Overview
In exploring arbitration law, we recognize its importance in providing a compassionate approach to resolving disputes. At its core, arbitration emphasizes principles such as party autonomy, confidentiality, and enforceability. These principles are not just legal concepts; they are vital tools that help individuals and organizations navigate conflicts outside traditional court systems.
Imagine a scenario where you can resolve your disputes in a more private and efficient manner. This is where arbitration shines. By understanding the structured processes of both binding and non-binding arbitration, you can see how they enhance efficiency and adaptability. This flexibility makes arbitration a preferred alternative to litigation, especially in commercial and international contexts.
Consider how these benefits can alleviate the stress of conflict resolution. With arbitration, you can find a path that respects your needs and concerns, fostering a more harmonious outcome. As you reflect on this, think about how arbitration could serve you or your organization in the future.
Ultimately, we invite you to explore the possibilities that arbitration offers. By choosing this route, you can embrace a more supportive and understanding way to resolve disputes, ensuring that your voice is heard and valued.
Introduction
Arbitration law plays a vital role in helping us resolve disputes outside the traditional courtroom. It offers a structured and efficient alternative that many people find appealing. By understanding the core principles of this legal framework—such as party autonomy, confidentiality, and enforceability—you can navigate conflicts with greater ease and confidence.
As the landscape of conflict resolution evolves, it's important to reflect on how the various types of arbitration processes impact the effectiveness of dispute resolution. Which approach is best suited for your specific situation? We invite you to consider these questions as you explore your options, knowing that the right choice can lead to a more harmonious resolution.
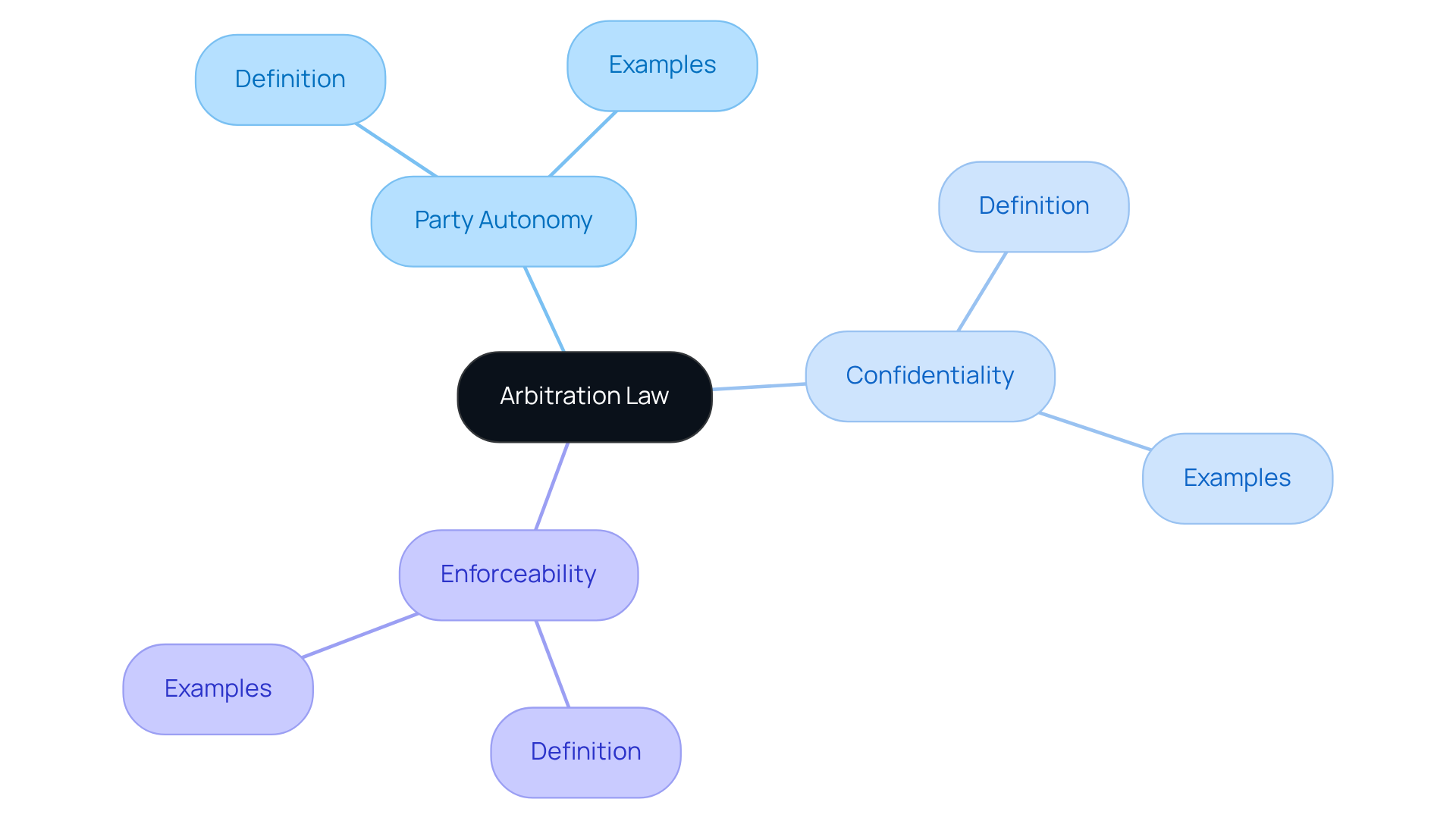
Define Arbitration Law: Core Principles and Significance
This legislation addresses a vital aspect of arbitration law meaning in resolving disputes outside of traditional court systems. Have you ever felt overwhelmed by the thought of litigation? This process allows individuals to agree to present their disputes to one or more impartial arbitrators, which is in line with arbitration law meaning, and who will provide binding decisions.
At the heart of arbitration law meaning are some fundamental principles that empower you. First, there's party autonomy, which means you have the freedom to choose your adjudicators and set the guidelines for your process. Then, we have confidentiality, ensuring that everything discussed remains private. Finally, enforceability allows the decisions made to be recognized and upheld by courts.
Understanding the arbitration law meaning is crucial. They highlight the importance of mediation as a practical alternative to litigation, offering a more efficient and less confrontational way to settle conflicts. Imagine a scenario where both parties feel heard and respected, leading to a resolution that works for everyone involved.
This approach not only alleviates stress but also fosters a collaborative environment. If you're seeking a more harmonious resolution to your disputes, consider exploring mediation and arbitration. Together, we can find a path that prioritizes understanding and cooperation.
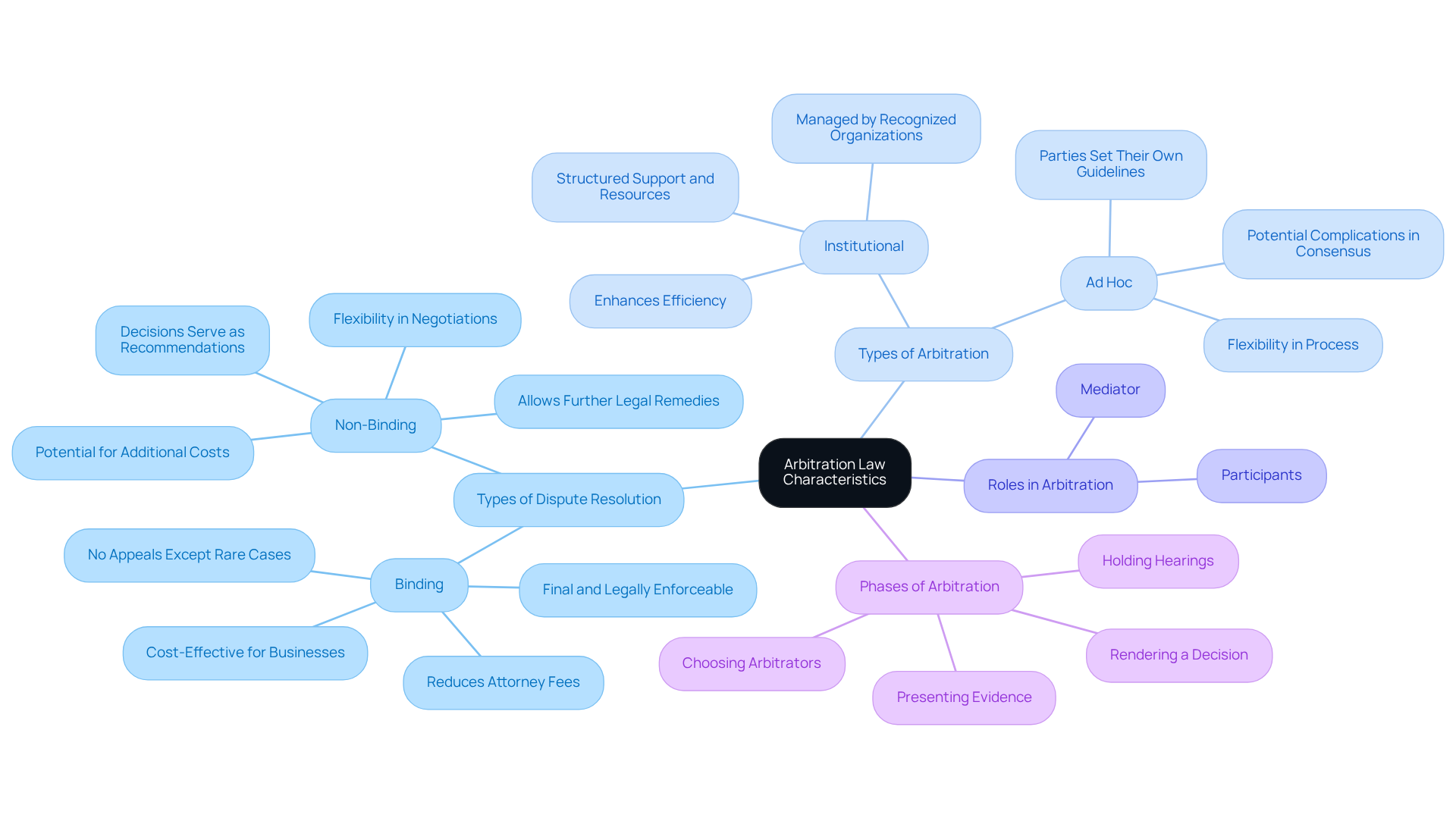
Contextualize Arbitration Law: Evolution and Relevance in Dispute Resolution
Arbitration has a rich and meaningful history, stretching back thousands of years, with roots in diverse cultures and legal systems. Initially, it served as an informal way for merchants and traders to resolve their conflicts. Can you imagine the relief they must have felt? In the 20th century, particularly with the introduction of the Federal Arbitration Act (FAA) in the United States in 1925, a more structured approach to conflict resolution began to take shape. This act provided legal recognition to conflict resolution agreements, paving the way for a more formalized process.
Over the years, alternative conflict resolution has become a favored method for addressing issues, especially in business settings. Why is that? Its efficiency and adaptability make it a practical choice for many. Today, alternative conflict resolution is recognized globally, supported by numerous international agreements and conventions. This growing acknowledgment highlights the arbitration law meaning as a fundamental aspect of the legal framework in both national and international matters.
As we navigate through conflicts in our lives, it's comforting to know that there are effective and compassionate ways to resolve them. Together, we can explore these options and find the best path forward.
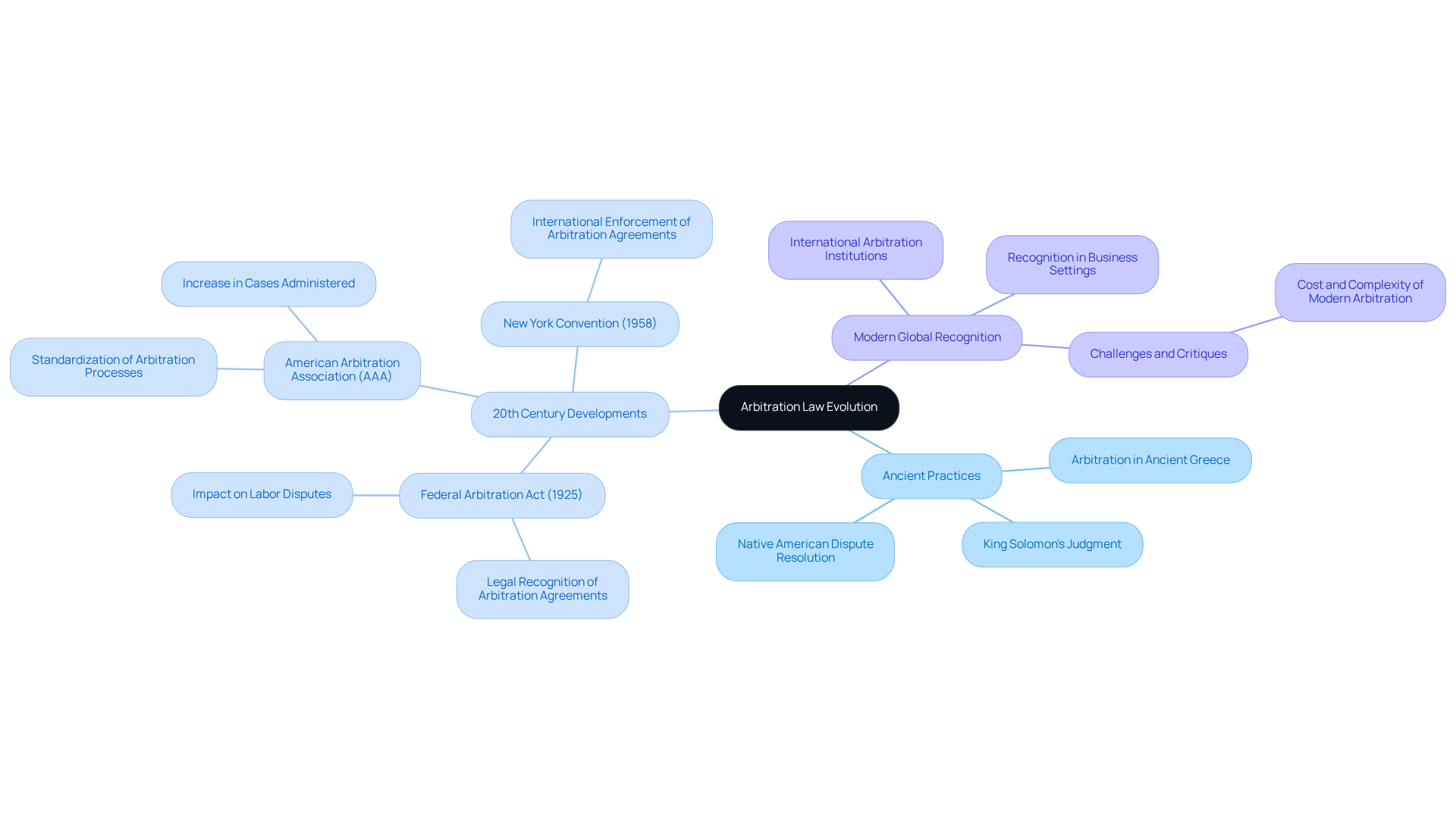
Explore Key Characteristics of Arbitration Law: Processes, Types, and Roles
The meaning of arbitration law encompasses various processes and types, each tailored to specific dispute contexts. Have you ever felt uncertain about how to resolve a conflict? Understanding the two main types of dispute resolution—binding and non-binding methods—can help you navigate these challenges.
In binding resolution, the adjudicator's determination is conclusive and legally enforceable. This offers a high level of certainty for everyone involved, which can be particularly beneficial for businesses. It reduces the unpredictability associated with court trials and minimizes attorney fees. However, it’s worth noting that binding resolution may be more costly compared to non-binding mediation.
On the other hand, non-binding dispute resolution allows parties to pursue additional legal remedies if they are dissatisfied with the outcome. This can be a flexible choice for those who wish to maintain relationships or continue discussions. Yet, this flexibility can lead to extra expenses if litigation arises, as highlighted in studies on the drawbacks of non-binding dispute resolution.
Arbitration can also be categorized into institutional or ad hoc types. Institutional dispute resolution involves a recognized organization that manages the process, providing structured support and resources. This approach can enhance efficiency and effectiveness, especially in complex disputes. In contrast, ad hoc dispute resolution allows the involved individuals to set their own guidelines and processes. While this can provide flexibility, it may also lead to complications if consensus on an arbitrator cannot be reached.
Key roles in dispute resolution include the mediator, who serves as the decision-maker, and the participants, who present their cases. The procedure typically involves several phases:
- Choosing arbitrators
- Presenting evidence
- Holding hearings
- Rendering a decision
Throughout this journey, principles of fairness and impartiality are crucial, ensuring that everyone has an equitable opportunity to present their arguments.
Recognizing the differences between binding and non-binding resolutions, as well as institutional and ad hoc processes, is vital for those navigating conflict resolution and understanding arbitration law meaning. Each type presents unique benefits and drawbacks, influencing the choice of method based on the nature of the conflict, the relationship between the parties, and the desired outcome. Courts often promote mediation to alleviate caseloads and encourage alternative conflict resolution techniques, reinforcing its position as a favored approach for settling disagreements.
As mediation specialist Daniel F. Quinn observes, this process has become a more preferred option compared to traditional litigation for resolving conflicts. If you find yourself in a dispute, consider exploring these options. Together, we can find a resolution that works for you.
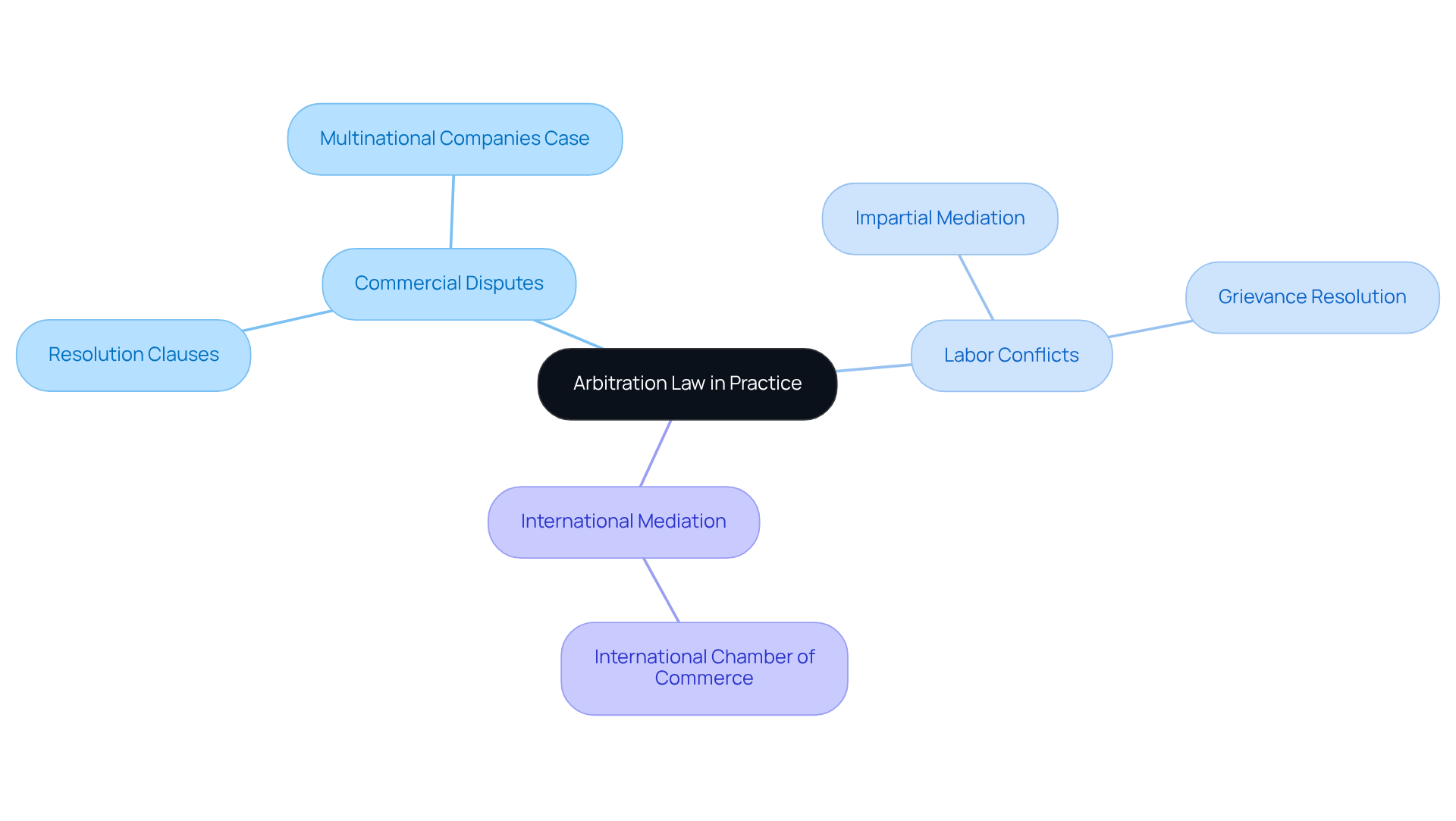
Illustrate Arbitration Law in Practice: Real-World Applications and Examples
The arbitration law meaning plays a vital role in various areas, including commercial, labor, and international conflicts. Have you ever considered how these processes can help resolve disputes effectively? In commercial mediation, for instance, companies often include resolution clauses in their contracts. This ensures that any conflicts can be settled smoothly, without the need for lengthy legal battles.
A noteworthy example is the dispute between two multinational companies over a breach of contract. Here, the mediation process facilitated a quick resolution, saving both time and legal expenses. Isn’t it comforting to know that there are efficient ways to handle such situations?
In labor conflicts, mediation serves as a valuable tool to address grievances between employers and workers. It provides an impartial platform for both sides to share their perspectives, fostering understanding and collaboration.
Furthermore, international mediation has gained significant traction, especially in resolving cross-border disputes. Institutions like the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) play a crucial role in facilitating conflict resolution for parties from different jurisdictions. This highlights just how versatile and effective arbitration law meaning can be in addressing diverse conflict scenarios.
By embracing these mediation processes, we can navigate disputes with compassion and understanding. Let's consider how we can apply these principles in our own lives to create a more harmonious environment.
Conclusion
Understanding arbitration law is vital for effectively navigating the complexities of dispute resolution. This legal framework provides a structured approach to resolving conflicts outside traditional court systems, emphasizing party autonomy, confidentiality, and enforceability. By choosing arbitration, individuals can create a more collaborative environment, alleviating the stress often tied to litigation.
The evolution of arbitration law is significant, highlighting its growing relevance in modern legal systems. Have you considered the difference between binding and non-binding resolutions? Understanding these distinctions, along with institutional versus ad hoc arbitration, can help you select the most suitable method for your specific circumstances. Each type presents unique advantages and challenges, allowing for tailored solutions. Furthermore, real-world applications in commercial, labor, and international contexts showcase the practical benefits of arbitration in achieving efficient and amicable resolutions.
Ultimately, embracing arbitration law can lead to more harmonious outcomes in both personal and professional disputes. As you explore these avenues, it’s important to recognize the value of understanding and cooperation in conflict resolution. By prioritizing these principles, we can achieve a more peaceful and effective approach to resolving disagreements, paving the way for better relationships and mutual understanding in our interactions. How might you apply these insights in your own life?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is arbitration law?
Arbitration law refers to the legislation that governs the resolution of disputes outside of traditional court systems, allowing individuals to present their disputes to impartial arbitrators who provide binding decisions.
What are the core principles of arbitration law?
The core principles of arbitration law include party autonomy (the freedom to choose adjudicators and set process guidelines), confidentiality (ensuring discussions remain private), and enforceability (recognition and upholding of decisions by courts).
Why is understanding arbitration law important?
Understanding arbitration law is crucial as it highlights mediation as an efficient and less confrontational alternative to litigation, allowing for resolutions that are mutually beneficial and respectful to all parties involved.
How does arbitration law benefit individuals in dispute resolution?
Arbitration law benefits individuals by alleviating stress associated with litigation, fostering a collaborative environment, and facilitating a more harmonious resolution to disputes.
What alternative does arbitration provide to traditional litigation?
Arbitration provides a practical alternative to traditional litigation by offering a more efficient and less confrontational way to settle conflicts, enabling both parties to feel heard and respected.




