Introduction
California's labor laws for breaks truly stand out, offering robust protections that significantly differ from the more lenient federal standards. Workers in California are entitled to specific benefits, like a guaranteed 30-minute unpaid meal break for shifts over five hours and paid rest periods - protections that aren’t mandated at the federal level.
This raises an important question: how do these differences impact your rights and overall well-being at work? Understanding these regulations is crucial for both you and your employer. By ensuring compliance, we can foster a healthier work environment and protect against potential legal issues.
Imagine feeling secure in your workplace, knowing that your rights are upheld. It’s not just about the law; it’s about creating a supportive atmosphere where everyone can thrive. Let’s explore these vital regulations together, so you can feel empowered and informed.
Overview of Break Laws: California vs. Federal Standards
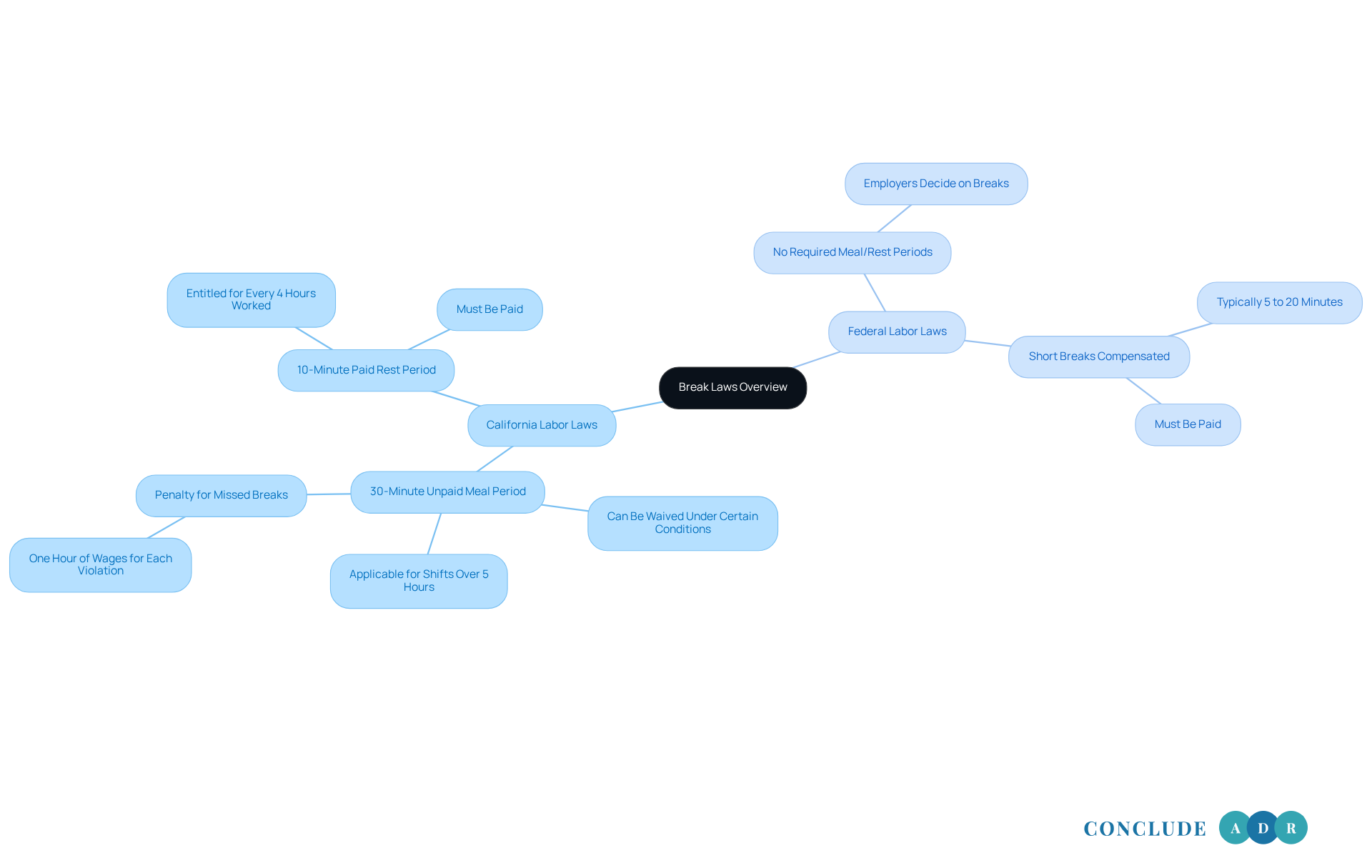
In our region, the California labor laws for breaks are notably stricter than what you might find at the national level. Did you know that according to California labor laws for breaks, workers are entitled to a 30-minute unpaid meal period for shifts longer than five hours? Furthermore, according to California labor laws for breaks, employees are entitled to a paid 10-minute rest period for every four hours worked. This is a significant benefit that many may not be aware of.
In contrast, federal law, governed by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), doesn’t require meal or rest periods. This means it’s up to employers to decide whether to offer them. While federal law does mandate that short breaks - typically lasting 5 to 20 minutes - be compensated, it doesn’t specify how often these breaks should occur. This creates a more flexible framework, yet less protective compared to the California labor laws for breaks.
Understanding these differences is crucial. It’s important to know your rights and advocate for them. Are you aware of how these regulations impact your daily work life? By staying informed, you can ensure that your needs are met and that you’re treated fairly in the workplace.
California Meal and Rest Break Requirements: Key Provisions
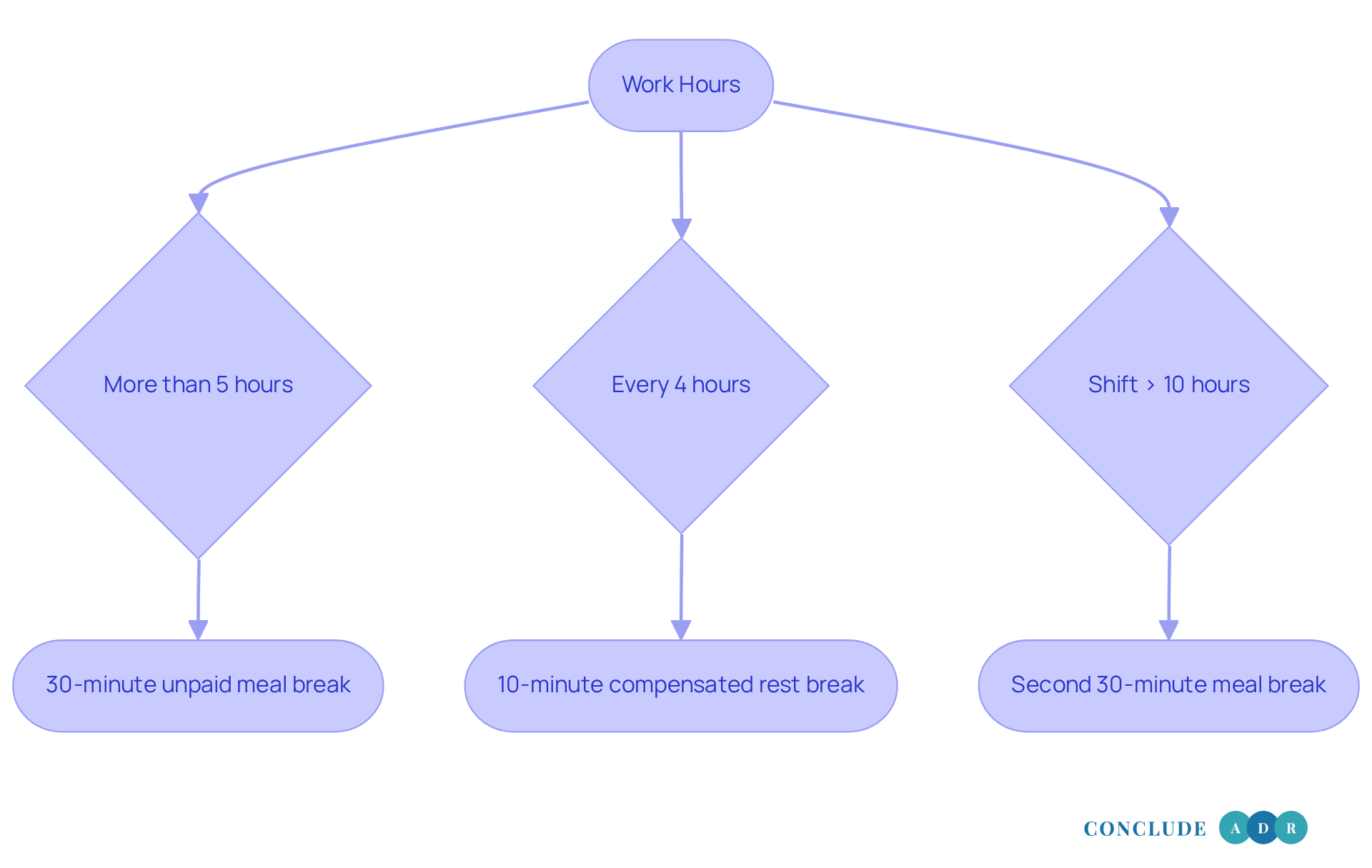
According to California labor laws for breaks, if you’re working more than five hours, it’s important to know that you’re entitled to a 30-minute unpaid meal break. This break should ideally happen before you reach that fifth hour. Additionally, under California labor laws for breaks, for every four hours you work, or a significant portion of that time, you deserve a compensated 10-minute rest pause. If your shift goes beyond 10 hours, you’ll get a second 30-minute meal break.
These pauses aren’t just rules; they’re essential for your well-being. Taking time to relax and recharge can significantly enhance your workplace wellness and efficiency. Studies show that regular breaks can lead to better focus and reduced fatigue, ultimately boosting your overall performance.
Employers are responsible for ensuring that these breaks are uninterrupted, allowing you to step away from your duties completely. If these regulations aren’t followed, it could result in penalties according to California labor laws for breaks, including an extra hour of pay for each day a rule is broken. It’s crucial that you inform HR if you’re denied your rest periods or if your break time is interrupted. This communication is vital for tracking compliance and ensuring your rights are upheld.
By discussing time-off policies openly, we can foster a supportive environment that enhances morale and adherence to these important regulations. Organizations that prioritize these breaks often see happier employees and increased productivity, demonstrating the positive impact of adhering to California labor laws for breaks. Remember, your well-being matters, and taking these breaks is a step towards a healthier work life.
Federal Labor Laws on Breaks: Essential Guidelines
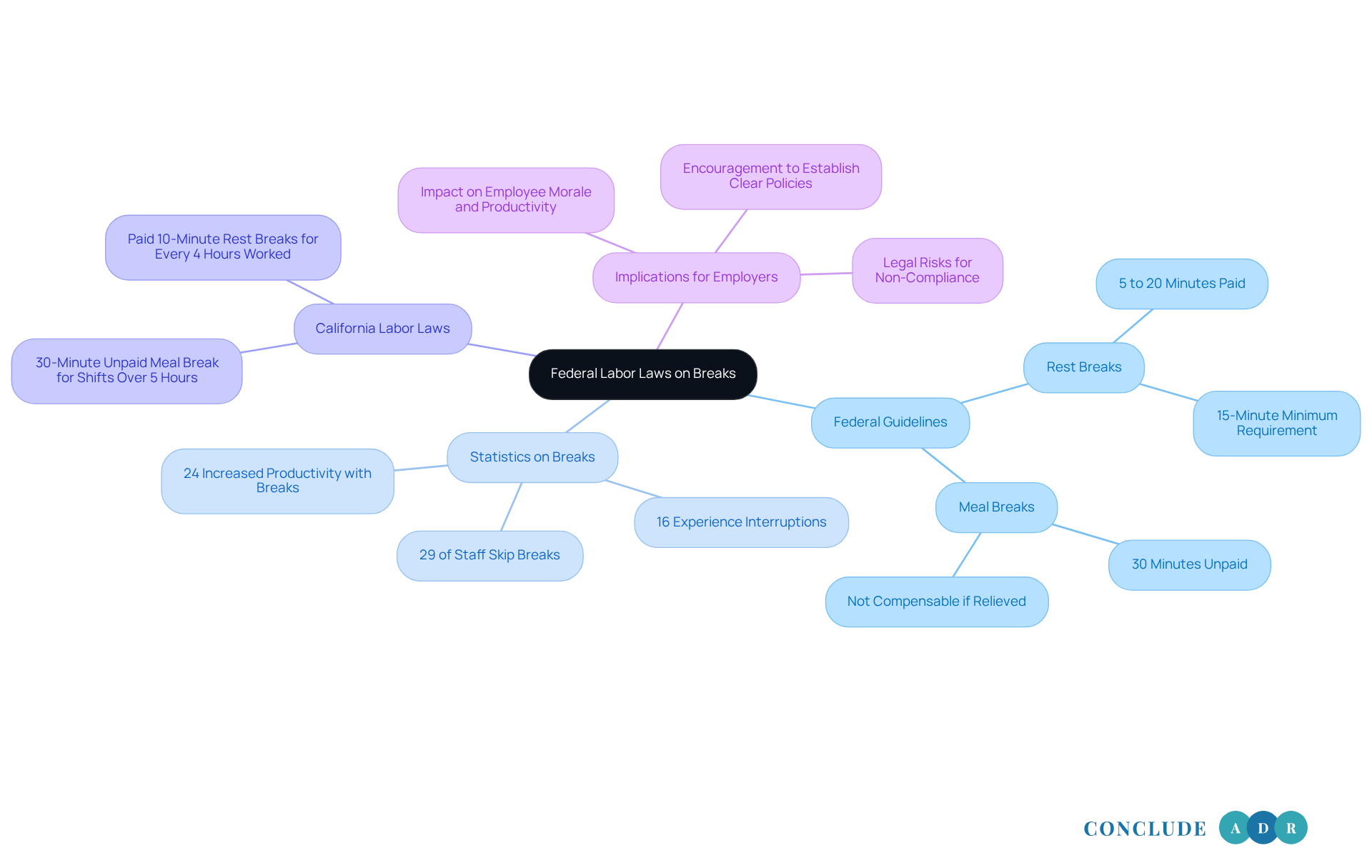
Under federal law, there aren’t specific requirements for meal or rest breaks, which can be concerning for many workers. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) mentions that if employers choose to provide rest periods lasting between 5 to 20 minutes, these must be paid, as they count as work time. But what about those longer breaks? Meal intervals of 30 minutes or more don’t require compensation, as long as employees are completely free from their duties during that time.
This lack of mandated breaks can lead to situations where workers don’t get enough rest, especially in demanding roles. Did you know that 29% of staff often skip their breaks? It’s a troubling statistic that highlights the need for better policies. Employers are encouraged to create their own rest policies, but these can vary significantly, which might lead to inconsistent treatment of employees across different workplaces.
According to California labor laws for breaks, employers are required to provide a 30-minute unpaid meal break for shifts longer than 5 hours. This is crucial for promoting a healthier work environment. It’s important to remember that employers who don’t follow these rest regulations could face lawsuits and damage to their reputation. This underscores the need for compliance with these guidelines, not just for legal reasons, but for the well-being of all employees.
Consequences of Non-Compliance: California vs. Federal Laws
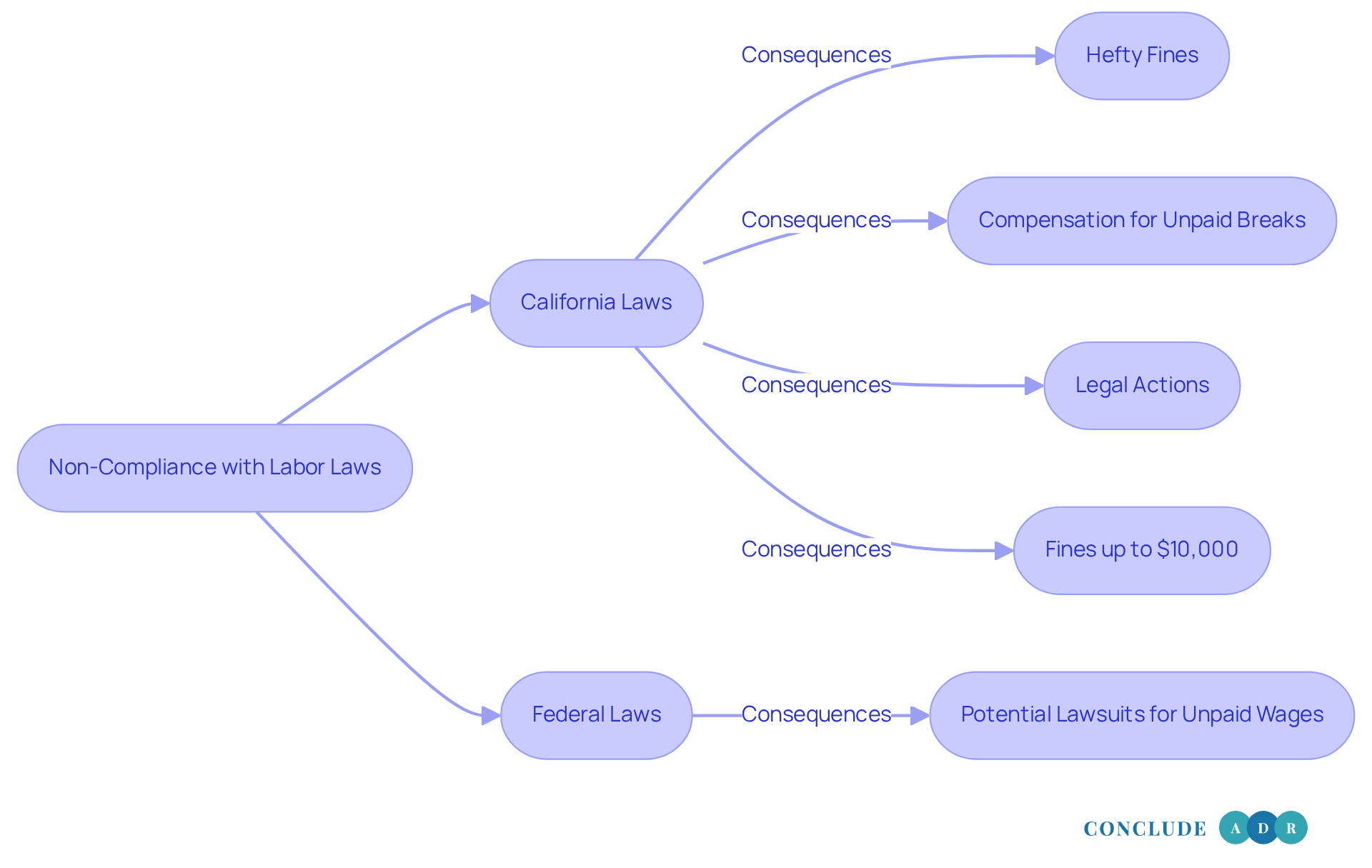
In our region, it’s crucial to understand California labor laws for breaks, as not following meal and rest period regulations can lead to serious consequences for employers. Have you considered the impact of these transgressions? They can result in hefty fines, compensation for unpaid breaks, and even legal actions from staff. The California Labor Commissioner's Office is committed to upholding these regulations, with fines soaring up to $10,000 per worker for breaches of emergency-contact provisions, along with additional compensation for missed rest periods.
For instance, employers who fail to provide compliant rest periods may face waiting time penalties and legal fees. This clearly shows California's dedication to protecting worker rights. In contrast, federal law doesn’t impose specific penalties for interruption violations, although employers can still be sued for unpaid wages under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) if they don’t follow its guidelines regarding compensable interruptions.
This difference highlights how California labor laws for breaks proactively ensure that workers receive the necessary breaks to support their health and productivity. Studies have shown that employees who take regular breaks experience improved performance and reduced fatigue. As California continues to enhance its labor laws for breaks, it’s essential for employers to stay vigilant. By doing so, they can avoid the significant financial repercussions that come with non-compliance. Let’s work together to create a supportive environment for everyone.
Conclusion
Understanding California labor laws for breaks is essential for both employees and employers. These laws are designed to protect and support workers, offering more than what federal standards provide. California mandates specific meal and rest periods, ensuring that you have the time to recharge during your shifts. This commitment to your well-being not only boosts productivity but also creates a healthier work environment.
Have you ever felt overwhelmed at work? The differences between California and federal regulations are significant. While federal law offers minimal guidance, leaving break policies largely to employers' discretion, California's strict requirements enforce a structured approach to breaks. This includes mandatory unpaid meal breaks and compensated rest periods, highlighting the importance of stepping away from work duties. The consequences for non-compliance in California are serious, with penalties that show the state's dedication to protecting your rights as a worker.
Ultimately, being aware of these labor laws is crucial. By understanding and advocating for your rights, you can ensure you receive the breaks you deserve. Employers, on the other hand, can avoid costly penalties and foster a more positive workplace culture. Staying informed about California labor laws for breaks empowers you and contributes to a more equitable and productive workforce. Let's work together to create a supportive environment where everyone can thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the break laws in California for meal periods?
According to California labor laws, workers are entitled to a 30-minute unpaid meal period for shifts longer than five hours.
How many rest periods are employees entitled to under California labor laws?
Employees in California are entitled to a paid 10-minute rest period for every four hours worked.
How do California break laws compare to federal standards?
California labor laws for breaks are stricter than federal standards. Federal law, governed by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), does not require meal or rest periods, leaving it up to employers to decide whether to offer them.
Are short breaks required to be paid under federal law?
Yes, federal law mandates that short breaks, typically lasting 5 to 20 minutes, must be compensated.
Does federal law specify how often breaks should occur?
No, federal law does not specify how often breaks should occur, creating a more flexible but less protective framework compared to California laws.
Why is it important to understand the differences between California and federal break laws?
Understanding these differences is crucial for knowing your rights and advocating for fair treatment in the workplace. Staying informed helps ensure that your needs are met.




