Introduction
Restorative justice is changing how we, as communities, handle conflict. Instead of focusing solely on punishment, it encourages healing and understanding. This approach not only prioritizes the needs of victims and offenders but also highlights the vital role of community involvement in the mediation process.
But let’s be honest - becoming a restorative justice mediator isn’t without its challenges. It requires specific skills and strategies to navigate the complexities of this role. How can aspiring mediators effectively foster genuine dialogue and promote lasting resolutions?
Imagine a space where everyone feels heard and valued. That’s the essence of restorative justice. It’s about creating connections and understanding, and it starts with you. Together, we can explore how to embrace this transformative journey.
Define Restorative Justice and Its Core Principles
Restorative practices offer a caring approach that focuses on healing the harm caused by criminal behavior. Instead of just punishing the offender, these practices prioritize the needs of victims, offenders, and the community. Let’s explore the core principles of restorative justice:
-
Encounter: This principle encourages open dialogue between victims and offenders. It fosters understanding and empathy, leading to profound insights and healing for both parties. As Howard Zehr reminds us, it’s all about respecting everyone involved.
-
Repair: Here, the goal is to address and mend the harm done to victims and the community. This promotes a sense of fairness that goes beyond mere retribution. Research shows that successful reparative programs significantly enhance victim satisfaction rates. Victims often feel more acknowledged and appreciated through these processes. In fact, studies indicate that rehabilitation programs can reduce reoffending rates by 10% to 25% compared to traditional methods.
-
Transform: This principle aims to change the relationships and dynamics that led to the conflict. By promoting healing and reconciliation, restorative practices help rebuild community bonds and reduce the chances of future offenses. As Martin Luther King Jr. wisely said, "Injustice anywhere is a threat to fairness everywhere," highlighting how interconnected our community healing truly is.
These principles guide restorative justice mediators in creating a safe space for dialogue, ensuring that everyone feels acknowledged and valued. As we see these reparative approaches evolve, their impact on community healing and victim satisfaction remains crucial. Many practitioners advocate for broader implementation to enhance fairness outcomes.
Have you considered how restorative practices could benefit your community? Together, we can foster a more compassionate and understanding environment.

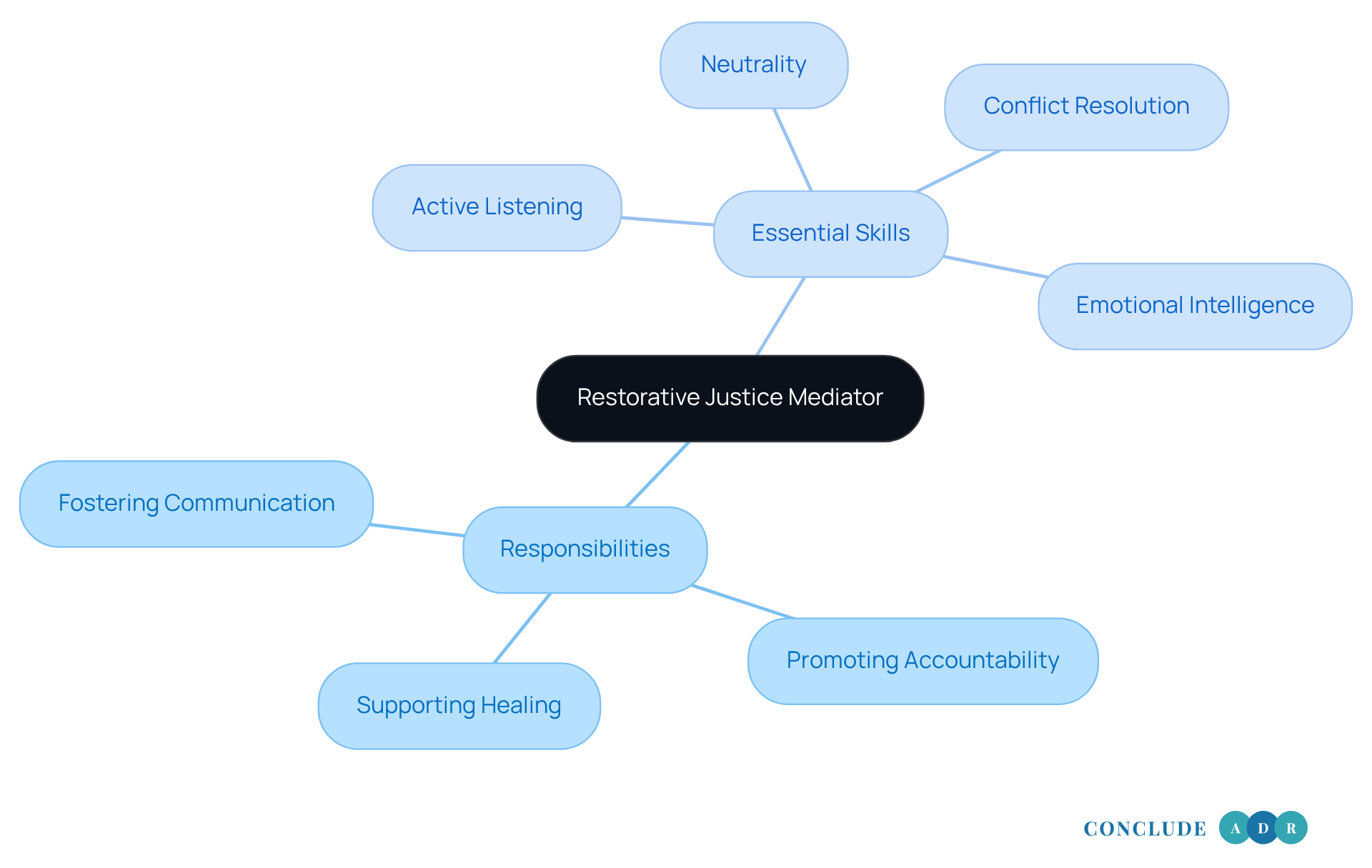
Outline the Responsibilities and Skills of a Restorative Justice Mediator
A restorative justice mediator plays a vital role in fostering positive communication between opposing parties. They create a safe environment where everyone feels secure to share their experiences and emotions openly. By facilitating dialogue, they ensure that every voice is acknowledged and respected, nurturing an inclusive atmosphere.
These restorative justice mediators also promote accountability by helping offenders recognize their actions and understand the impact on victims and the wider community. They support healing by assisting victims in articulating their feelings and needs, working collaboratively towards resolutions that truly address those needs.
Essential skills for effective restorative justice mediation include:
- Active Listening: This means listening attentively and empathetically to all parties involved.
- Neutrality: Upholding an impartial stance builds trust among participants, ensuring fairness throughout the process.
- Conflict Resolution: Navigating and de-escalating tensions during discussions promotes constructive dialogue.
- Emotional Intelligence: Understanding and managing one’s own emotions, as well as those of others, is crucial for facilitating healing and resolution.
Current trends in reparative practices emphasize the importance of skills utilized by a restorative justice mediator. Mediators, particularly restorative justice mediators, are increasingly required to adapt to various situations, including online environments. Did you know that studies show reparative measures can decrease reoffending rates by 10% to 25% compared to traditional approaches? This emphasizes its effectiveness. Moreover, 81.8% of professionals in Nigeria support rehabilitative measures, indicating a growing approval.
This evolution underscores the need for a restorative justice mediator to be equipped with a comprehensive toolkit that not only addresses immediate conflicts but also fosters long-term healing and community reintegration. Historically, reparative measures gained traction in the 1970s as a response to dissatisfaction with conventional criminal systems, further emphasizing its relevance today. As technology continues to influence conflict resolution methods, the incorporation of virtual processes is becoming increasingly significant, enhancing accessibility and adaptability in reparative initiatives.
Explain the Mediation Process in Restorative Justice
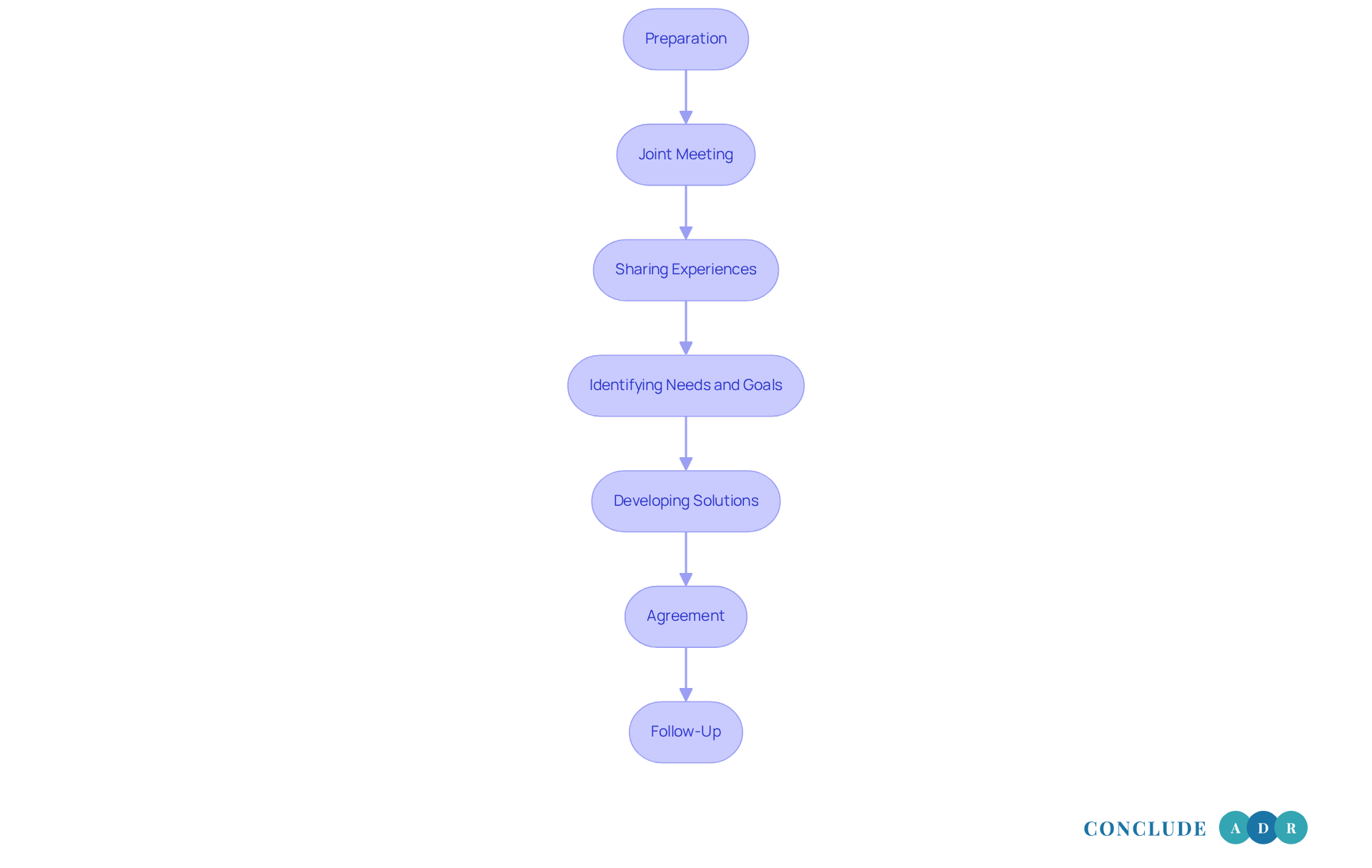
The mediation process in restorative justice is a journey that unfolds through several essential stages, each designed to foster understanding and healing:
-
Preparation: Imagine sitting down with a mediator who genuinely wants to understand your feelings and hopes. In this initial stage, mediators meet individually with each party, gaining insight into their perspectives and emotions. This step is crucial for building trust and rapport, laying the groundwork for a meaningful dialogue.
-
Joint Meeting: Picture a safe space where everyone comes together, guided by a compassionate facilitator. Here, ground rules are established, creating an environment that encourages open communication and respect.
-
Sharing Experiences: Each participant has the chance to share their story, highlighting how the conflict has affected their lives. The facilitator ensures that everyone can express themselves without interruption, nurturing empathy and understanding among all parties.
-
Identifying Needs and Goals: With gentle guidance, the facilitator helps everyone articulate their needs and aspirations for the mediation outcome. This clarity is vital for understanding what each person hopes to achieve.
-
Developing Solutions: Together, the parties brainstorm potential solutions that address their needs. The facilitator supports this collaborative effort, ensuring that the solutions are realistic and acceptable to everyone involved.
-
Agreement: Once a consensus is reached, the facilitator documents the agreement, clearly outlining each party's responsibilities moving forward. This step is essential for fostering accountability and commitment.
-
Follow-Up: To reinforce the commitment to resolution, the mediator may arrange follow-up sessions. These check-ins help ensure that the agreement is honored and provide a space to address any new issues that may arise.
Research shows that restorative practices can significantly enhance victim satisfaction. In Nigeria, for instance, 81.1% of victims support restorative approaches as a more economical alternative to traditional prosecution. Participants often report positive psychological impacts and a sense of empowerment through communication with offenders. Successful conflict resolution processes, like the London Borough of Hounslow's new framework, demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach in fostering healing and accountability. This ultimately contributes to lower recidivism rates-by 10% to 25% compared to conventional methods-while strengthening community ties.
Isn't it inspiring to see how restorative justice can transform lives? By embracing these practices, we can create a more compassionate and understanding community.
Identify Challenges Faced by Restorative Justice Mediators
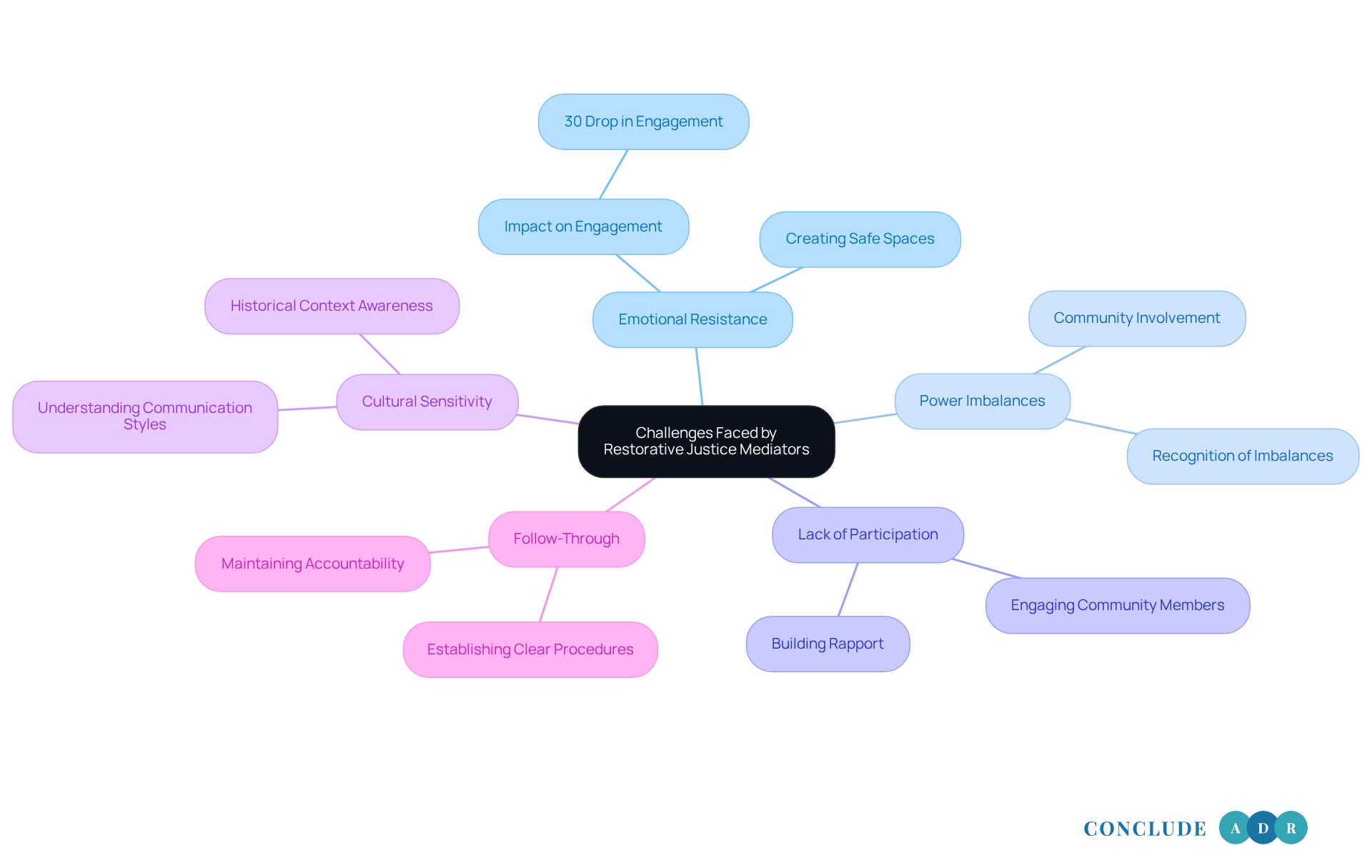
Challenges that restorative justice mediators often face can impact the effectiveness of the mediation process. Let’s explore some of these hurdles together:
-
Emotional Resistance: It’s common for participants to feel emotions like anger, fear, or mistrust. These feelings can make open dialogue tough. Did you know that emotional resistance can lead to a 30% drop in engagement during conflict resolution? That’s why it’s so important for mediators to create a safe space where everyone feels comfortable to share.
-
Power Imbalances: Sometimes, one party holds more power, which can complicate negotiations. It’s crucial for mediators to recognize these imbalances and work to ensure that every voice is heard. In restorative justice, involving the community can help balance these dynamics and improve the overall process.
-
Lack of Participation: Reluctance to engage can be a real barrier in mediation. To overcome this, mediators should focus on building rapport with participants. Highlighting how each person’s contribution matters can encourage everyone to take part. Engaging community members in restorative circles can also foster a sense of belonging and support.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding cultural differences is vital, as they can shape communication styles and perceptions of fairness. To facilitate effective mediation, a restorative justice mediator needs to be aware of these nuances. Learning about the historical context of repairative practices can provide valuable insights for facilitators.
-
Follow-Through: After mediation, ensuring that agreements are honored can be challenging. Establishing clear follow-up procedures is essential for maintaining accountability and encouraging ongoing dialogue. As Nelson Mandela wisely said, effective communication is key to understanding and resolving conflicts. This highlights how important follow-through is in mending relationships.
By recognizing and addressing these challenges, we can enhance the effectiveness of restorative justice processes. Together, we can work towards more satisfactory outcomes for everyone involved.
Conclusion
Mastering the role of a restorative justice mediator is about more than just skills; it’s about embracing the core principles that make this practice truly transformative. By focusing on healing rather than punishment, restorative justice creates a space where victims, offenders, and communities can come together. Here, meaningful dialogue can flourish, relationships can be repaired, and conflicts can turn into opportunities for growth.
Have you ever thought about the power of conversation in healing? Throughout this article, we’ve explored the essential responsibilities and skills that effective mediators need. From active listening and maintaining neutrality to navigating emotional resistance and addressing power imbalances, it’s clear that restorative justice mediators require a well-rounded skill set. The mediation process, which includes stages from preparation to follow-up, highlights how structured dialogue is crucial for achieving resolutions that satisfy everyone involved and strengthen community ties.
The importance of restorative justice is profound. By embracing these practices, we can work together to foster a more compassionate and understanding environment. As the need for effective conflict resolution continues to grow, the role of restorative justice mediators becomes even more vital. They not only promote healing and accountability but also contribute to a broader culture of empathy and restoration in our society.
So, how can we engage with these principles? Let’s take action together. By supporting restorative justice, we can create a ripple effect of understanding and healing that benefits not just those directly involved in conflicts, but all of us. Together, we can cultivate a community where empathy thrives and restoration is possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is restorative justice?
Restorative justice is a caring approach that focuses on healing the harm caused by criminal behavior, prioritizing the needs of victims, offenders, and the community rather than just punishing the offender.
What are the core principles of restorative justice?
The core principles of restorative justice are Encounter, Repair, and Transform. These principles guide the process of open dialogue, addressing harm, and changing relationships that led to conflict.
What does the principle of Encounter involve?
The principle of Encounter encourages open dialogue between victims and offenders, fostering understanding and empathy, which can lead to healing for both parties.
How does the principle of Repair function in restorative justice?
The principle of Repair focuses on addressing and mending the harm done to victims and the community, promoting fairness beyond mere retribution and enhancing victim satisfaction rates.
What is the impact of reparative programs on reoffending rates?
Research indicates that rehabilitation programs can reduce reoffending rates by 10% to 25% compared to traditional methods.
What does the principle of Transform aim to achieve?
The principle of Transform aims to change the relationships and dynamics that led to the conflict, promoting healing and reconciliation to rebuild community bonds and reduce future offenses.
How do restorative justice practices benefit communities?
Restorative justice practices promote community healing and enhance victim satisfaction, encouraging a more compassionate and understanding environment.
Why is broader implementation of restorative practices advocated by practitioners?
Practitioners advocate for broader implementation of restorative practices to enhance fairness outcomes and improve the overall impact on community healing and victim satisfaction.




