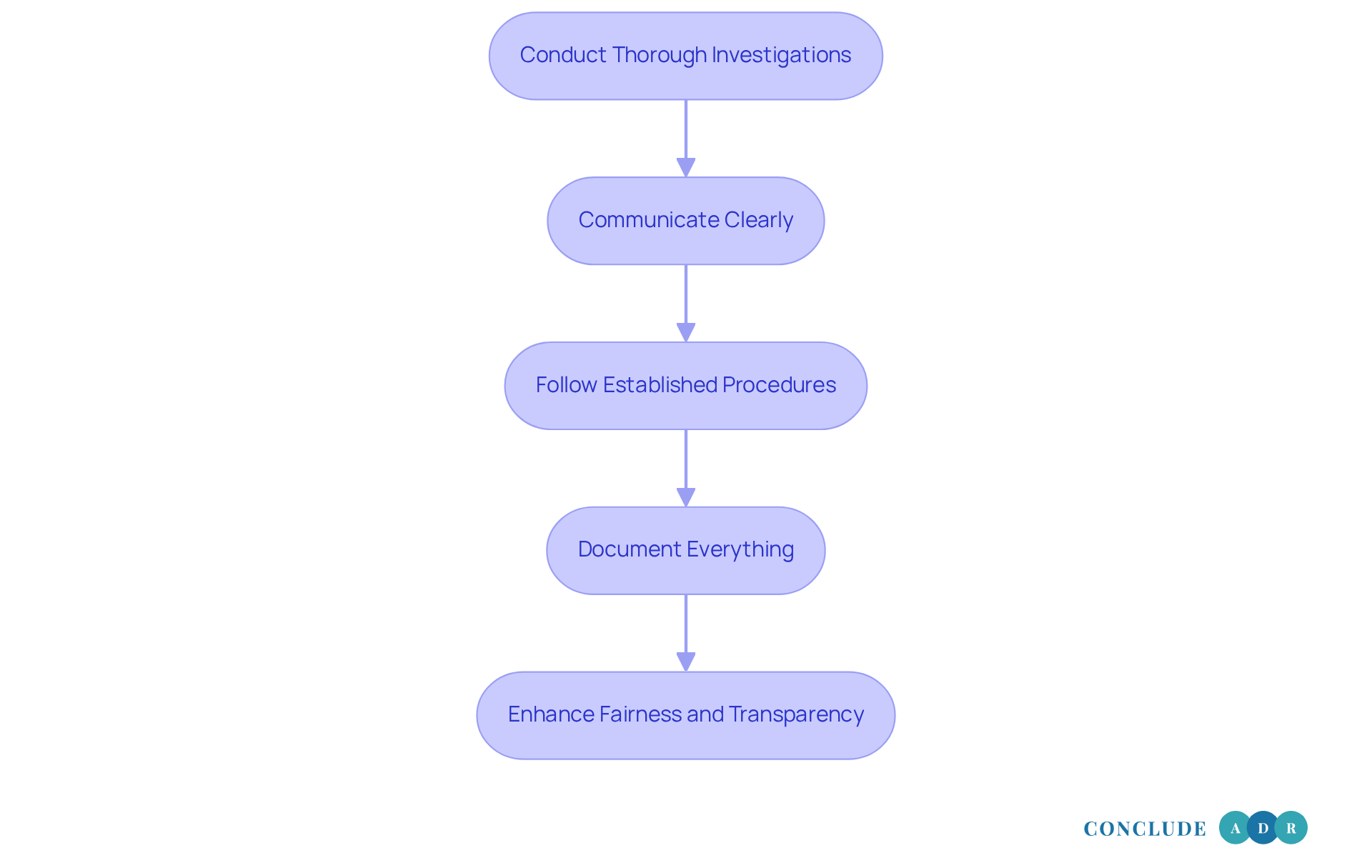
To ensure substantive fairness in terminations, it is essential for employers to approach the process with care and understanding. Here are some key practices to consider:
-
Conduct Thorough Investigations: Before deciding on a termination, take the time to investigate the situation fully. This means gathering evidence, talking to witnesses, and reviewing any relevant documents. It’s about understanding the whole picture.
-
Communicate Clearly: It’s vital to inform employees about the reasons for their termination in a respectful and clear manner. Allow them the chance to respond to the allegations. This not only fosters trust but also helps minimize disputes. Remember, clear communication can make a significant difference in how the situation is perceived.
-
Follow Established Procedures: Stick to your company’s policies and legal requirements when it comes to disciplinary actions and terminations. This includes providing written notifications and informing employees of their rights. It’s crucial to ensure substantive fairness in order for no one to feel unjustly treated during this process.
-
Document Everything: Keep detailed records of every step taken during the termination process, from investigations to communications and decisions. As Lisa Stickler wisely points out, "Recording termination activities aids employers in defending against discrimination, wrongful termination, or other employment-related claims." This documentation can be invaluable if disputes arise. Additionally, if a termination relates to performance issues, it’s essential that the employee was warned about these problems beforehand, as highlighted in the case study 'Importance of Warning for Unsatisfactory Performance.'
By following these practices, you can enhance the substantive fairness and transparency of your termination processes. Remember, it’s not just about the decision; it’s about how you handle it with compassion and respect.
Evaluate Benefits of Substantive Fairness in Dismissals
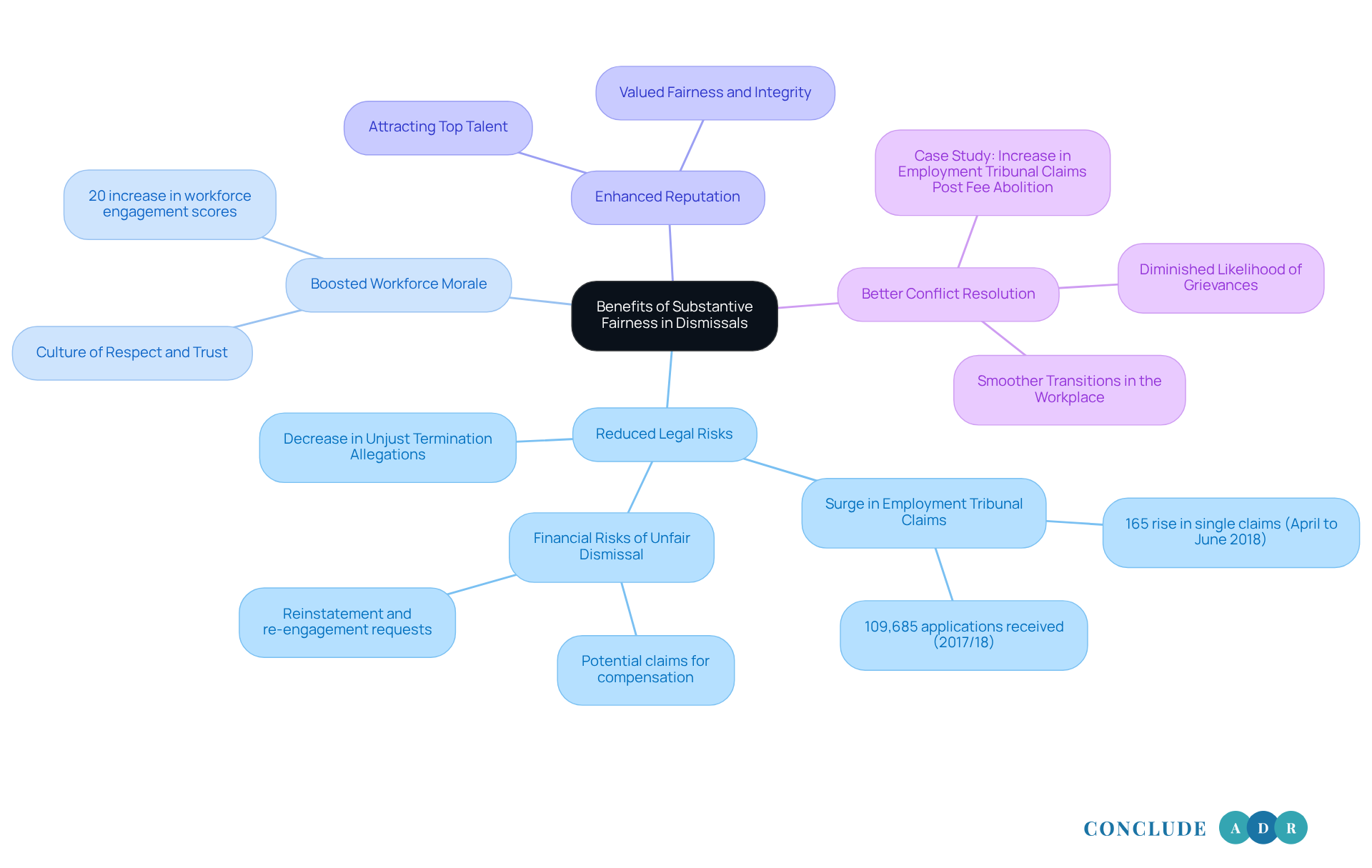
The advantages of guaranteeing substantial equity in terminations are significant and can truly make a difference in the workplace.
-
Reduced Legal Risks: When employers embrace principles of substantive fairness, they can decrease the likelihood of facing unjust termination allegations. This not only protects the organization but also alleviates the stress that comes with potential legal disputes. As Jatinder Tara points out, "Employers might occasionally contemplate the financial risks associated with terminating an employee unjustly, and when an employee asserts unfair termination, the possible requests would include: compensation, reinstatement, re-engagement." Since the abolition of fees for Employment Tribunal claims in July 2017, claims have surged, with a staggering 165% rise in single claims reported from April to June 2018 compared to the previous year. This trend underscores the importance of fair termination practices to help mitigate legal challenges.
-
Boosted Workforce Morale: Treating employees equitably during separations fosters a culture of respect and trust within the organization. This nurturing environment leads to increased staff morale and engagement. Have you ever noticed how organizations that prioritize fairness in their termination processes often enjoy higher levels of staff satisfaction? Data shows that these organizations report a 20% rise in workforce engagement scores, which can translate into enhanced productivity and loyalty.
-
Enhanced Reputation: Organizations known for their fair termination methods are more likely to attract and retain top talent. Prospective employees are drawn to workplaces that value fairness and integrity.
-
Better Conflict Resolution: When terminations are handled fairly, the likelihood of conflict and grievances diminishes. This creates smoother transitions and minimizes disruptions in the workplace. The case study titled "Increase in Employment Tribunal Claims Post Fee Abolition" illustrates how fair dismissal practices can prevent legal disputes and foster a positive work environment.
Overall, prioritizing substantive fairness contributes to a positive organizational culture while also protecting the organization legally. By embracing these practices, we can create a workplace where everyone feels valued and respected.
Conclusion
Ensuring substantive fairness in employee dismissals is not just a legal requirement; it’s a cornerstone of a respectful and compliant workplace. Have you ever considered how terminations impact not only the individual but the entire team? It’s crucial that dismissals are based on legitimate, well-documented reasons that align with legal standards and ethical principles. By prioritizing fairness, organizations protect themselves from potential legal issues while nurturing a culture of trust and respect among employees.
Let’s explore some best practices together.
- Conducting thorough investigations
- Communicating clearly with employees
- Adhering to established procedures
- Maintaining comprehensive documentation
Each of these practices ensures that dismissals are justified and perceived as fair by everyone involved. By embracing principles like just cause, proportionality, consistency, and evidence-based decision-making, employers can navigate the complexities of terminations with integrity.
The benefits of implementing substantive fairness in dismissals go beyond mere compliance. They lead to improved workforce morale, enhance organizational reputation, and reduce conflict. Imagine working in an environment where every employee feels valued and respected. By committing to fair dismissal practices, employers can create just that—a thriving workplace culture. Remember, embracing these principles is not only a legal obligation; it’s a vital step toward building a more engaged and productive workforce.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is substantive fairness in employee dismissals?
Substantive fairness in employee dismissals refers to ensuring that the reasons for terminating an employee's contract are both legitimate and justified. It requires that the grounds for termination are lawful and demonstrate substantive fairness, supported by clear evidence in cases of misconduct or genuine business needs in operational terminations.
What does the Fair Work Act 2009 (Cth) say about unfair termination?
The Fair Work Act 2009 (Cth) states that a termination can be deemed unfair if it is harsh, unjust, or unreasonable. This emphasizes the need for a solid foundation for any termination decision to achieve substantive fairness.
What trends were observed in discrimination and retaliation charges in 2024?
In 2024, there were 88,531 discrimination charges submitted, marking a 9% increase from the previous year. Additionally, 42,301 charges of retaliation were filed, making it the most common claim. This highlights the growing scrutiny surrounding termination policies.
Why is documentation important in termination decisions?
Documentation is vital in termination decisions to ensure that the reasons for termination adhere to the principles of substantive fairness. Proper documentation helps mitigate potential legal risks, as evidenced by the 3,491 unfair termination applications lodged in 2024.
What changes are expected in the Code of Good Practice on incapacity terminations in 2025?
The revised Code of Good Practice on incapacity terminations, effective September 2025, will broaden the range of lawful reasons for termination. Employers need to stay informed about these changing regulations.
Can you provide an example of a recent case highlighting the importance of valid termination reasons?
A recent case involved disability discrimination where an individual was dismissed after being diagnosed with cancer. This case underscores the critical importance of adhering to valid reasons for termination to ensure substantive fairness.
How can employers foster a just workplace atmosphere regarding terminations?
Employers can foster a just workplace atmosphere by prioritizing substantive fairness, maintaining thorough records, and ensuring that all termination decisions are based on legitimate and justified reasons.




