Introduction
Understanding the complexities of contractual obligations is essential for anyone facing legal disputes. It’s not just about the law; it’s about the relationships and trust that can be affected. An uncured material breach can disrupt these connections and lead to significant financial consequences for those who haven’t violated the contract.
This article explores the defining characteristics of such breaches, the criteria for determining them, and the potential remedies available. We aim to provide valuable insights for those navigating these challenging waters.
How can you effectively manage the complexities of these breaches? How can you ensure fair outcomes amidst the turmoil? Let’s delve into this together, recognizing that you’re not alone in this journey.
Define Uncured Material Breach
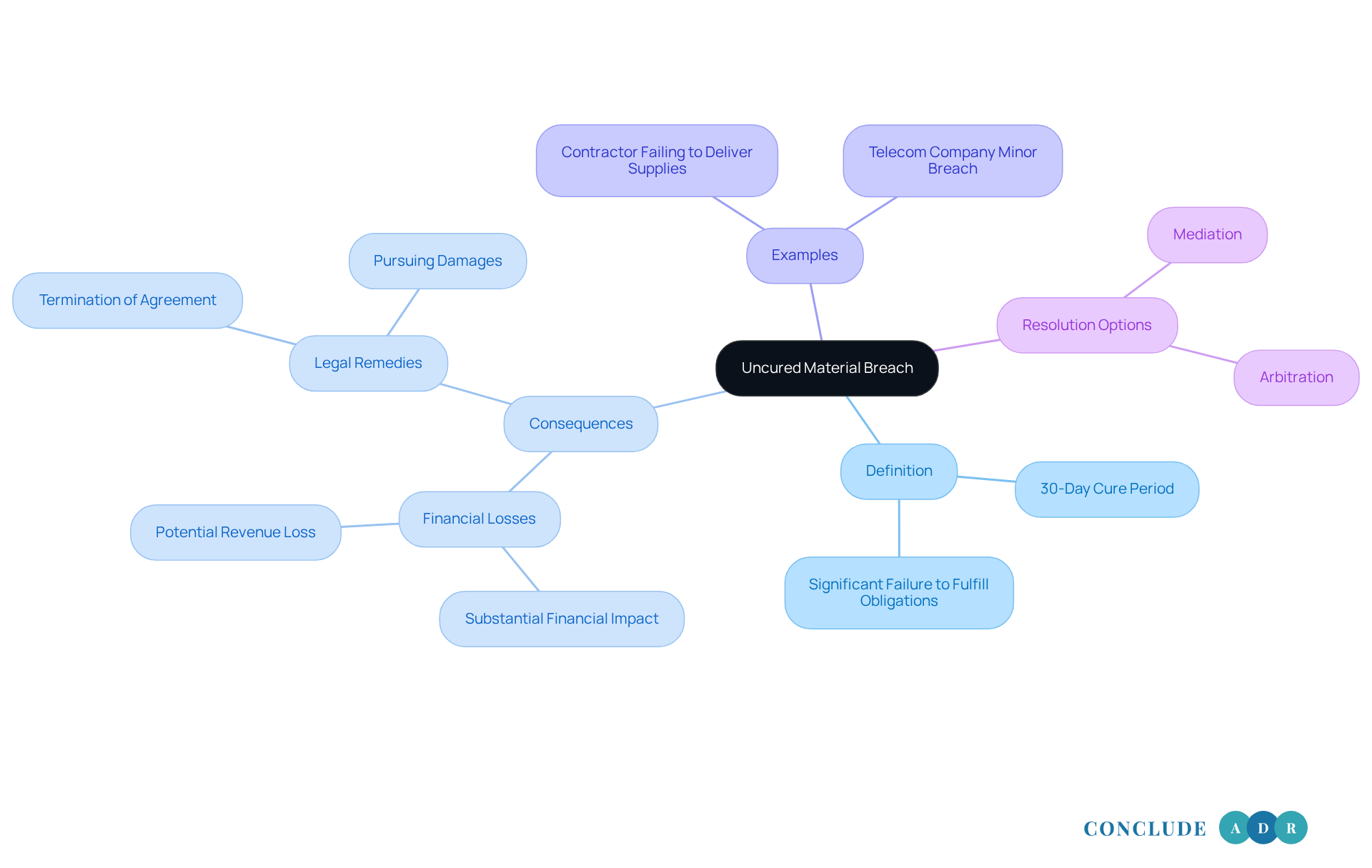
An uncured material breach occurs when an entity significantly fails to fulfill its contractual obligations and does not remedy this situation within a specified timeframe, typically thirty (30) days after receiving written notice. This kind of violation can really shake the foundation of an agreement, leaving the non-violating party feeling vulnerable. It’s important to know that they have the right to seek legal remedies, which might include terminating the agreement and pursuing damages.
Imagine a contractor who is supposed to deliver essential supplies for a project but doesn’t follow through. If they ignore the issue even after being notified, that’s a significant violation. It’s a tough situation, and as highlighted by the Bureau of Justice, over 27,000 agreement violations end up in court each year. This statistic underscores just how serious these matters can be.
The consequences of an uncured material breach can be quite severe. It’s not just about the breach itself; it can lead to substantial financial losses for the affected party. If you find yourself in such a situation, remember that you’re not alone. There are options available to help you navigate these challenges.
Have you considered mediation or arbitration? These processes can provide a supportive environment to resolve disputes without the stress of court. Let’s work together to find a resolution that respects your needs and rights.
Differentiate Between Material and Minor Breaches
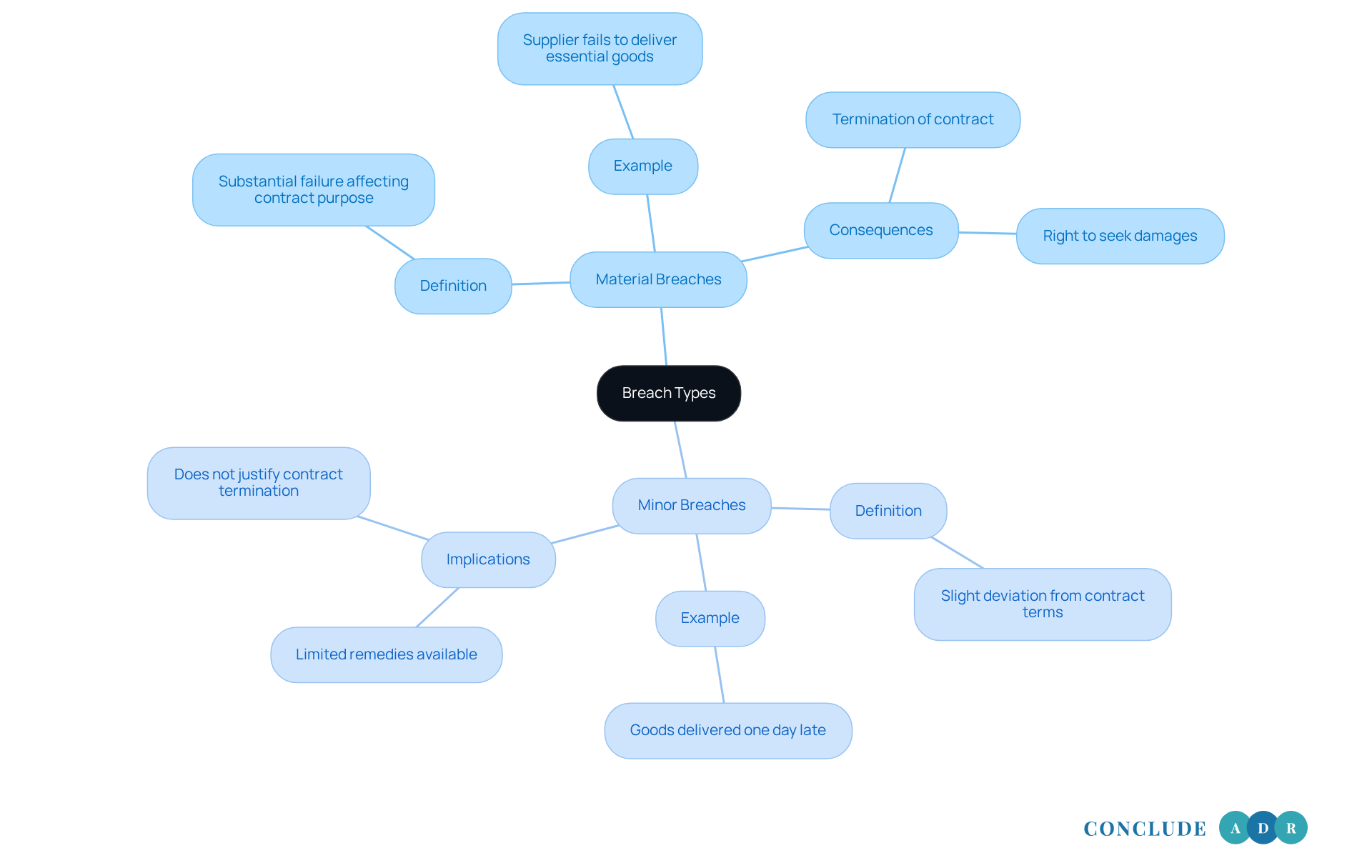
Material violations, also known as uncured material breaches, are serious issues that can deeply affect the purpose of an agreement. When these violations occur, they constitute an uncured material breach, enabling the non-violating party to terminate the agreement and seek damages. For example, imagine a supplier failing to deliver essential goods on time, jeopardizing a critical project. This situation clearly represents a significant violation that can have far-reaching consequences.
On the other hand, we have minor violations, often called immaterial violations. These do not substantially impact the overall purpose of the agreement. Picture a scenario where a supplier delivers goods just one day late, but it doesn’t cause any major disruption to the recipient's operations. Understanding these differences is vital for determining the best way to resolve disputes.
Did you know that many contracts experience substantial violations as a result of an uncured material breach? Recent statistics highlight the importance of identifying these issues early on. Legal experts emphasize that the severity of the violation, the contract's intent, and how much the non-violating party has lost are crucial factors in assessing the situation.
By familiarizing ourselves with these concepts, we can better navigate conflicts and seek the most appropriate remedies. Remember, recognizing the nuances of these violations can empower us to approach dispute resolution with confidence and compassion.
Assess Criteria for Material Breach Determination
When evaluating whether a violation is material, it’s important to consider several key criteria that can impact everyone involved:
-
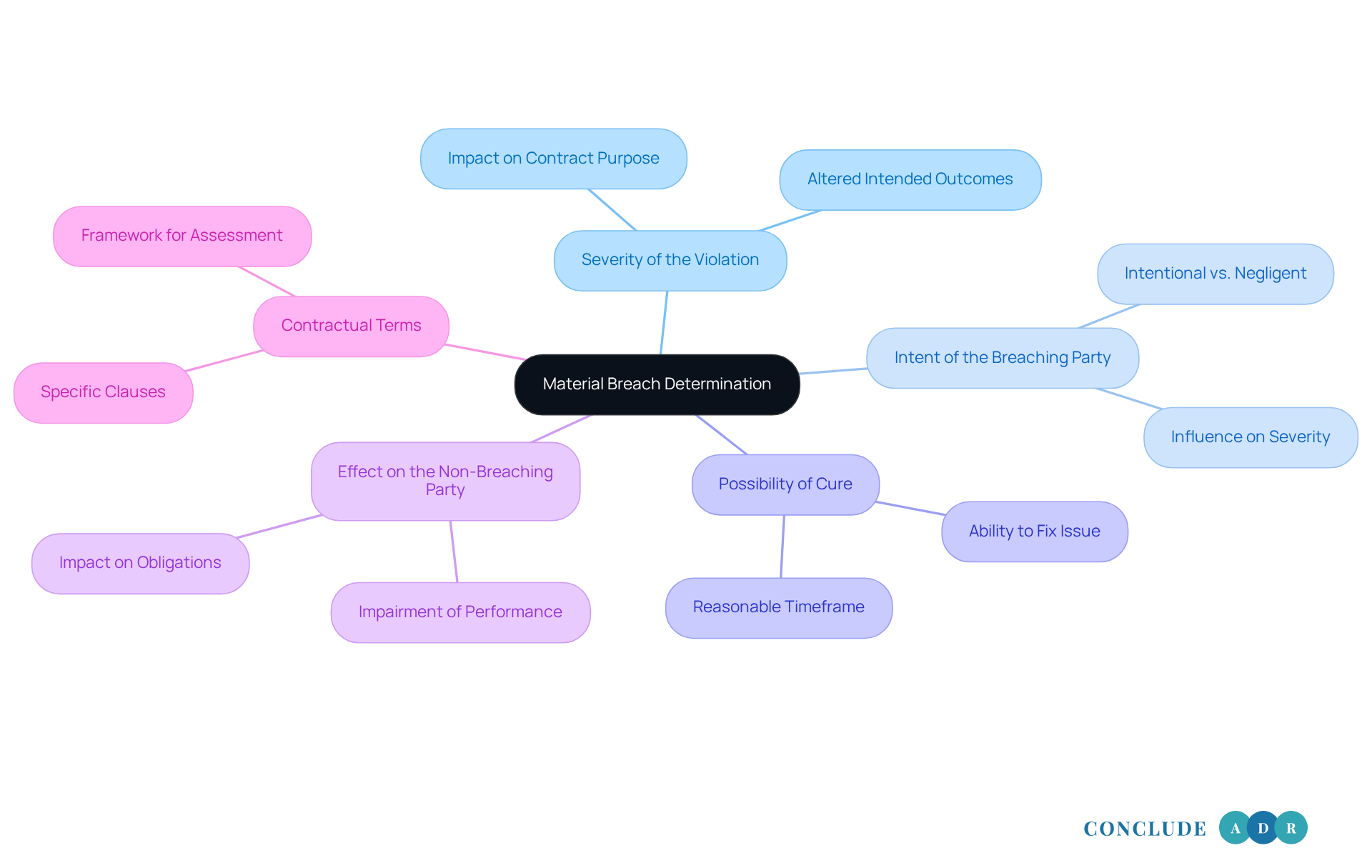
Severity of the Violation: Think about how much the violation affects the contract's purpose. An uncured material breach can significantly alter the intended outcomes of the agreement.
-
Intent of the Breaching Party: Was the violation intentional, or did it happen due to negligence? Understanding intent is crucial, as it can shape how severe the violation seems and what remedies might be available.
-
Possibility of Cure: Can the violating party fix the issue within a reasonable timeframe? If so, this can help lessen the impact of the violation.
-
Effect on the Non-Breaching Party: How does the violation affect the non-breaching party's ability to meet their obligations? If it significantly impairs their performance, it may be considered an uncured material breach.
-
Contractual terms sometimes include specific clauses that clearly define what constitutes an uncured material breach, providing a helpful framework for assessment.
By understanding these criteria, we can navigate complex legal situations more effectively. It’s all about ensuring fair outcomes for everyone involved. Remember, you’re not alone in this process; we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Explore Consequences and Remedies for Material Breach
The results of an uncured material breach can be profound, impacting everyone involved. It’s important to understand what an uncured material breach means for you and your situation. Here are some key outcomes to consider:
-
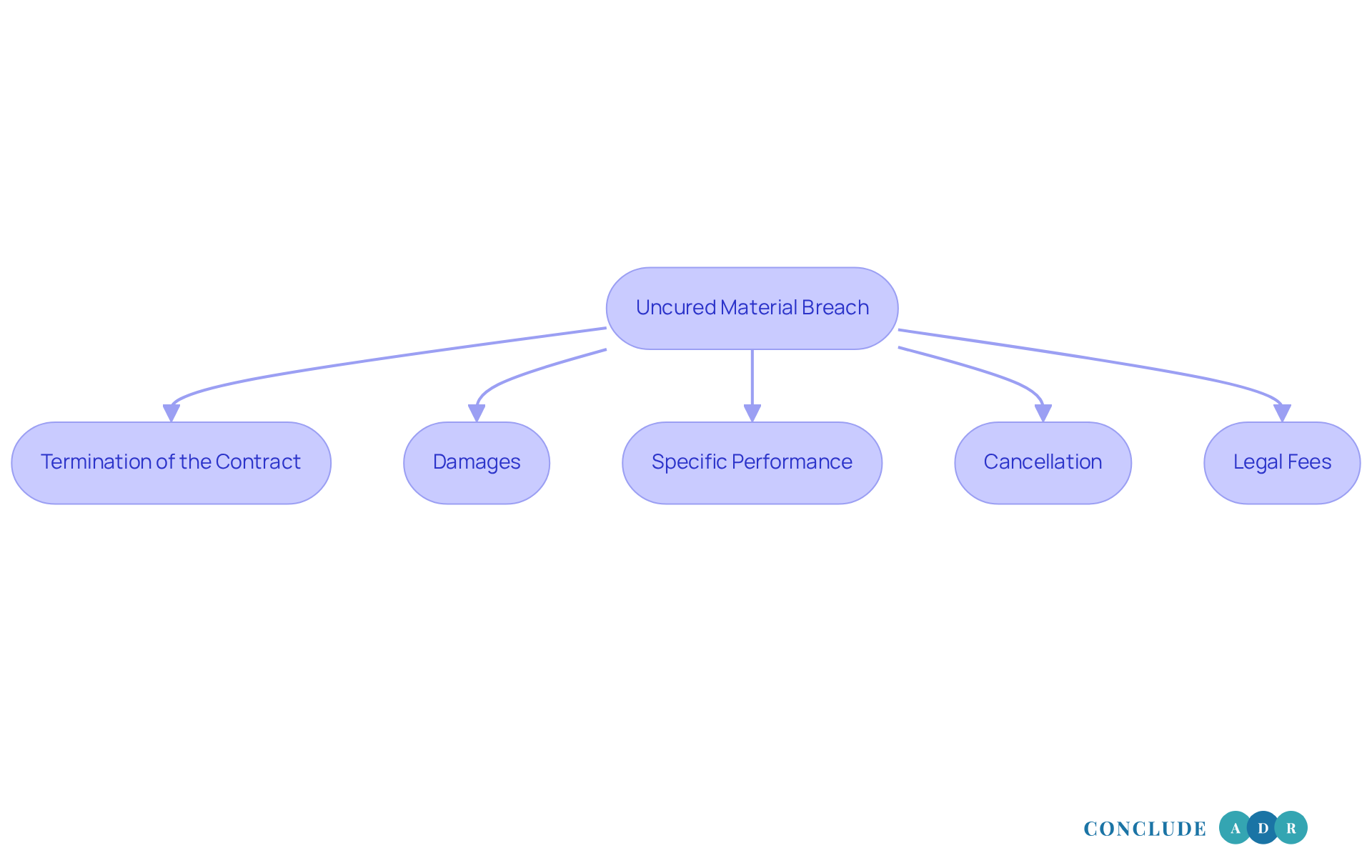
Termination of the Contract: If an uncured material breach occurs, the non-breaching side has the right to terminate the agreement, thereby ending their obligations. This can feel like a heavy decision, but it’s a necessary step to protect your interests.
-
Damages: The non-breaching party can seek compensatory damages, which aim to restore their financial position as if the violation had not taken place. Imagine facing lost profits due to someone else’s actions; the damages can be considerable. In fact, average awards often mirror the actual losses incurred. Did you know that the estimated cost of poor contract management globally is around $2 trillion per year? This highlights just how serious an uncured material breach can be.
-
Specific Performance: In certain situations, courts may require the breaching individual to fulfill their contractual obligations. This is especially true when monetary damages aren’t enough, like in cases involving unique goods or services. For instance, a court might order someone to deliver a one-of-a-kind bus that was once owned by a famous singer. It’s a reminder that some things are irreplaceable.
-
Cancellation: The agreement may be revoked, freeing both sides from their responsibilities and returning them to their pre-agreement statuses. This can be a relief, but it also means reassessing your next steps.
-
Legal Fees: The party at fault may be responsible for the legal costs incurred by the innocent party in pursuing remedies. This further emphasizes the financial consequences of a violation.
In Michigan, the statute of limitations for breach of agreement claims usually spans from 3 to 10 years. This is vital for dispute resolvers to consider when advising clients. Understanding these consequences equips you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of contract law and advocate effectively for your needs. Remember, you’re not alone in this; we’re here to help you through it.
Conclusion
An uncured material breach can feel overwhelming, representing a significant failure to meet contractual obligations. This situation leaves the non-violating party with the right to seek legal remedies, which can be daunting. Understanding this concept is crucial for anyone involved in contract management or dispute resolution. It highlights the importance of timely communication and remediation in preserving agreements, ensuring that everyone feels heard and supported.
Throughout this article, we've shared essential insights about uncured material breaches, the differences between material and minor breaches, and how to assess the severity of a breach. The potential consequences - like contract termination, damages, and specific performance - underscore the serious implications of such violations. With statistics showing how often contract violations lead to legal disputes, it’s clear that being aware of these issues is paramount.
Recognizing the complexities surrounding uncured material breaches empowers you and your organization to navigate disputes more effectively. Have you considered options like mediation or arbitration? These approaches can help you find resolutions that honor your rights and needs, fostering a sense of partnership in the process.
It’s vital to approach contract management with diligence and an understanding of the legal landscape. By doing so, you can mitigate risks and protect your interests. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an uncured material breach?
An uncured material breach occurs when an entity significantly fails to fulfill its contractual obligations and does not remedy the situation within a specified timeframe, typically thirty (30) days after receiving written notice.
What happens if an entity commits an uncured material breach?
If an entity commits an uncured material breach, the non-violating party has the right to seek legal remedies, which may include terminating the agreement and pursuing damages.
Can you provide an example of an uncured material breach?
An example of an uncured material breach is when a contractor fails to deliver essential supplies for a project and ignores the issue even after being notified.
How common are agreement violations that lead to legal action?
According to the Bureau of Justice, over 27,000 agreement violations end up in court each year, highlighting the seriousness of these matters.
What are the potential consequences of an uncured material breach?
The consequences of an uncured material breach can be severe, potentially leading to substantial financial losses for the affected party.
What options are available for resolving disputes related to an uncured material breach?
Options for resolving disputes include mediation and arbitration, which can provide a supportive environment to resolve issues without the stress of court.




