Overview
Mutual arbitration agreements in employment are contracts that require both employers and employees to resolve disputes through arbitration instead of litigation. This means that both parties are waiving their rights to pursue court action.
Have you ever felt overwhelmed by the thought of navigating a legal dispute? It's understandable. These agreements can offer some advantages, such as being cost-effective and quicker than traditional court processes. However, it’s crucial to consider the significant concerns that come with them.
For instance, workers may face limited options for appeal and potential bias in the arbitration process. This raises important questions about fairness and transparency. We must carefully weigh these factors before entering into such agreements.
Ultimately, it’s about ensuring that your rights are protected while finding a resolution that works for everyone involved. Let’s approach this topic with care and consideration, keeping in mind the best interests of all parties.
Introduction
In today’s evolving workplace, the increasing use of mutual arbitration agreements is a notable shift in how we handle disputes. These agreements, which ask both employers and employees to set aside litigation for arbitration, promise a more efficient and confidential process. Yet, we must pause and reflect on what this trend means for workers' rights and their access to justice.
As more organizations embrace these agreements, it becomes essential for both employees and employers to understand their implications in this complex landscape.
How might this affect you or your colleagues? Let’s explore these important questions together.
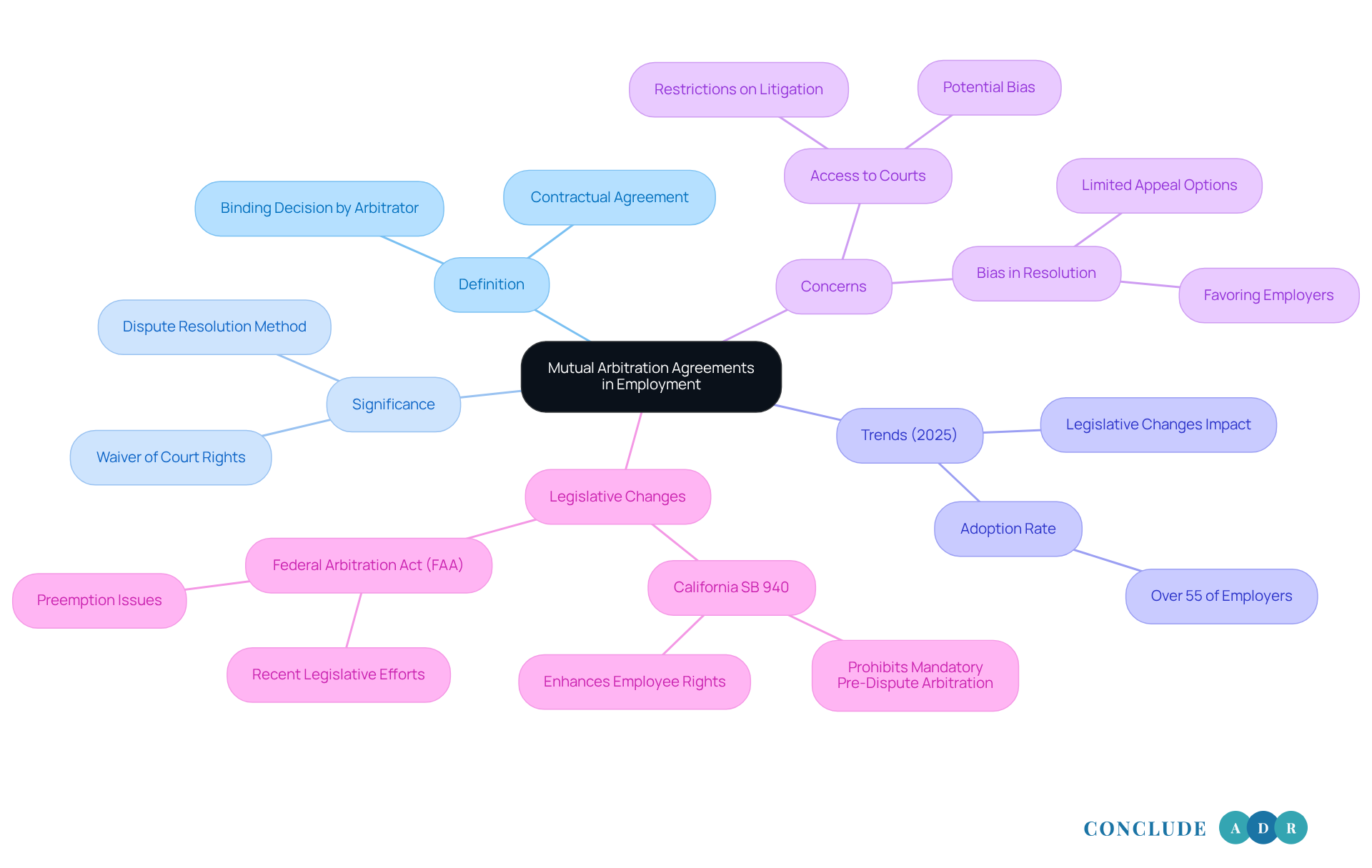
Define Mutual Arbitration Agreements in Employment
A mutual arbitration agreement employment is a contract between an employer and an employee in which both parties agree to resolve disputes through arbitration rather than through litigation. This arrangement means that if conflicts arise—such as employment discrimination, wage disputes, or wrongful termination—both parties waive their rights to pursue the matter in court. Instead, they agree to submit their case to a neutral third party, known as an arbitrator, who will render a binding decision.
Typically included in employment contracts, these documents are often prerequisites for employment in many organizations. The mutual arbitration agreement employment ensures that both the employer and worker are equally bound by the terms, thus preventing either party from unilaterally opting for court litigation. Have you ever felt uncertain about your rights in the workplace? As of 2025, over 55% of employers are employing mutual arbitration agreement employment, reflecting a significant trend towards their adoption in the workplace.
However, this trend raises important concerns about restricting access to courts for workers and the potential for bias in dispute resolution processes. Recent legislative changes in California, such as SB 940, are reshaping the landscape by prohibiting mandatory pre-dispute conflict resolution for wage-related disputes. This change is a step towards enhancing employee rights and access to the courts.
This law aims to provide workers with greater protections and the ability to seek redress through traditional litigation when facing wage-related issues. It’s essential to understand your rights and feel empowered to take action when necessary. Together, we can navigate these complexities and ensure that your voice is heard.
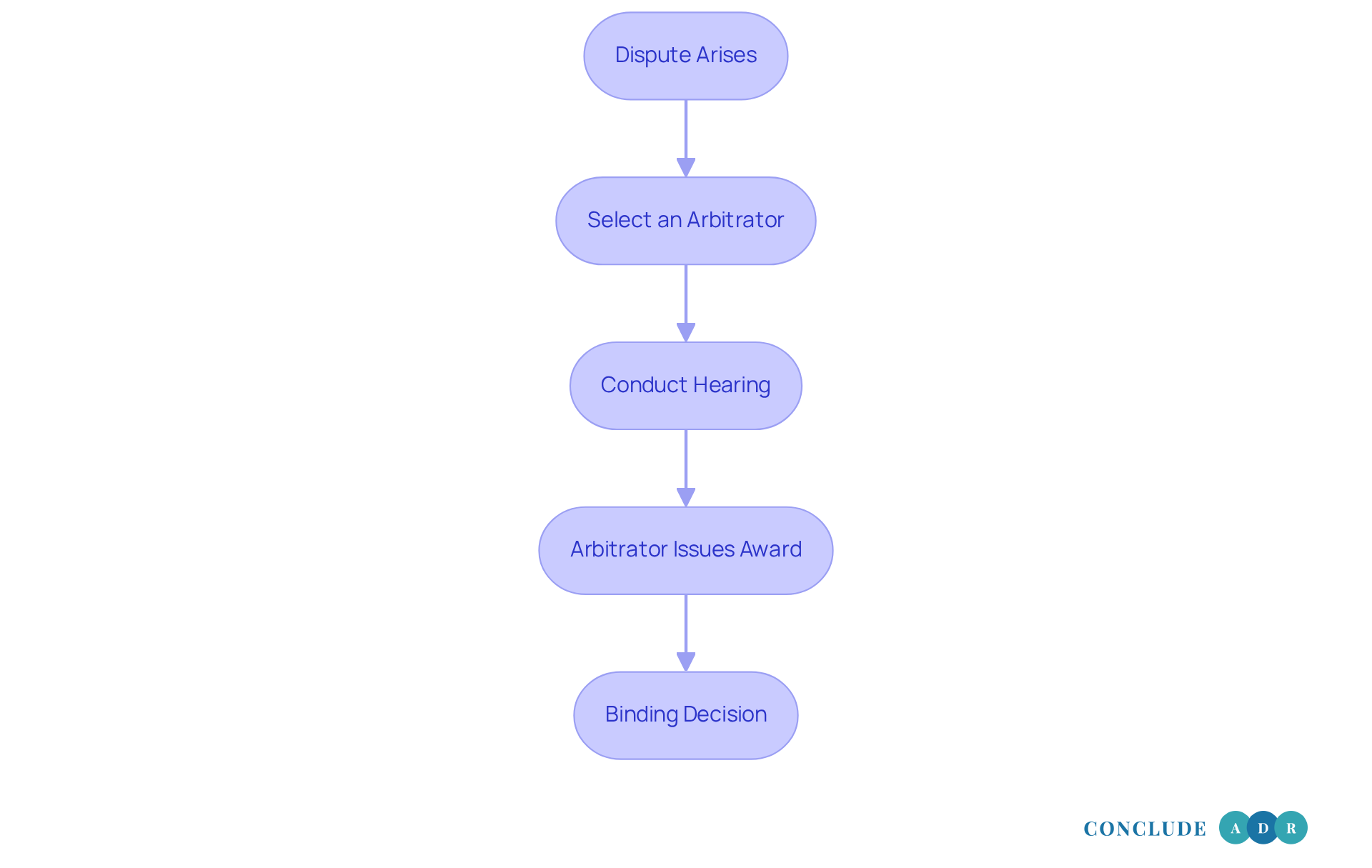
Explain How Mutual Arbitration Agreements Work
When disputes arise, it’s natural to feel overwhelmed. The structured process typically followed by mutual arbitration agreement employment can help ease those feelings. First, the parties involved select an arbitrator—often a professional with expertise in the relevant field. This selection can be a collaborative effort, allowing both sides to agree on a neutral arbitrator who understands their needs.
Once selected, the arbitrator conducts a hearing where both parties can present their evidence and arguments. Unlike traditional court proceedings, this alternative dispute resolution method is generally less formal and offers more flexibility in scheduling and procedures. This means you can focus on what matters most, without the stress of a rigid courtroom setting.
After carefully reviewing the case, the arbitrator issues a decision, known as an 'award.' This award is binding and enforceable in court, which means that all parties must adhere to the ruling. It’s important to note that there are limited grounds for appeal, ensuring that the process remains straightforward.
The entire procedure is designed to be quicker and less costly than traditional litigation. This makes the mutual arbitration agreement employment an appealing choice for many employers and employees alike. If you’re facing a dispute, consider this compassionate approach to resolution. It could be the key to finding peace and moving forward.
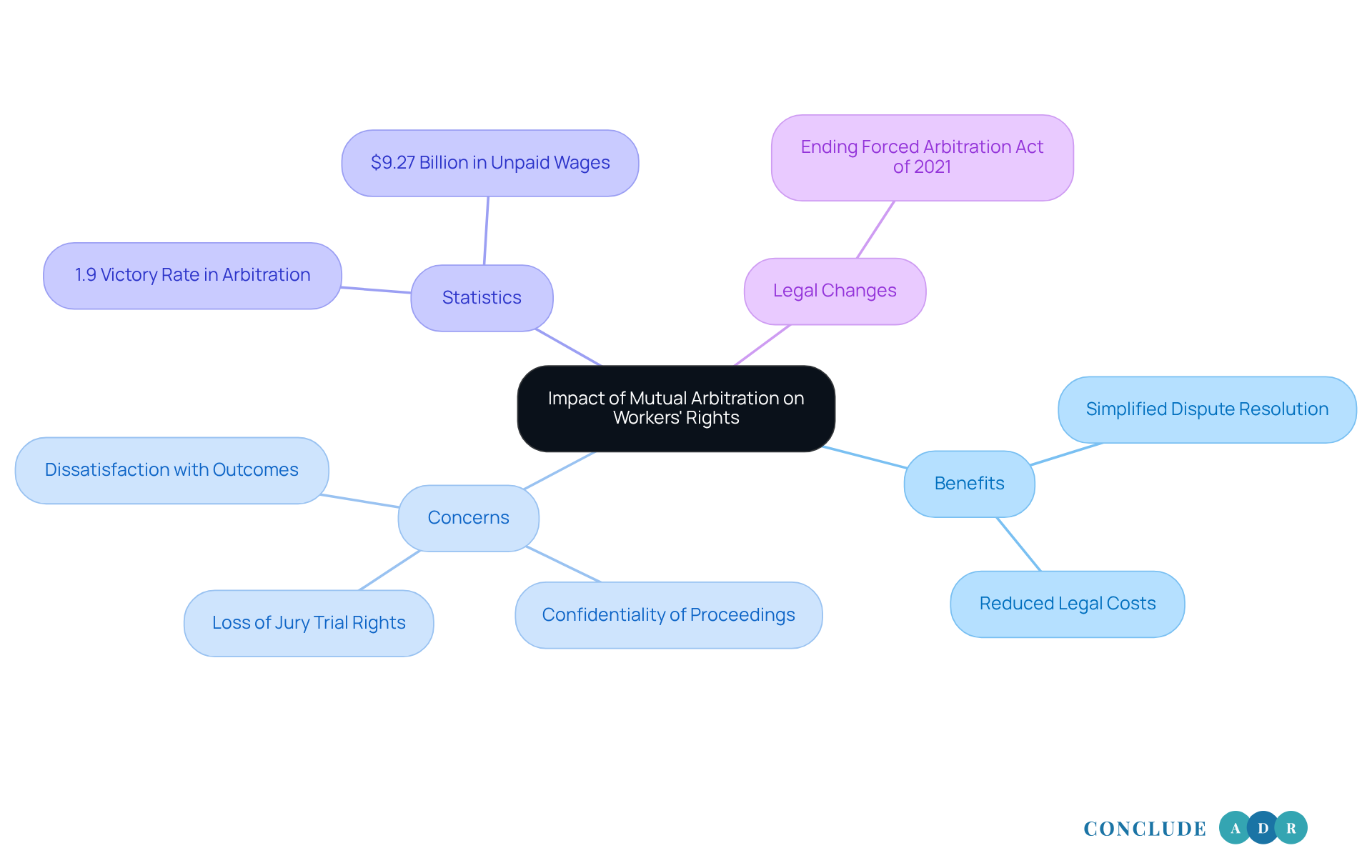
Assess the Impact of Mutual Arbitration on Workers' Rights
The effect of mutual arbitration agreement employment contracts on employees' entitlements is a complex and often troubling subject that many of us may feel deeply about. These agreements can simplify dispute resolution, potentially leading to quicker outcomes and reduced legal costs. However, it's essential to recognize the significant concerns they raise regarding the protection of workers' interests.
When employees engage in mediation, they often give up their right to a jury trial. This can limit their options in cases of discrimination or wrongful termination, leaving them feeling vulnerable. Moreover, the confidentiality of dispute resolution proceedings means that outcomes are rarely made public. This lack of transparency can hinder accountability, raising valid concerns about biased decisions that may favor employers, particularly when arbitrators rely on repeat business from these companies.
Recent research highlights that many workers are dissatisfied with dispute resolution outcomes. In 2022, only 80 individuals received monetary awards through compulsory mediation, resulting in a victory rate of just 1.9%. Additionally, around 4.5 million low-income employees are subject to mandatory dispute resolution, unable to reclaim over $9.27 billion in unpaid wages. While mutual arbitration agreement employment might offer efficiency, labor rights advocates stress that it can also erode essential protections and rights for workers.
It's crucial for both employees and employers to carefully evaluate the mutual arbitration agreement employment. Significantly, the Ending Forced Arbitration of Sexual Assault and Sexual Harassment Act of 2021 marks an important shift in the legal landscape, allowing employees to pursue claims in court. This change represents a step forward in ensuring that workers' voices are heard and their rights are protected.
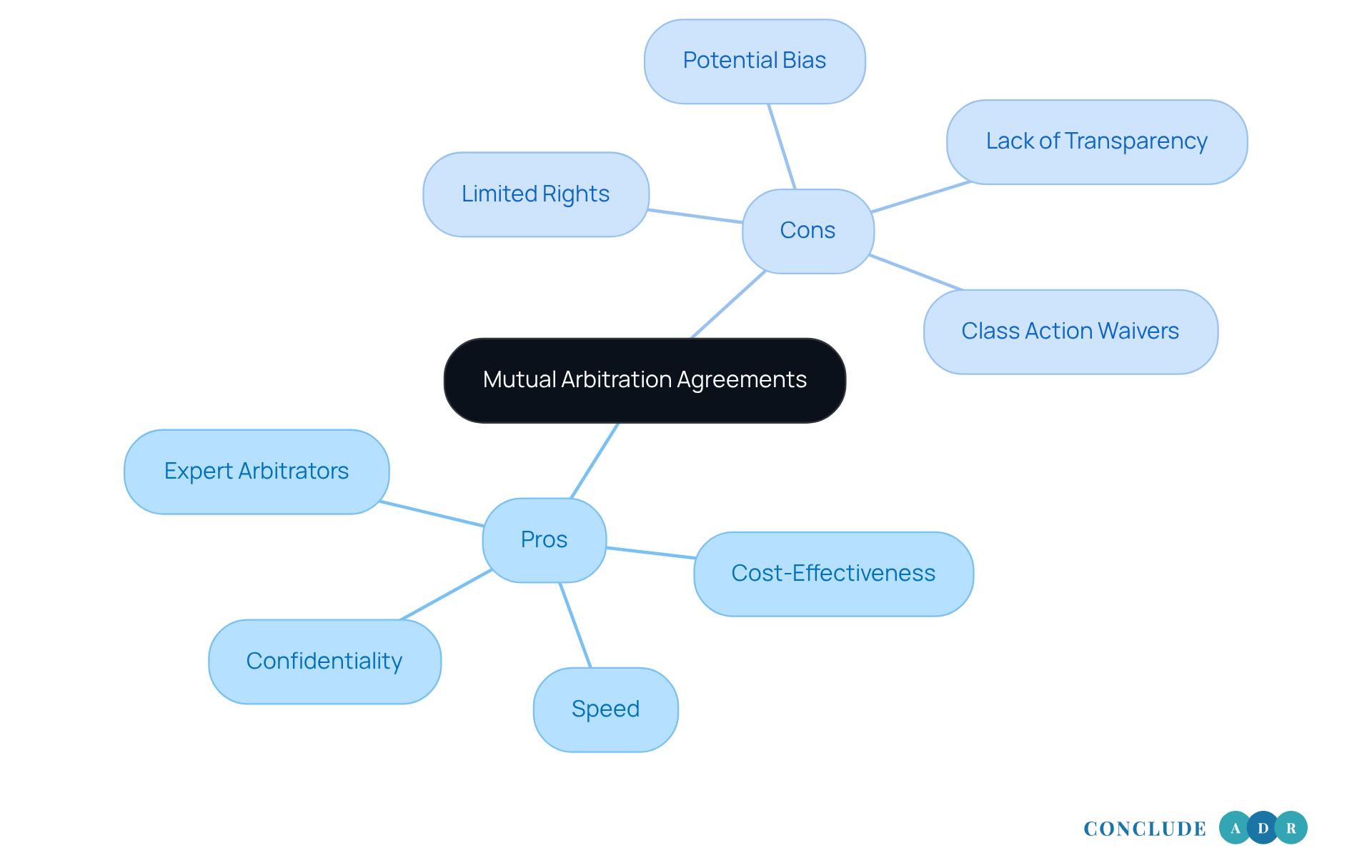
Evaluate the Pros and Cons of Mutual Arbitration Agreements
Mutual dispute resolution agreements can evoke mixed feelings, and it's important to consider both their advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Arbitration often proves to be less expensive than litigation, as it sidesteps many costs tied to court proceedings, like extensive discovery and lengthy trials.
- Speed: The mediation process typically unfolds more quickly than court litigation, allowing disputes to be resolved in a timely manner.
- Confidentiality: With arbitration, proceedings remain private, which can safeguard sensitive information and uphold the parties' reputations.
- Expert Arbitrators: You have the opportunity to select arbitrators with specific expertise related to your dispute, potentially leading to more informed decisions.
Cons:
- Limited Rights: It's crucial to recognize that employees may waive essential rights, including the right to a jury trial and the ability to appeal decisions.
- Potential Bias: Concerns about arbitrator bias can arise, especially if they frequently collaborate with the same employers.
- Lack of Transparency: The confidential nature of dispute resolution may lead to a lack of accountability and public scrutiny, which can disadvantage workers.
- Class Action Waivers: Many dispute resolution contracts include clauses that prevent employees from joining forces in class actions, limiting their ability to address systemic issues.
In conclusion, while mutual arbitration agreement employment can provide a more efficient and cost-effective way to resolve disputes, they also carry significant risks to workers' rights and protections. It's essential to weigh these factors carefully as you consider your options. Remember, you are not alone in navigating these challenges—support is available to help you make informed decisions.
Conclusion
Mutual arbitration agreements in employment signify a profound transformation in how disputes between employers and employees are managed. By choosing arbitration over litigation, both parties can embrace a structured process that often leads to quicker and potentially less costly resolutions. Yet, this arrangement raises important questions about workers' rights and the implications of giving up access to traditional court systems.
This article explores the mechanics of mutual arbitration agreements, shedding light on their increasing prevalence and the effects of recent legislative changes designed to safeguard workers. Consider the efficiency and confidentiality of arbitration, but also reflect on the risks associated with limited rights and possible bias in decision-making. It's essential for both employees and employers to weigh the benefits of a streamlined process against concerns over transparency and fairness.
Ultimately, understanding mutual arbitration agreements is crucial for navigating the complexities of employment law. As workers strive to protect their rights, being aware of these agreements and the ongoing legal developments can empower them to make informed choices. Engaging in open discussions about the implications of arbitration can nurture a more equitable workplace, ensuring that every voice is heard and respected. How can we foster such conversations? Together, we can create a supportive environment that values all perspectives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a mutual arbitration agreement in employment?
A mutual arbitration agreement in employment is a contract between an employer and an employee where both parties agree to resolve disputes through arbitration instead of litigation. This means that if conflicts arise, such as employment discrimination or wrongful termination, both parties waive their rights to go to court and submit their case to a neutral arbitrator for a binding decision.
Why are mutual arbitration agreements included in employment contracts?
Mutual arbitration agreements are typically included in employment contracts to ensure that both the employer and employee are equally bound by the terms, preventing either party from unilaterally opting for court litigation. They are often prerequisites for employment in many organizations.
What percentage of employers were using mutual arbitration agreements as of 2025?
As of 2025, over 55% of employers are employing mutual arbitration agreements, indicating a significant trend towards their adoption in the workplace.
What concerns are raised about mutual arbitration agreements?
Concerns about mutual arbitration agreements include the restriction of access to courts for workers and the potential for bias in the dispute resolution process.
What recent legislative changes in California affect mutual arbitration agreements?
Recent legislative changes in California, specifically SB 940, prohibit mandatory pre-dispute conflict resolution for wage-related disputes. This law aims to enhance employee rights and provide greater access to traditional litigation for wage-related issues.
How do these legislative changes impact employee rights?
These legislative changes provide workers with greater protections and the ability to seek redress through traditional litigation when facing wage-related issues, thereby enhancing their rights in the workplace.




