Overview
This article delves into the implications and mechanics of mandatory arbitration clauses in dispute resolution, particularly focusing on their impact on employees' rights and access to justice. Have you ever felt restricted in your legal options? These clauses often favor employers, leading to lower recovery outcomes for employees. Statistics reveal a significant disparity in success rates between arbitration and court litigation, raising important questions about fairness in the process.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial. By acknowledging the challenges posed by mandatory arbitration, we can explore the benefits of mediation and arbitration as alternatives. It’s essential to recognize how these mechanisms can sometimes offer a more supportive environment for resolving disputes.
As we navigate this complex landscape, it's vital to advocate for employees' rights and ensure that everyone has access to justice. Together, we can work towards a resolution that not only addresses these concerns but also empowers individuals in their pursuit of fairness. Let's consider how we can take action to promote a more equitable approach to dispute resolution.
Introduction
In today's contractual landscape, understanding the intricacies of mandatory arbitration clauses is more important than ever. These provisions increasingly dictate how disputes are resolved, leaving many individuals feeling overwhelmed. As more employers and businesses incorporate such clauses into their agreements, you may find yourself navigating a maze of limited legal options and potential inequities.
What does this mean for you as an employee or consumer? What implications do these clauses hold for your rights to seek justice and fair resolutions? These are crucial questions that deserve attention. Exploring these issues reveals a pressing need for awareness and advocacy, especially in an era where the arbitration process can significantly impact accountability and access to recourse.
Together, we can shed light on these challenges and work towards a more equitable future. It's essential to stay informed and engaged, ensuring that your voice is heard in the conversation surrounding arbitration and its effects on your rights.
Define Mandatory Arbitration Clauses
A mandatory arbitration clause is a contractual term that requires participants to settle conflicts through alternative dispute resolution instead of litigation. This means that if a conflict arises, the individuals involved are not able to take their claims to court; instead, they must engage in a private resolution process overseen by an arbitrator. These provisions, such as the mandatory arbitration clause, are often found in employment contracts, consumer agreements, and various business agreements, significantly limiting the legal options available to those involved.
By 2025, it's estimated that around 25% of all workers in nonunion settings will be subject to compulsory dispute resolution. Furthermore, over half of nonunion private-sector employers now require such arrangements, highlighting the widespread nature of these agreements. Understanding the is crucial for anyone navigating contracts, as it can profoundly affect rights and choices regarding dispute resolution.
Consider the case of Stephanie Sutherland, who faced challenges due to binding agreements. She was unable to pursue her overtime pay claims in court because of such a provision. In 2022, only 80 employees received a monetary award through compulsory mediation, resulting in a win rate of just 1.9%. This situation underscores the importance of being aware of the mandatory arbitration clause, as it can restrict access to justice and diminish the ability to seek fair resolutions.
Additionally, class-action waivers often included in these provisions impede collective legal action against corporations, further limiting employees' rights and options for recourse. It's essential to reflect on how these factors may impact you or someone you know. By being informed and proactive, we can work towards ensuring that our rights are protected and that we have access to fair dispute resolution processes.
Explain How Arbitration Clauses Work
A mandatory arbitration clause is an essential tool that outlines the procedures for resolving disputes, ensuring a structured and compassionate resolution process. When a claim is initiated, the individuals involved come together to select an arbitrator or a panel to adjudicate the case. Here’s how the arbitration process typically unfolds:
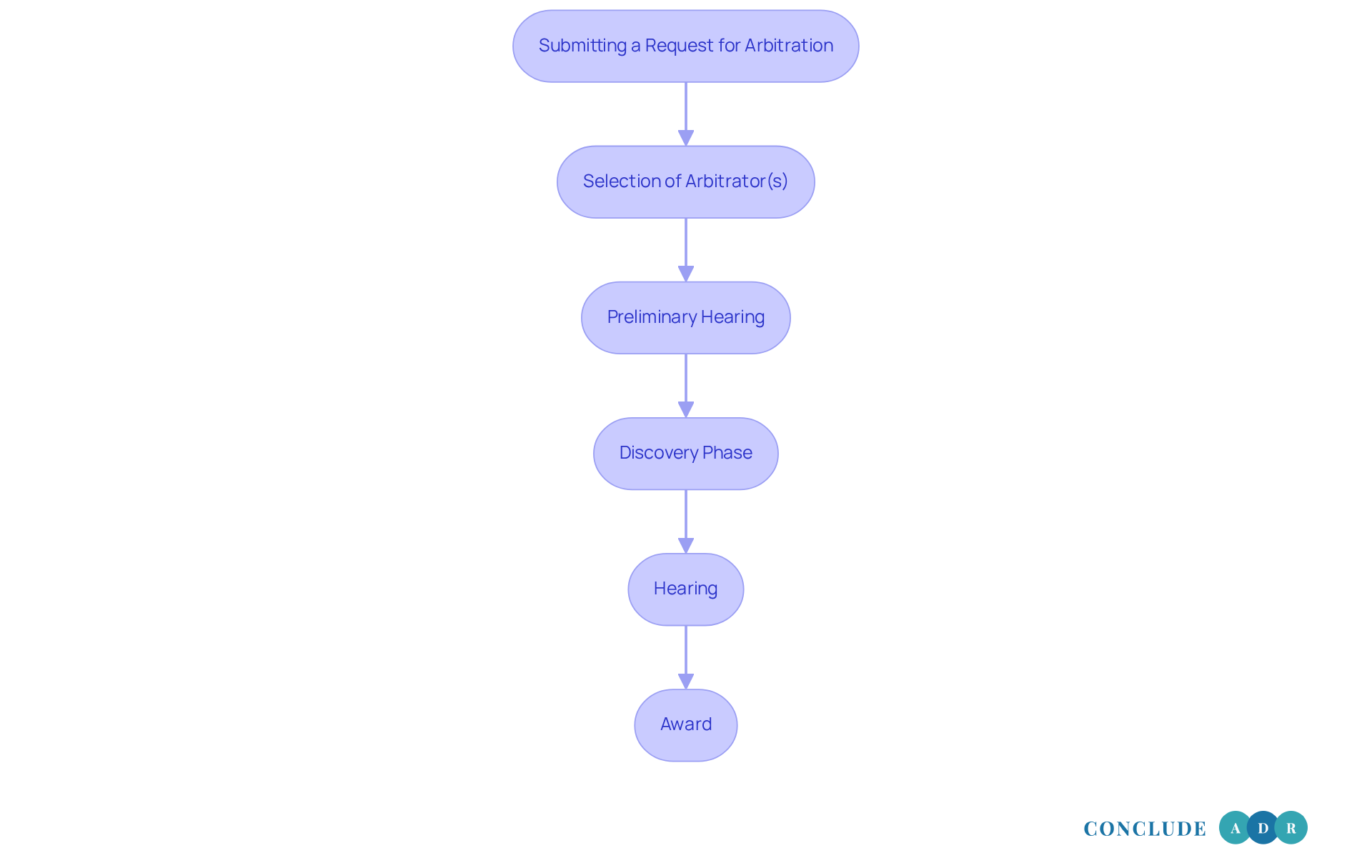
- Submitting a Request for Arbitration: The initiating entity presents a request to the appointed dispute resolution organization, detailing the nature of the conflict.
- Selection of Arbitrator(s): Both sides collaboratively choose an arbitrator or panel, often from a list provided by the dispute resolution organization.
- Preliminary Hearing: A preliminary hearing may be convened to establish the rules and timeline for the dispute resolution proceedings.
- Discovery Phase: Limited exploration allows both sides to collect evidence and prepare their respective cases.
- Hearing: During the arbitration hearing, both parties present their evidence and arguments. Unlike conventional legal proceedings, the rules of evidence may be more adaptable.
- Award: Following deliberation, the arbitrator issues a decision, known as an award, which is generally binding and enforceable in court.
Understanding the within dispute resolution clauses is vital for anyone entering into contracts. These clauses, such as the mandatory arbitration clause, dictate how potential conflicts will be resolved, providing a sense of security. Recent modifications in dispute resolution rules, like the introduction of virtual hearings as the default format, enhance accessibility and efficiency, making it easier for everyone involved.
Consider this: in 2025, 31% of customer claimant cases led to awards for the customers. This statistic highlights the effectiveness of mediation in settling disputes. We encourage you to explore these options, as they can lead to a more harmonious resolution. Remember, you are not alone in this process; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Compare Recovery Outcomes: Arbitration vs. Court
When considering recovery outcomes between arbitration and court litigation, it's important to recognize several key differences that may impact your decision.
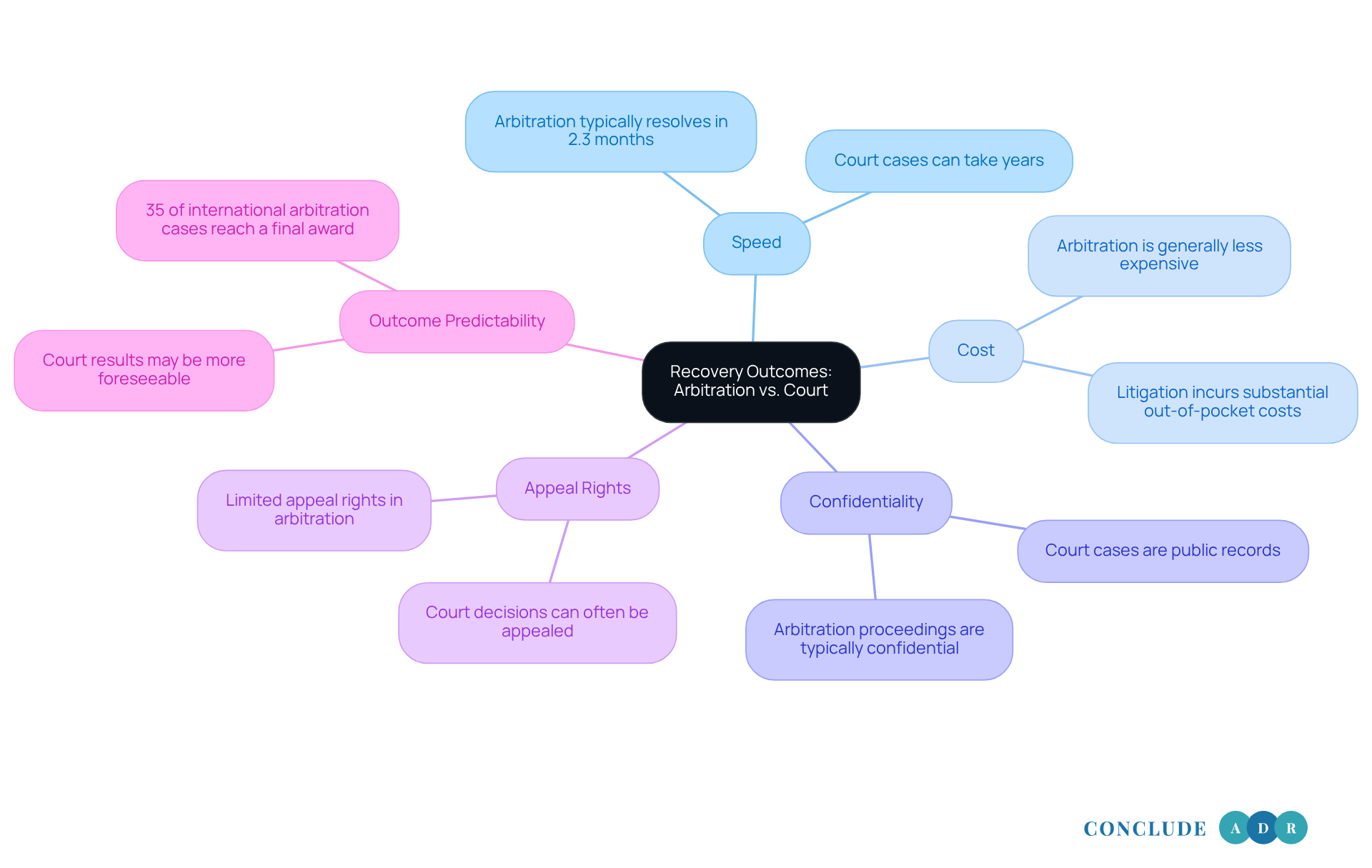
- Speed: Have you ever felt overwhelmed by the lengthy nature of legal proceedings? Arbitration typically offers a quicker resolution than traditional court cases. While court disputes can drag on for years due to crowded dockets, alternative dispute resolution often wraps up within just a few months. In fact, large B2B claims can be awarded in as little as 2.3 months, providing a more timely path to resolution.
- Cost: It's natural to worry about expenses when pursuing a dispute resolution. While can often be less expensive than litigation, it's essential to be aware of potential costs related to arbitrator fees and administrative expenses. Litigation can lead to substantial out-of-pocket costs, including attorney fees and discovery expenses, often leaving successful individuals with minimal net recoveries after expenses. Overall, arbitration tends to be more cost-effective than prolonged legal disputes.
- Confidentiality: Are you concerned about keeping your disputes private? Arbitration proceedings are typically confidential, which can be a significant advantage for parties wishing to keep their matters out of the public eye. In contrast, court cases are generally public records, which can inadvertently damage reputations and benefit competitors.
- Appeal Rights: Understanding your rights in dispute resolution is crucial. In arbitration, the right to appeal is very limited. Choosing alternative dispute resolution often means relinquishing the right to appeal, which can be a significant consideration for those involved in disputes. Once an arbitrator makes a decision, it is usually final and binding. On the other hand, court decisions can often be appealed to higher courts, which may prolong the resolution process.
- Outcome Predictability: Have you thought about how predictable the outcomes are? Court results may be more foreseeable due to established legal precedents, while outcomes from alternative dispute resolution can vary significantly based on the arbitrator's discretion. A study found that only 35% of international commercial dispute resolution cases reach a final award, indicating that many disagreements settle before completion. Additionally, approximately 80-90% of commercial disputes resolve through negotiation or mediation before formal proceedings commence, emphasizing the process's role as a negotiation catalyst.
Grasping these distinctions is essential for anyone contemplating whether to consent to a mandatory arbitration clause in their agreements. By understanding these key differences, you can make more informed decisions that align with your needs and values.
Assess Impact on Employee Accountability
Mandatory arbitration clauses can significantly impact employee accountability in several ways:
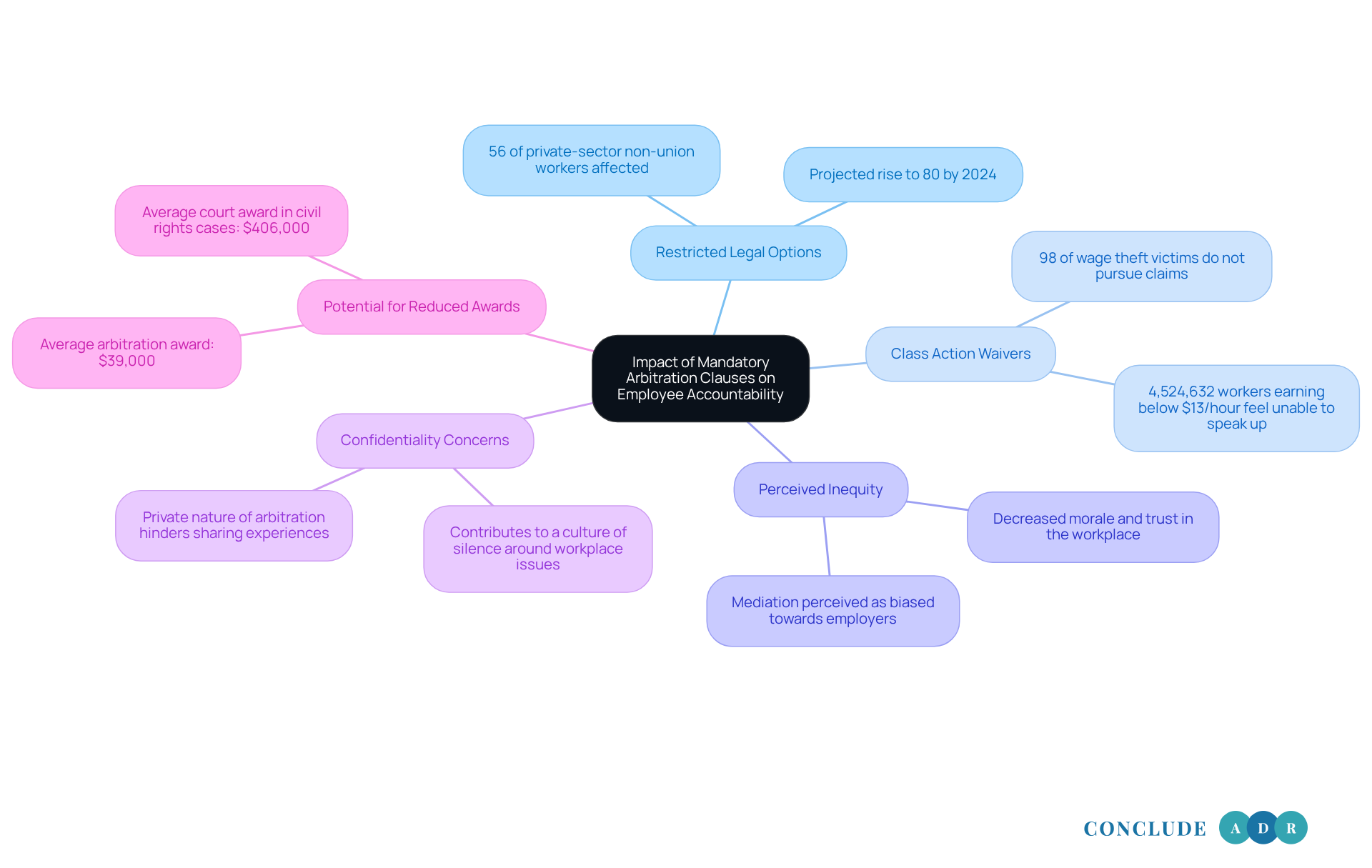
- Restricted Legal Options: If you find yourself bound by a mandatory settlement agreement, you may feel like you’ve given up your right to seek justice in court. This can be especially concerning in cases of discrimination or wrongful termination. Currently, 56% of private-sector non-union workers are affected by a mandatory arbitration clause for dispute resolution, and this number is projected to rise to 80% by 2024. The thought of losing legal options can be daunting for many.
- Class Action Waivers: Many dispute resolution agreements include clauses that prevent employees from joining together in class action lawsuits. This can weaken your collective bargaining power and make it more challenging to tackle systemic issues within your workplace. It's alarming to note that 98% of employees who experience wage theft choose not to pursue their claims. Imagine the estimated 4,524,632 private-sector non-union workers earning below $13 per hour who feel they cannot speak up.
- Perceived Inequity: You might feel that mediation is tilted in favor of employers, especially if the process seems biased or lacks transparency. Such feelings can lead to decreased morale and trust within the workplace, leaving you feeling vulnerable when seeking redress.
- Confidentiality Concerns: The private nature of the dispute resolution process can create barriers. You may feel unable to share your experiences, which can contribute to a culture of silence around workplace issues. This lack of openness can hinder the identification and resolution of systemic problems, allowing harmful practices to persist unchallenged.
- Potential for Reduced Awards: Research indicates that employees often receive lower financial awards in mediation compared to court outcomes. For instance, the average compensation in dispute resolution is about $39,000, significantly less than the average court award of $406,000 in civil rights cases. As Theodore J. St. Antoine points out, while alternative dispute resolution might seem more affordable, the disparity in awards can discourage you from pursuing legitimate claims.
Understanding these impacts is essential for grasping the broader implications of the mandatory arbitration clause in employment contexts, especially concerning your rights and accountability. While these challenges are significant, it’s important to recognize the potential for to empower workers and foster collective action. This aspect of our current environment should not be overlooked, as it holds the promise of a more equitable future for all employees.
Trace the History of Mandatory Arbitration Use
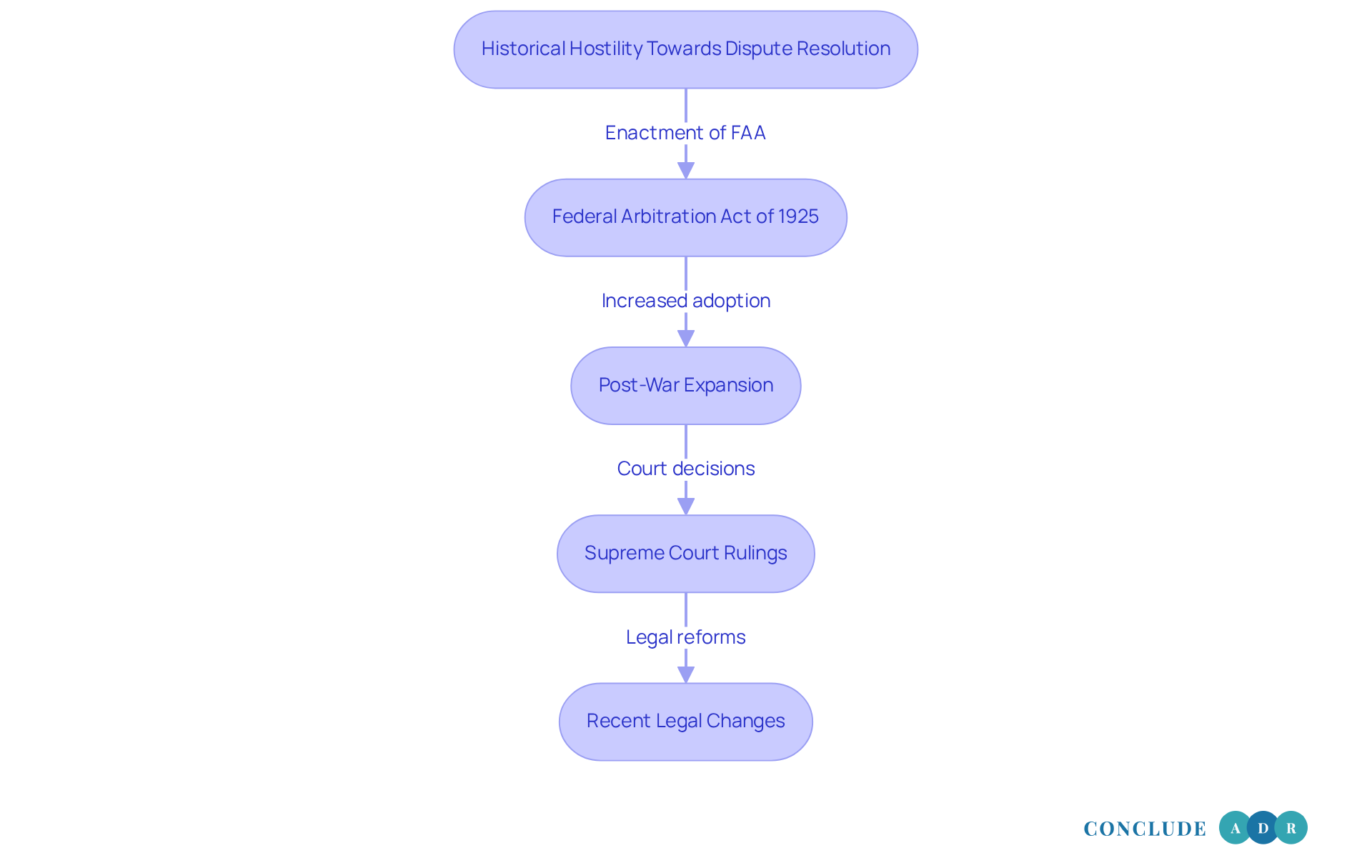
The history of the mandatory arbitration clause is marked by significant milestones that have shaped its current use. Understanding this context is essential, as it highlights the emotional and practical implications for those affected.
- Historical Hostility Towards Dispute Resolution: Before the enactment of the Federal Arbitration Act (FAA) in 1925, American courts were generally hostile towards this method. Many viewed it as a way for parties to evade judicial scrutiny, creating a challenging landscape for those seeking resolution.
- Federal Arbitration Act of 1925: This pivotal legislation laid the groundwork for enforcing dispute resolution agreements. It led to a substantial increase in this method's role in commercial conflicts, reflecting a national policy that supports such mechanisms. The FAA sought to guarantee that these agreements were regarded as legitimate and enforceable, fostering a sense of trust in the process.
- Post-War Expansion: After World War II, businesses began to seek efficient alternatives to court litigation. This shift resulted in the widespread adoption of dispute resolution in various contracts, including employment agreements. It marked a significant change in how disputes were resolved in the business sector, offering a more accessible avenue for resolution.
- Supreme Court Rulings: Throughout the late 20th century, a series of Supreme Court decisions strengthened the enforceability of dispute resolution provisions. Notable cases, such as Citizens Bank v. Alafabco and Green Tree Financial Corp. v. Randolph, illustrated how the Court's interpretations expanded the scope of the FAA. However, this often came at the expense of consumer and employee rights, raising important questions about fairness.
By the 1990s, the rise of employment dispute resolution was characterized by the standard use of a mandatory arbitration clause in employment contracts. Often imposed as a condition of employment, these clauses restricted employees' access to judicial recourse. It's disheartening to note that statistics show employees generally succeed only around 21.4% of the time in compulsory dispute resolution, compared to greater win rates in federal and state courts.
- Recent Legal Changes: Recently, the prevalence of compulsory dispute resolution has ignited discussions about its fairness and implications for workers' rights. This has prompted calls for reform and increased transparency in these practices. Significantly, as of March 3, 2022, mandatory dispute resolution clauses for sexual harassment claims are prohibited, marking a major legal shift that many see as a step toward greater justice.
Understanding this historical context is crucial for grasping the current dynamics of the mandatory arbitration clause and its effects on dispute resolution. We must continue to in these practices, ensuring that everyone's rights are respected.
Conclusion
Mandatory arbitration clauses significantly influence how disputes are resolved, often pushing individuals toward private arbitration instead of traditional court litigation. This shift can deeply limit your legal options, impacting your ability to seek justice and fair compensation. As more employers adopt these clauses, it becomes increasingly vital for you to understand their implications.
In exploring the mechanics of mandatory arbitration, we compare recovery outcomes between arbitration and court processes, shedding light on the historical context that has shaped our current landscape. Key insights reveal how these clauses restrict legal recourse, affect employee accountability, and often lead to lower financial awards for those seeking resolution. It's essential to be informed about these agreements to navigate their complexities effectively.
Looking at the broader implications, we must recognize the potential for collective action and advocacy for fairer dispute resolution practices. As the prevalence of mandatory arbitration continues to rise, empowering you with knowledge and encouraging transparency can help ensure that your rights are upheld. Engaging in dialogue about these issues can foster a more equitable future, where everyone has access to just and effective means of resolving conflicts.
Together, let’s advocate for a system that respects your rights and seeks equitable solutions for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a mandatory arbitration clause?
A mandatory arbitration clause is a contractual term that requires parties to resolve conflicts through alternative dispute resolution, such as arbitration, instead of litigation in court.
Where are mandatory arbitration clauses commonly found?
These clauses are often included in employment contracts, consumer agreements, and various business agreements.
What is the estimated prevalence of mandatory arbitration clauses by 2025?
It is estimated that by 2025, around 25% of all workers in nonunion settings will be subject to compulsory dispute resolution, with over half of nonunion private-sector employers requiring such arrangements.
How do mandatory arbitration clauses affect individuals' legal options?
Mandatory arbitration clauses significantly limit the legal options available to individuals, as they cannot take their claims to court and must engage in a private resolution process instead.
Can you provide an example of the impact of mandatory arbitration clauses?
In the case of Stephanie Sutherland, she was unable to pursue her overtime pay claims in court due to a binding arbitration agreement. In 2022, only 80 employees received monetary awards through compulsory mediation, highlighting the limited access to justice.
What are class-action waivers in relation to arbitration clauses?
Class-action waivers, often included in mandatory arbitration clauses, prevent collective legal action against corporations, further limiting employees' rights and options for recourse.
How does the arbitration process work?
The arbitration process typically involves several steps: submitting a request for arbitration, selecting arbitrator(s), holding a preliminary hearing, conducting a discovery phase, presenting evidence during a hearing, and finally receiving a binding decision known as an award.
What changes have been made to the arbitration process recently?
Recent modifications include the introduction of virtual hearings as the default format, which enhances accessibility and efficiency for all parties involved.
What is the success rate of mediation in resolving disputes?
In 2025, it is projected that 31% of customer claimant cases will lead to awards for the customers, indicating the effectiveness of mediation in settling disputes.




